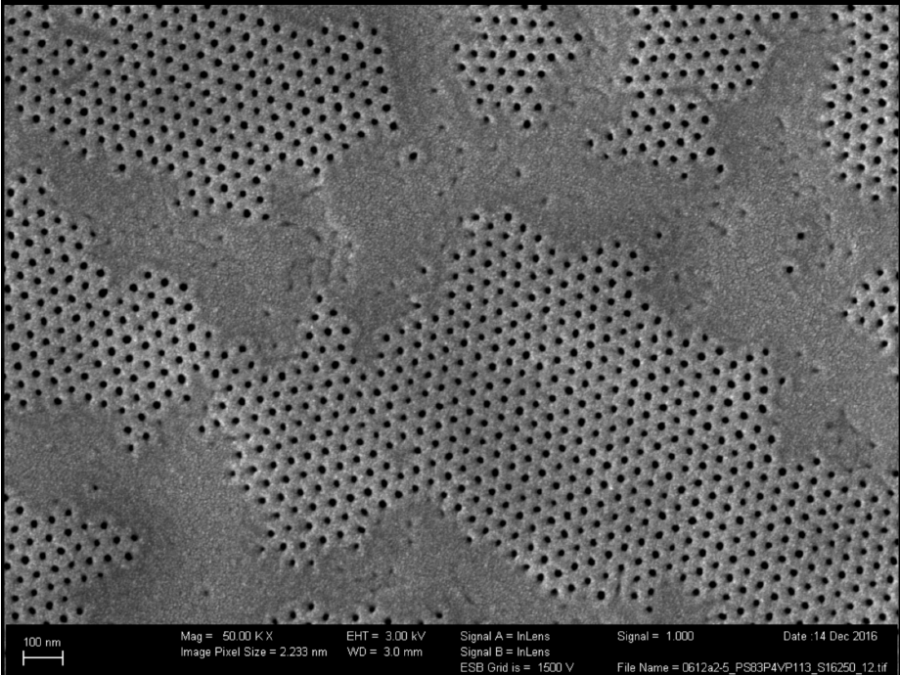
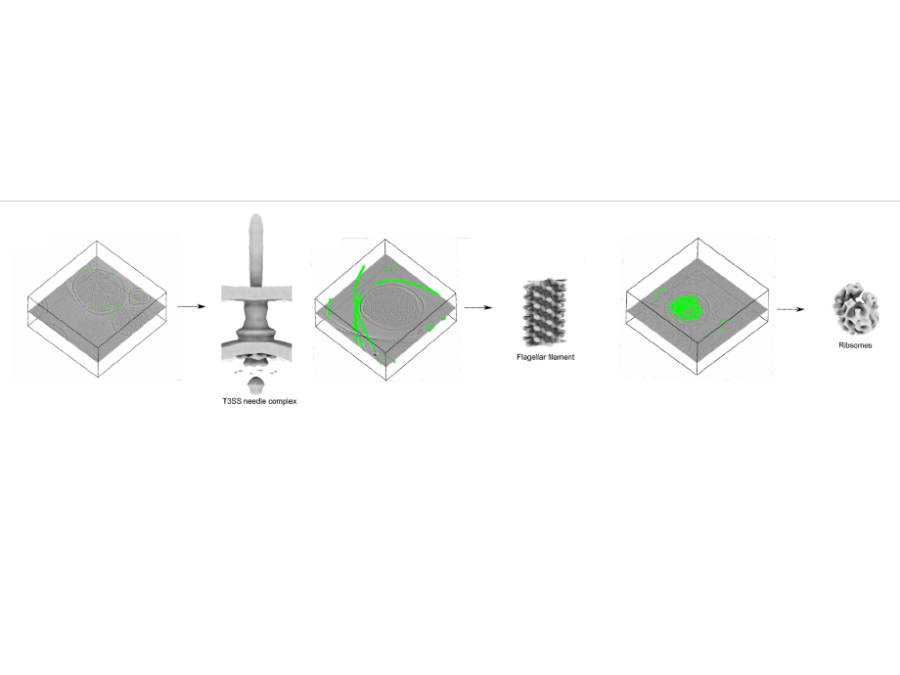
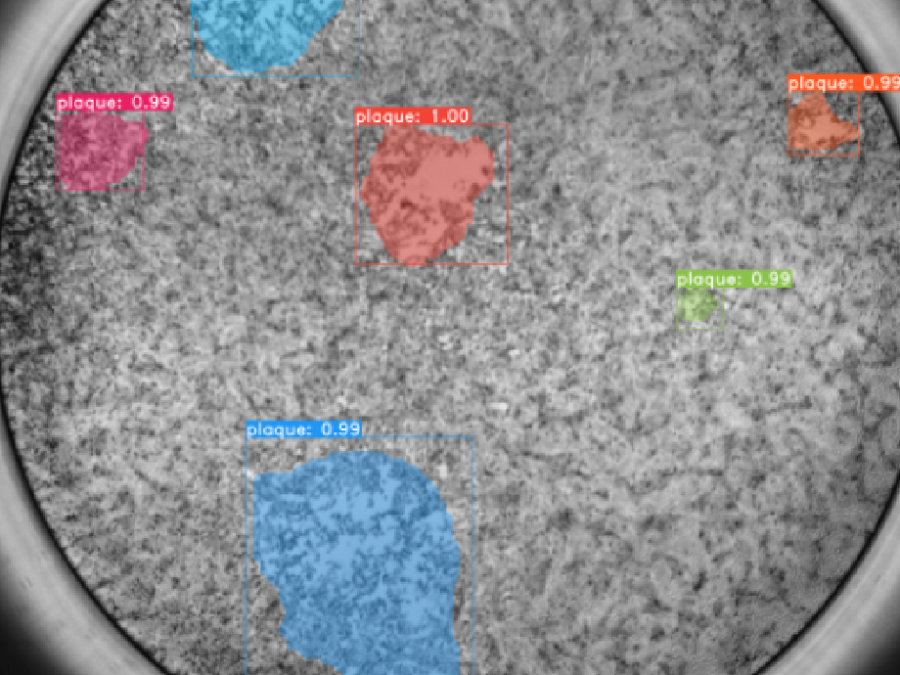
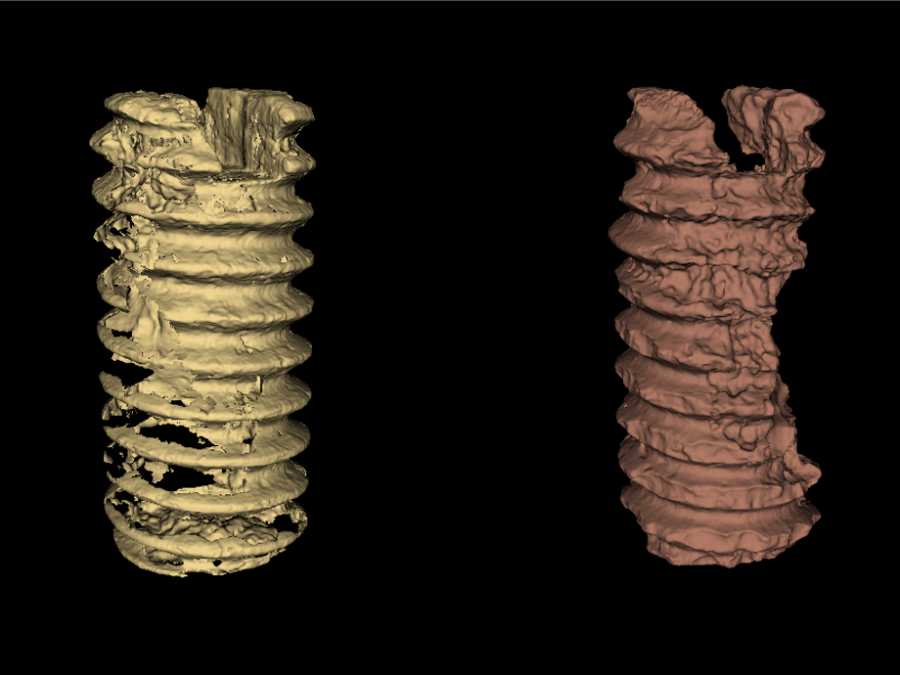
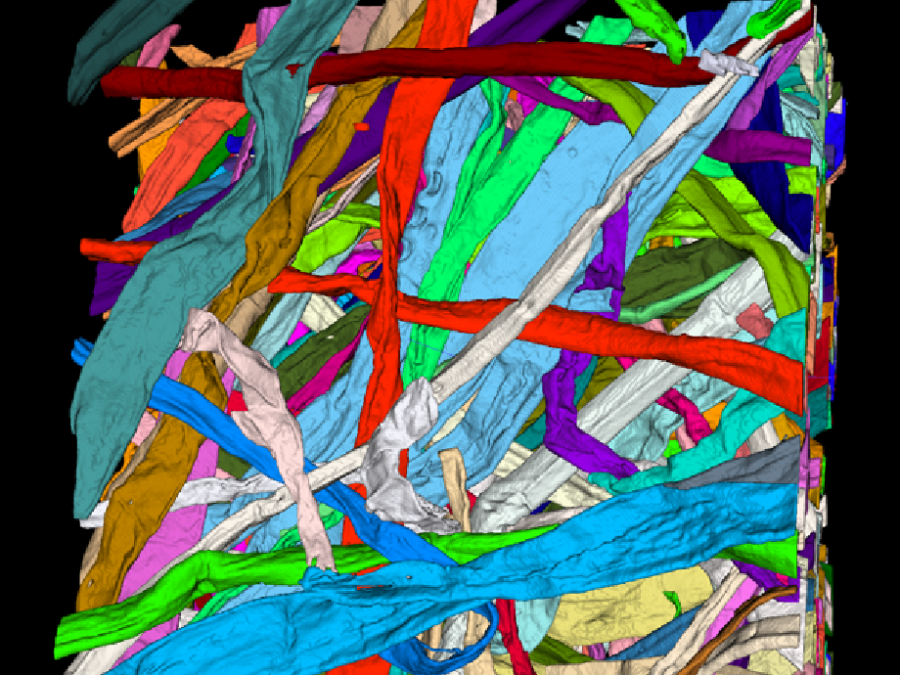
Collaborations
Solving imaging challenges together.
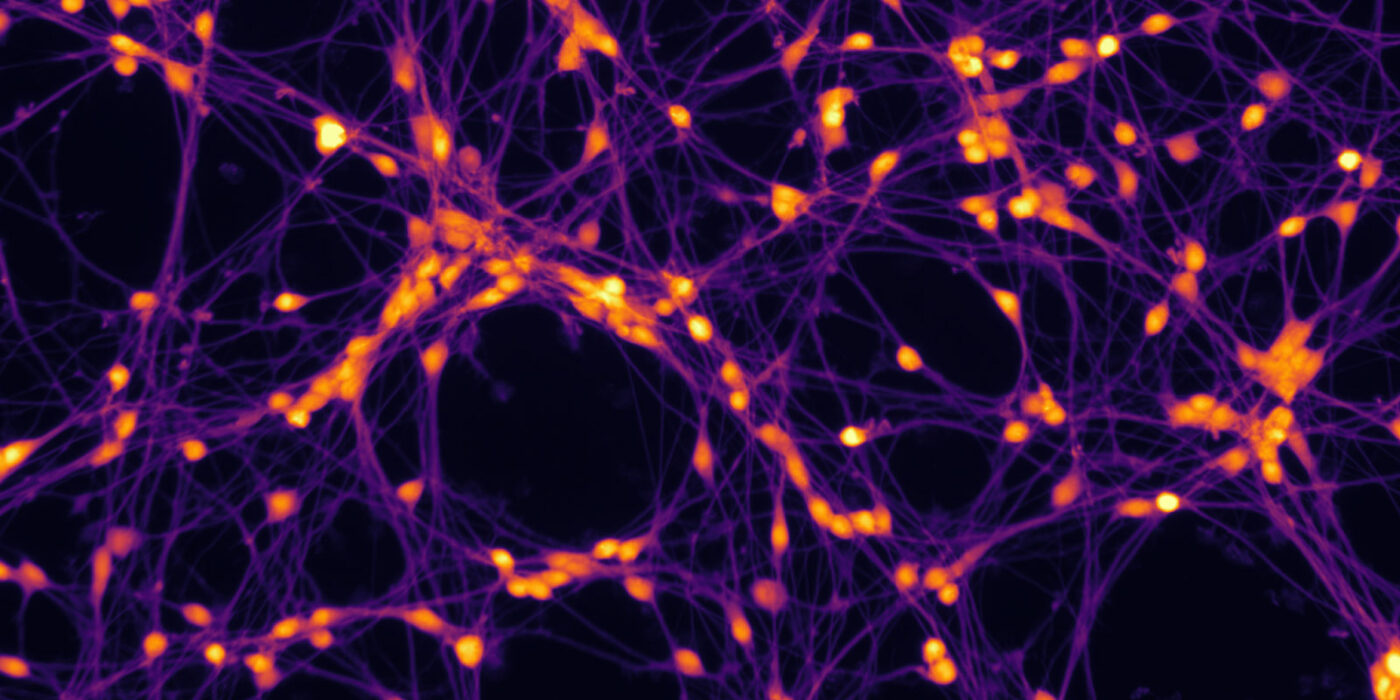
Image: Jo Nyffeler, Luisa Reger, Nicole Teßendorf, UFZ | info
Collaboration Gallery
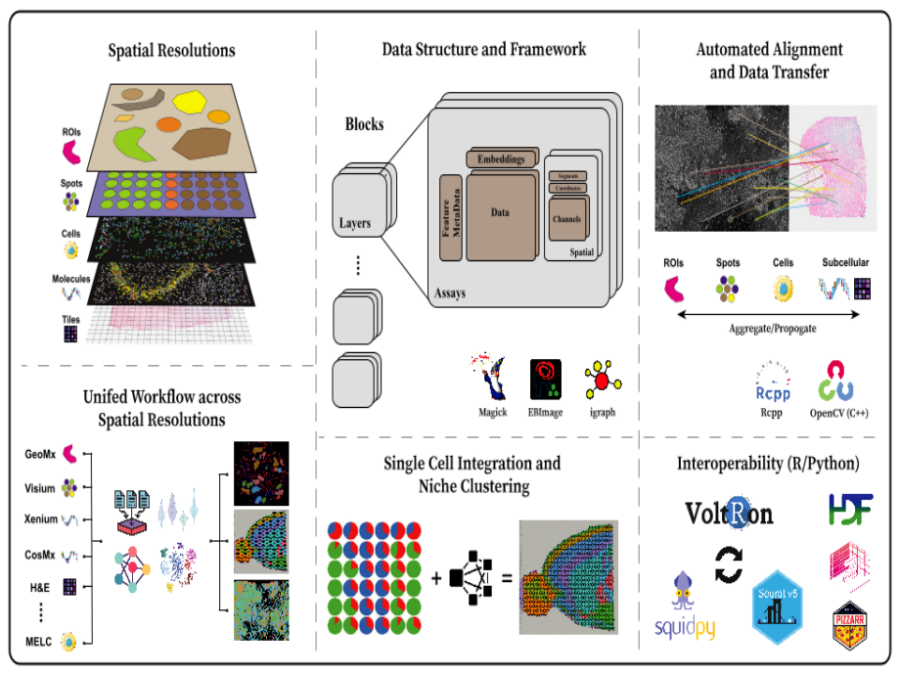
Image Registration for VolTron
VoltRon is an R based spatial omic analysis toolbox designed for multi-omics integration through spatial image registration. Focused on image registration, VoltRon leverages OpenCV – fully embedded into the package using Rcpp – to detect common features across images, ensuring precise alignment of multiple spatially-aware data modalities. The toolbox includes built-in mini Shiny apps that […]Capturing Reality at BESSY II
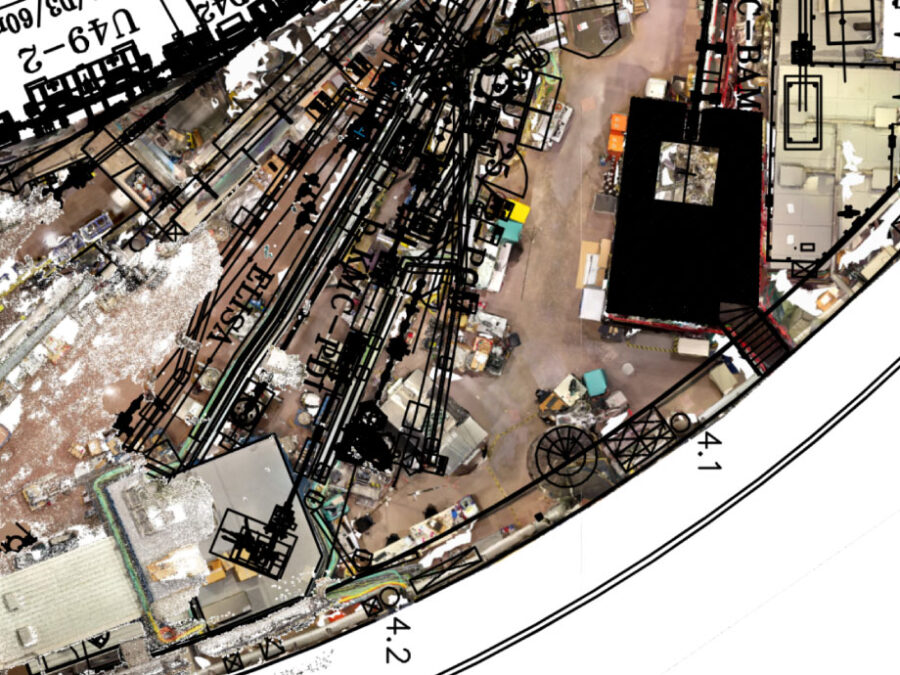
The experimental hall at BESSY II (Berliner Elektronenspeicherring) is a constantly evolving space, featuring a diverse range of structures, devices, and experiments managed by various departments, companies, and individuals. This dynamic nature necessitates regular updates to ensure the floor plan accurately reflects the hall’s current state. To address this, a video drone is deployed to […]AI-based classification of phytoplankton community composition from field samples
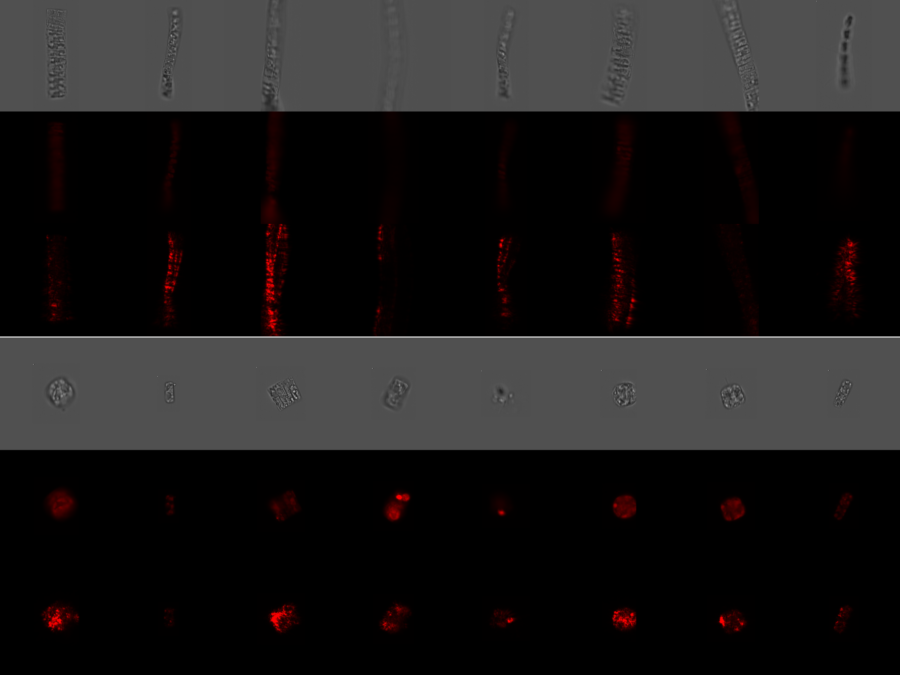
Phytoplankton biodiversity is a key indicator of marine ecosystems health. Due to climate change derived impacts, phytoplankton communities worldwide are being affected by changes in the water temperatures and the access to nutrients and light. Current methods to quantitatively classify phytoplankton samples require taxonomy experts to manually count and classify the individual cells they see […]BetaSeg
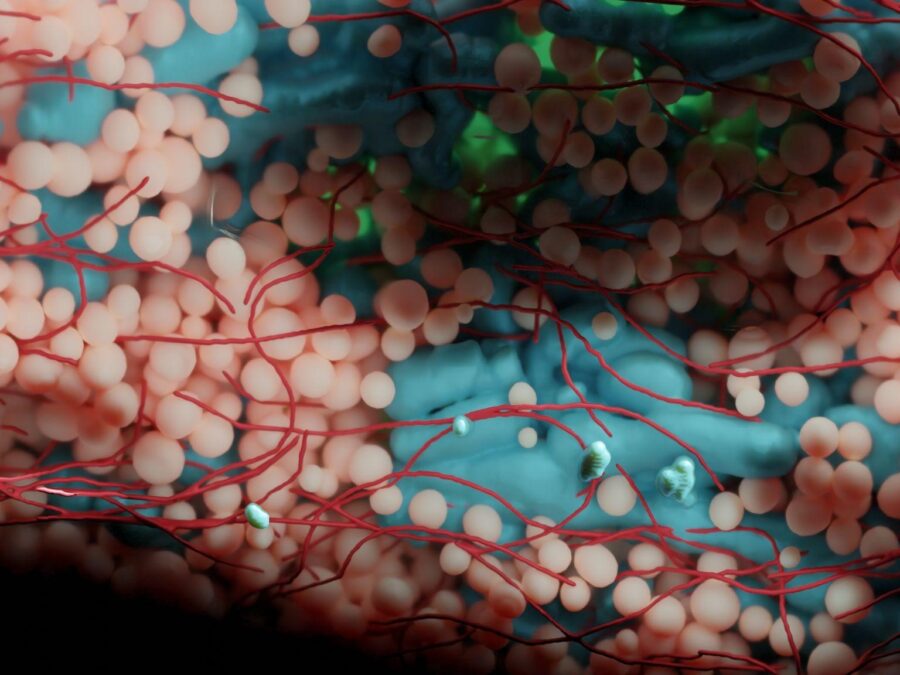
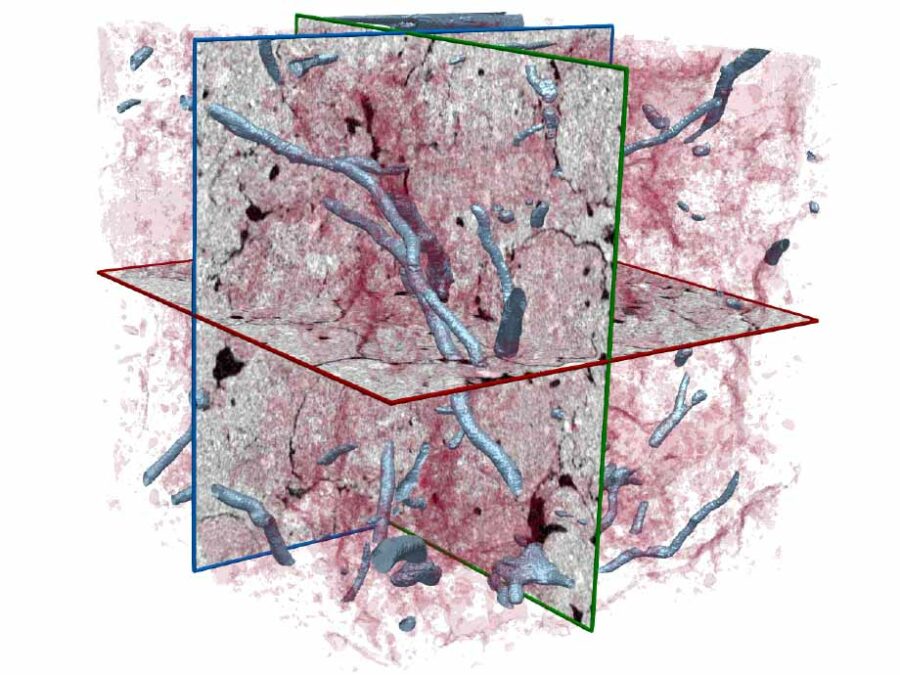
Volume electron microscopy is the method of choice for the in situ interrogation of cellular ultrastructure at the nanometer scale, and with the increase in large raw image datasets generated, improving computational strategies for image segmentation and spatial analysis is necessary. Here we describe a practical and annotation-efficient pipeline for organelle-specific segmentation, spatial analysis and […]MSPaCMAn
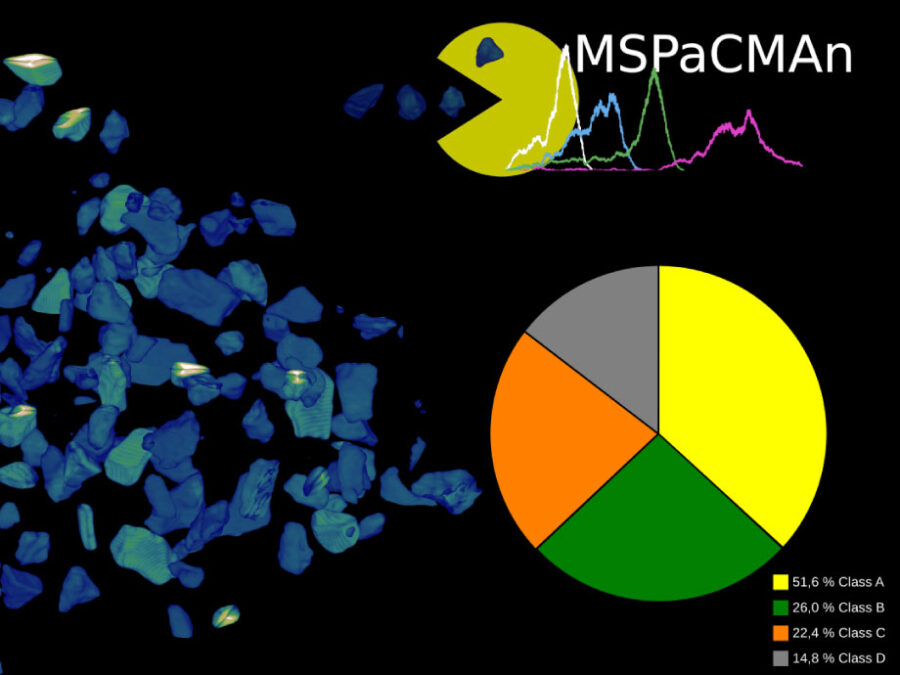
MSPaCMAn is a workflow for quantifying mineral phases in 3D images of particulate materials using X-ray computed micro-tomography, designed to minimize imaging artifacts. It involves dispersing particles into samples, optimizing image processing to label individual particles, and identifying phases at the particle level by interpreting the grey-values of all voxels within each particle. This method […]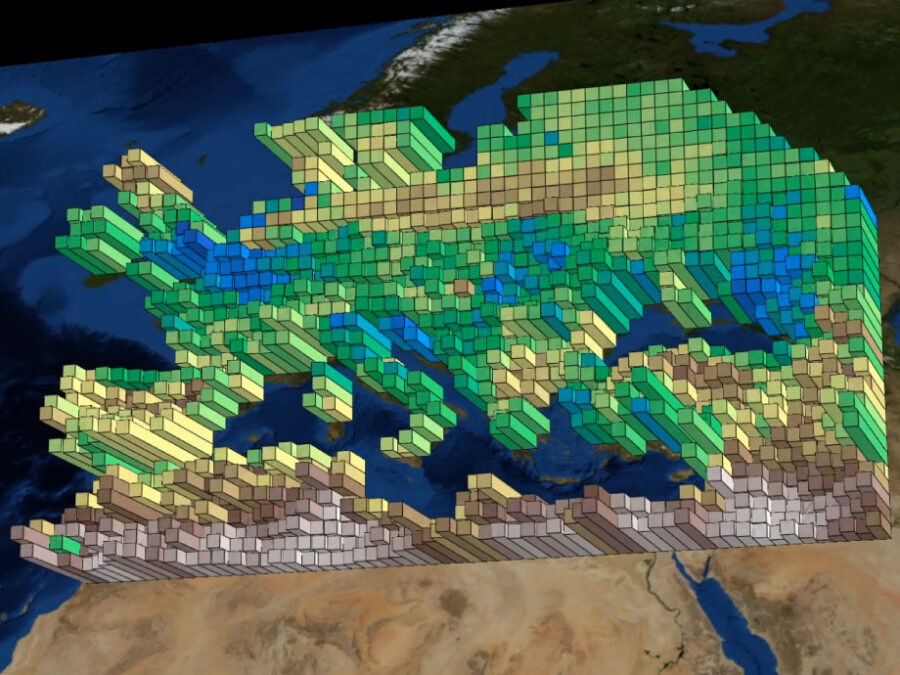
Image: Snapshots taken from videos created by the tool - original data by Almudena Garcia-Garcia and Jian Peng of Umweltforschungszentrum (UFZ) | info
EarthWatch
Earth-Watch introduces a Python package that visualizes spatiotemporal netCDF data on world maps by generating dynamic videos with PyVista. Designed to enhance the understanding and presentation of geospatial datasets over time, the tool allows users to overlay multiple observations, enabling comparative analyses and revealing correlations between different datasets. Additionally, it facilitates effective communication and presentations. By […]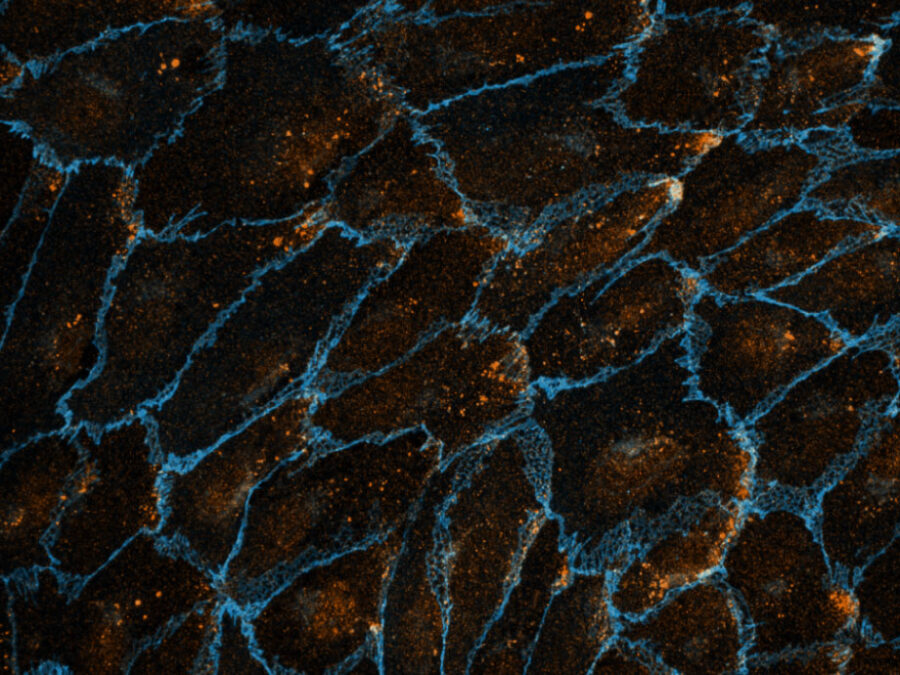
Image: Olya Oppenheim, MDC, Emir Bora Akmeriç, MDC, Jan Philipp Albrecht, MDC, Wolfgang Giese, MDC | info