3DforestSIF
Understanding the solar-induced fluorescence (SIF) signal of natural, complex tree canopies
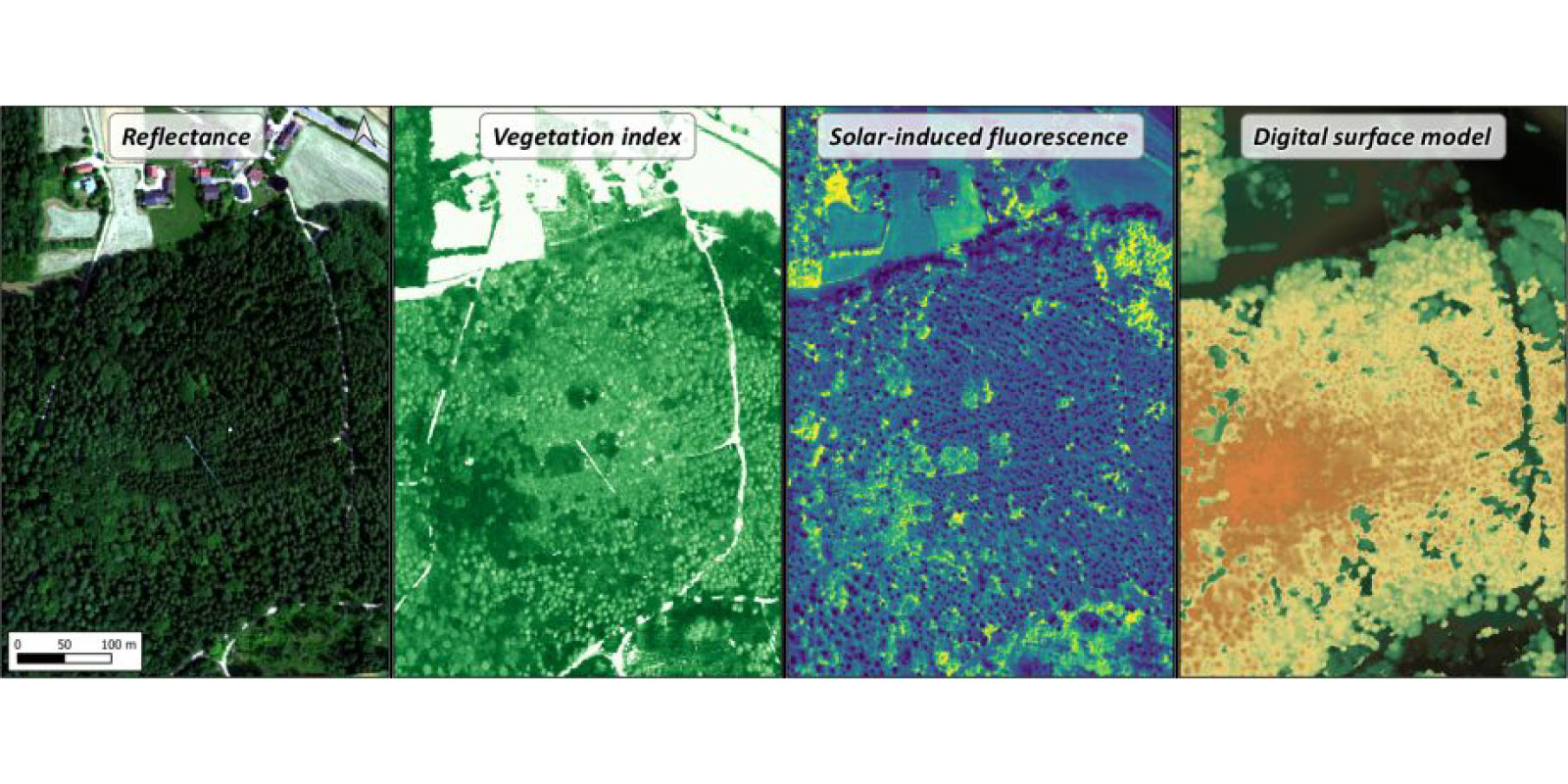
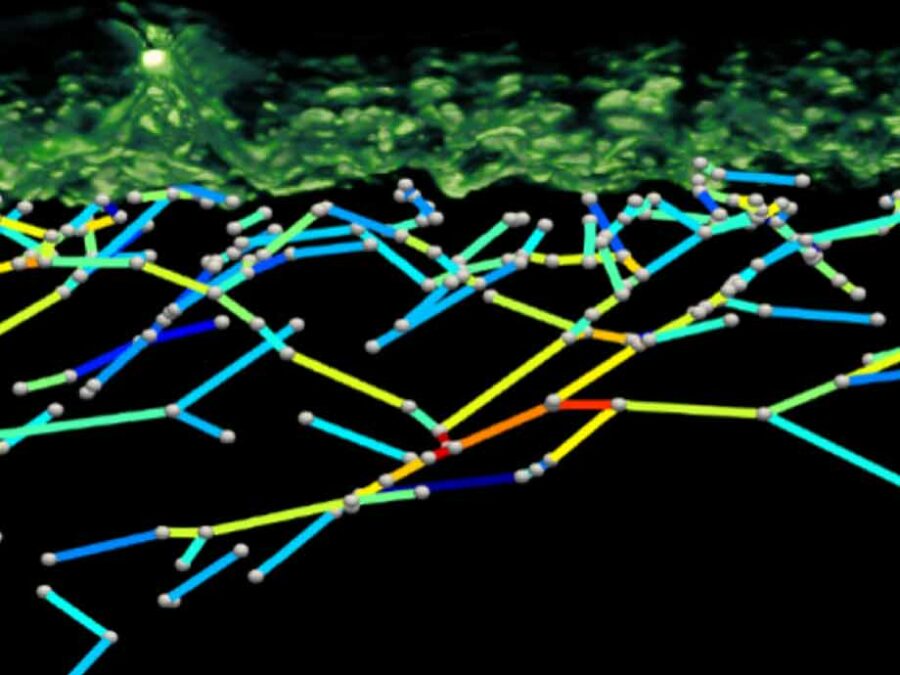
The airborne sensor HyPlant captures images that can be used to derive solar-induced fluorescence (SIF) data from forests. SIF is a novel signal in remote sensing that tracks changes in photosynthesis. However, the SIF signal measured at the canopy level differs from that measured at the leaf scale, making it challenging to directly detects variations in plant physiology. Therefore, it is crucial to correct the SIF signal for the effects of canopy structure and illumination distribution in the canopy.
In the 3DforestSIF project, canopy structure information from optical and LiDAR data will be derived and applied within a 3D radiative-transfer model. This approach will help separate the functional and structural contributions to the canopy SIF signal. Additionally, the gained knowledge will be leveraged to adapt a novel neural network-based SIF estimator specifically for forests. This will allow for normalizing HyPlant SIF images to determine leaf SIF emission efficiency, a parameter that enables the pre-visual detection of stress in forest ecosystems.
Other projects
Deep4OM
Deep learning powered optoacoustic mesoscopy for non-invasive diagnostics of skin diseases
Deep4OM aims to develop a deep learning-based framework for optoacoustic mesoscopy image analysis, enabling quantification of human skin biomarkers for non-invasive skin disease diagnosis. Deep4OM has the potential to change the landscape of non-invasive skin imaging, and could significantly promote the diagnostic and prognostic applications of RSOM in clinical routine.JIMM
Geophysical Joint Inversion for Accurate Brain Myelin Mapping
The aim of this project is to develop a method for clinically diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases. The content of myelin in the brain – a substance that becomes degraded in diseases – will be quantified using methods from geophysics in order to facilitate early detection and treatment.SIM
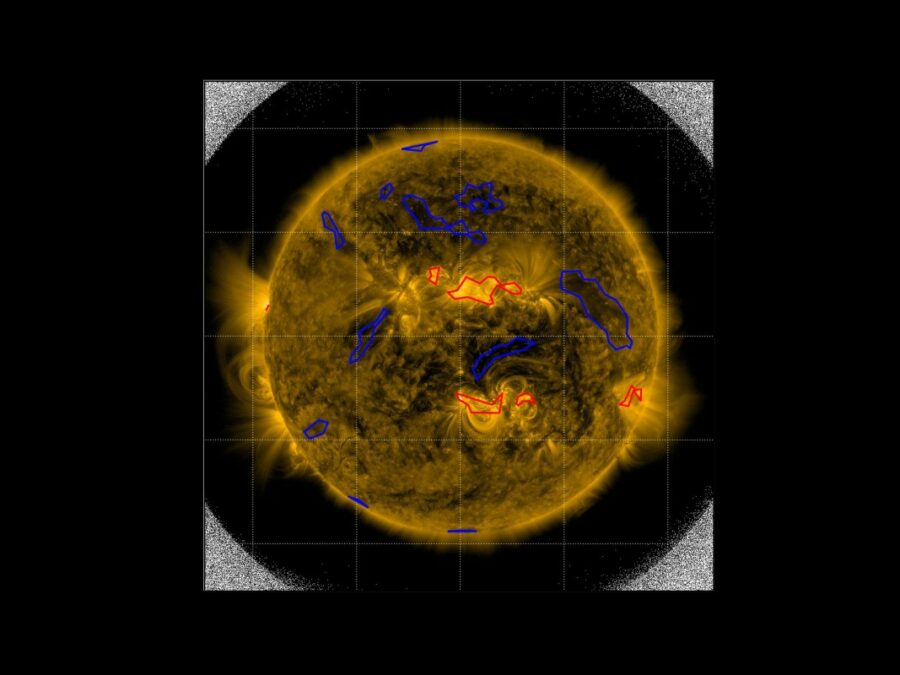
Solar Image-based Modelling
The aim of the project is to develop an algorithm by which computers can automatically predict the space weather. This will make use of datasets of solar images that have been captured from space. The method could replace computationally demanding physics-based models and deliver space weather forecasts long before the effects of solar events are […]