Helmholtz Imaging Projects
Published on 28.08.2023
Deep4OM
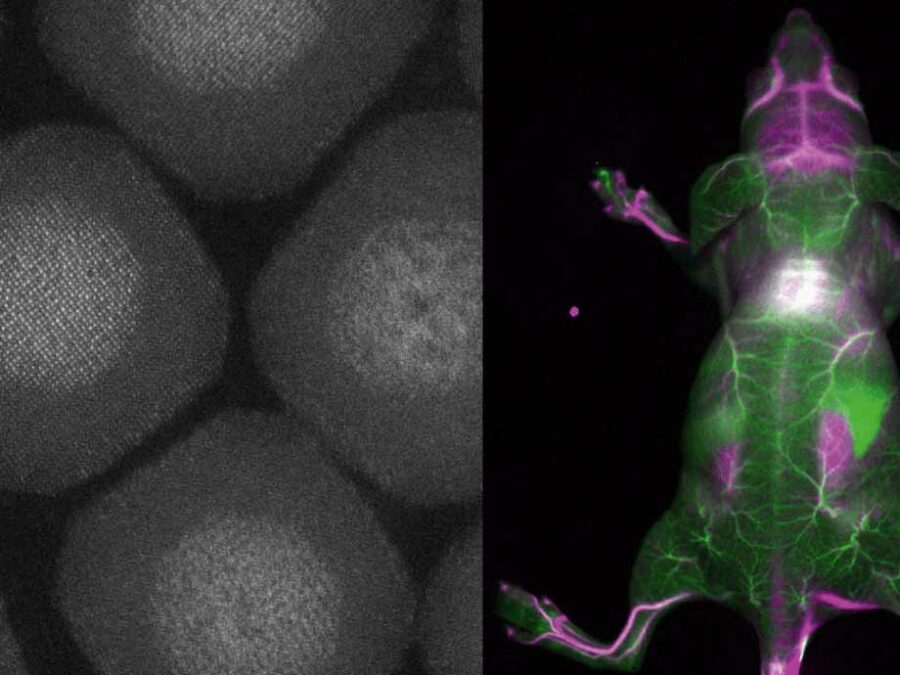
Deep4OM aims to develop a deep learning-based framework for optoacoustic mesoscopy image analysis, enabling quantification of human skin biomarkers for non-invasive skin disease diagnosis. Deep4OM has the potential to change the landscape of non-invasive skin imaging, and could significantly promote the diagnostic and prognostic applications of RSOM in clinical routine.
Published on 28.08.2023
BENIGN
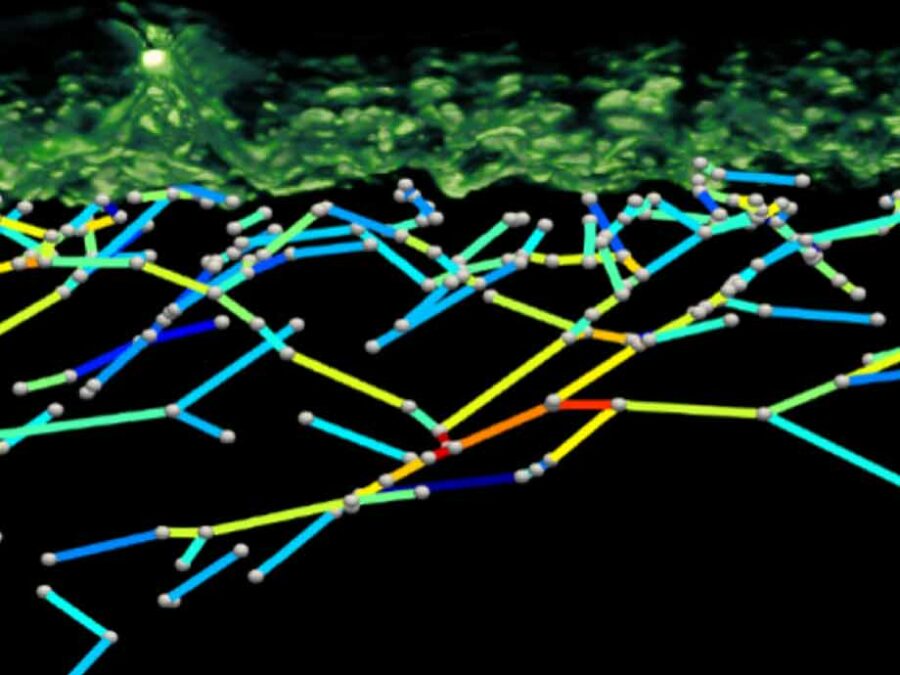
The BENIGN project aims to enable non-invasive molecular imaging with cellular resolution in vivo at depths of several millimeters. This will be achieved using light from the shortwave infrared (SWIR) range (1000-2000 nm), which has less scattering and autofluorescence compared to the visible and near-infrared spectral range. Bright and targeted imaging agents are needed to fully exploit this range. The project will develop a new approach using lanthanide-based core-shell structures that emit light in the 1500-2000 nm range.
Published on 28.08.2023
AutoCoast
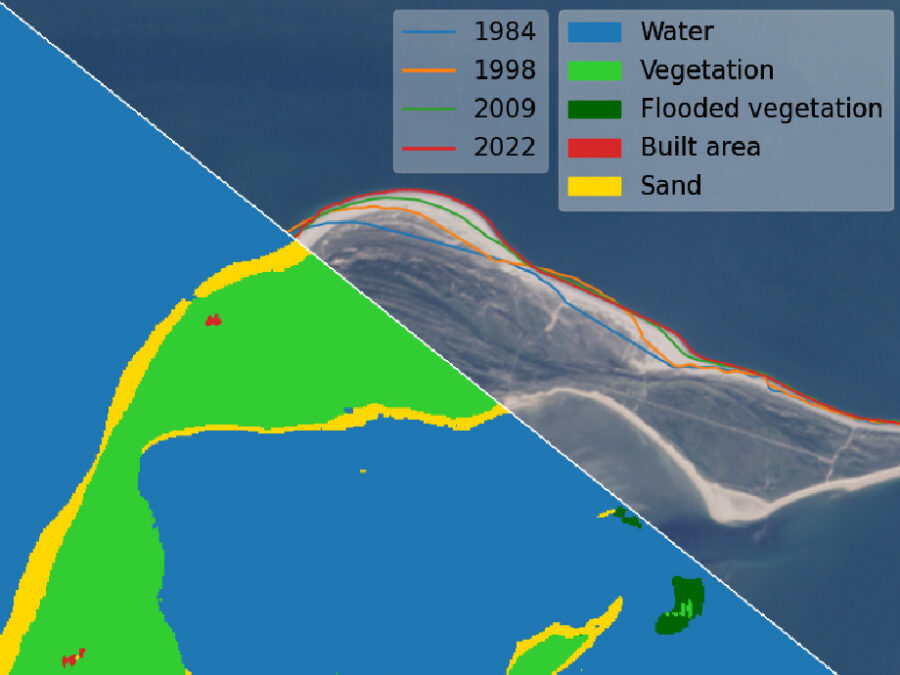
Coastal erosion enhanced by climate change has become an increasing global threat, which requires rapid detection and reliable risk assessment. AutoCoast aims to provide advanced and reliable remote sensing-based AI tools to quantify coastline change rate at high-resolution and unravel the linkage between coastline change rate and natural and anthropogenic drivers at regional to global scale.
Published on 28.08.2023
AIOrganoid
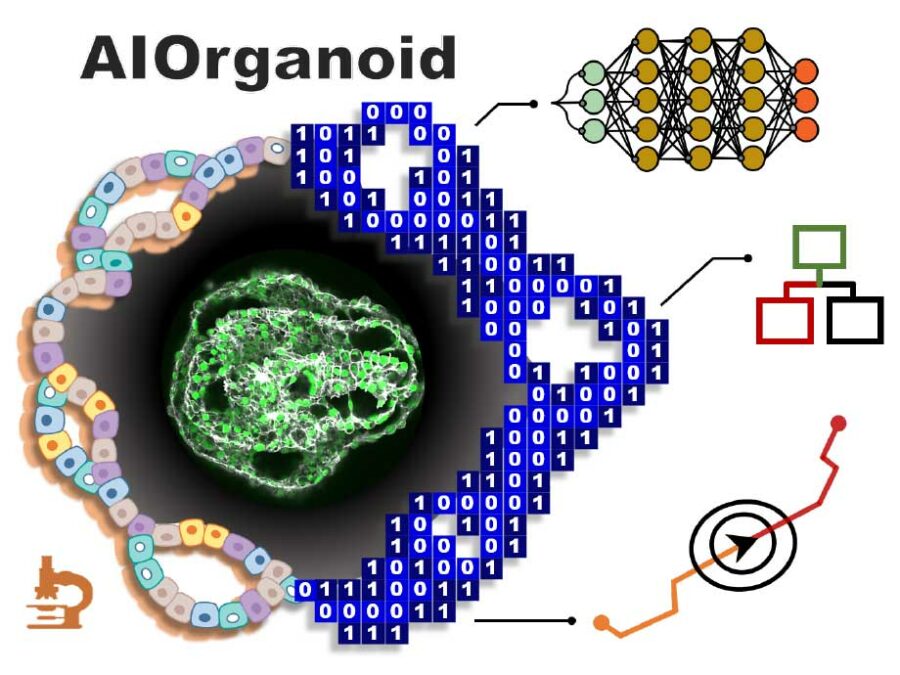
AIOrganoid will apply cutting-edge imaging techniques and develop novel AI-based solutions to facilitate human lung organoid formation with high yield and fidelity, bridging the gap between cell biology and computational imaging.
Published on 21.03.2023
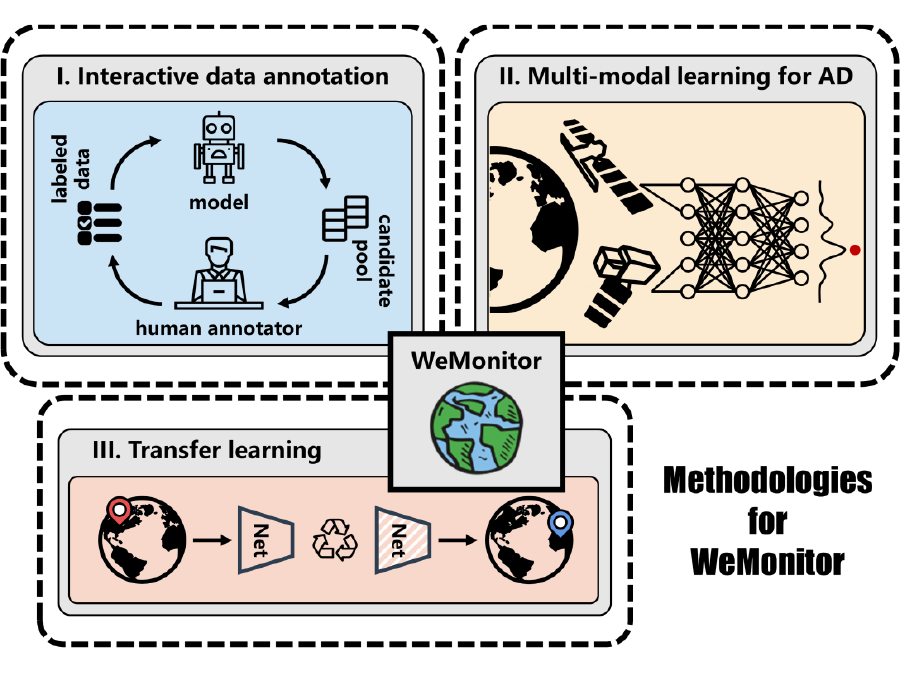
WeMonitor
Satellite imagery makes it possible to detect spatio-temporal anomalies on the Earth’s surface, including natural hazards such as landslides, deforestation, or the emergence of large waste dump sites. This project aims to use artificial intelligence to detect these changes at an early stage and to be able to monitor their progress.
Published on 20.01.2023
UTILE
Research into green materials for clean energy generation is moving at full speed – yet still requires a long time to complete. This project is working on an open source image processing application that uses artificial intelligence to drive the analysis and management of image data from experiments across the energy materials community.
Published on 20.01.2023
TerraByte-DNN2Sim
Researchers still face a mystery when it comes to the laws by which glaciers calve. This project aims to use satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, mathematical optimisation and a new data processing pipeline to track the movements of glacier fronts in Antarctica to get closer to solving the mystery.
Published on 20.01.2023
Avanti
How can the manufacturing processes of materials be mapped at the smallest level? How do you train an artificial intelligence to analyze these processes automatically? That’s the focus of the Avanti project, which aims to improve X-ray tomoscopy – the imaging and quantification of three-dimensional images of very fast-moving processes.
Published on 20.01.2023
SmartPhase
In order to be able to improve materials, it helps to take a look at their microstructures. This is because valuable information about their properties and behaviour can be found there – for example information about when which ageing processes begin. The aim of this project is to automate and accelerate access to this information with the help of a smart imaging technique.
Published on 20.01.2023
UCS
A method will be developed in which selected biomarkers in tumour and bone marrow cells from cancer patients will be examined and analysed automatically. The novel technology is based on ultra content screening technology, which allows detailed insights at the single cell level.
Published on 20.01.2023
NImRLS
The aim is to develop a software solution that can analyse enormous amounts of data on tens of thousands of subjects from large-scale health studies. Using restless leg syndrome as an example, genomic data will be combined with neuroimaging data in order to identify new biomarkers with the help of machine learning methods.
Published on 20.01.2023
Hyper 3D-AI
The aim is to develop an artificial intelligence that can achieve the fusion of two-dimensional data with three-dimensional information. Based on this, the software would simultaneously be able to recognise image characteristics as well as the spatial relationships between different objects.
Published on 20.01.2023
SATOMI
An artificial intelligence will observe the growth of bacteria: from microscope images of bacterial cultures taken at regular intervals, it will precisely track the development and division of individual cells – even when multiple bacterial species are cultivated together.
Published on 20.01.2023
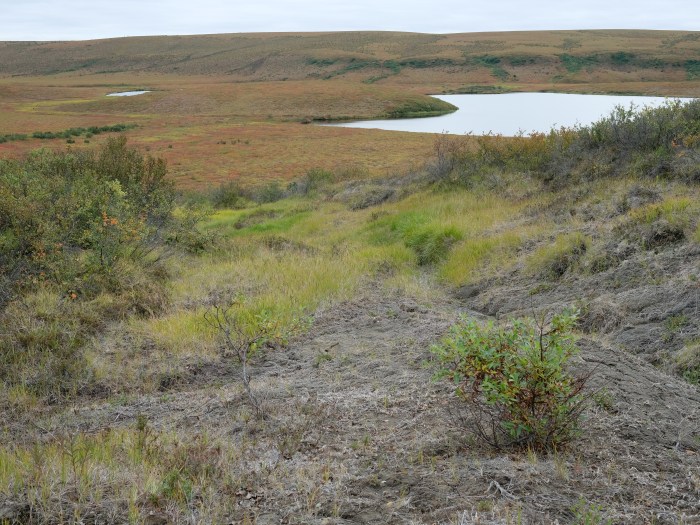
HIT Permafrost
The project aims to develop a method for determining just how extensively thaw processes have already progressed in permafrost regions. The machine learning approach to be developed will be used to analyse radar images from aircraft in order to learn more about the properties of the subsurface permafrost.