Helmholtz Imaging Projects
Helmholtz Imaging Projects aim to initiate cross-cutting research collaborations and identify innovative research topics in the field of imaging and data science.
Funds for Helmholtz Imaging Projects are annually granted to cross-disciplinary research teams for collaborative mid-term projects.
Ideally, Helmholtz Imaging Projects are co-created with users and non-academic stakeholders to ensure the quick adoption of results.
Funding for the first Helmholtz Imaging projects started in December 2020. Many teams have since begun work on major challenges and pressing issues facing society to develop sustainable solutions for tomorrow and beyond.
Discover these outstanding and fascinating research projects with us or become a part of Helmholtz Imaging Projects and apply for your own project. The next call for Helmholtz Imaging Projects is OPEN until July 30, 2025. Find out more about the project call in this summary.
Helmholtz Imaging Projects – ongoing
ImageTox
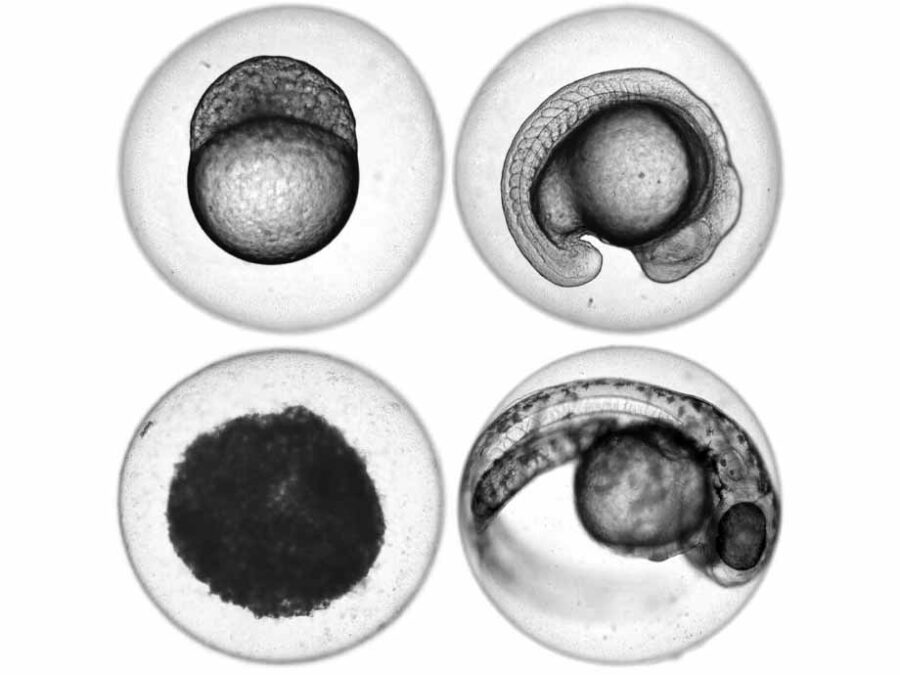
Automated image-based Detection of Early Toxicity Events in Zebrafish Larvae
ImageTox wants to establish an automated image-based system to assess zebrafish larval development. This will allow for a fast and unbiased evaluation of pathophysiological events during toxicological studies. To achieve this, the imaging process has to be optimized and a reliable model for sequence recognition based on deep learning has to be developed.
JIMM2
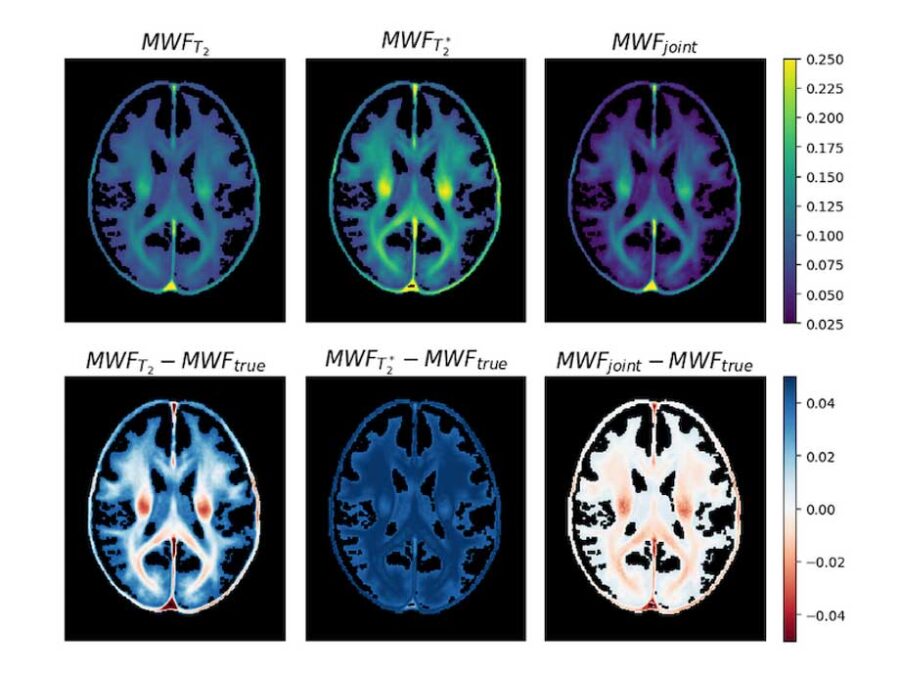
3D Myelin Mapping with AI and Uncertainty Quantification
Changes in brain myelin are linked to many neurological diseases. This project aims to improve myelin water imaging, enabling more accurate and accessible diagnostics.
PlastoView
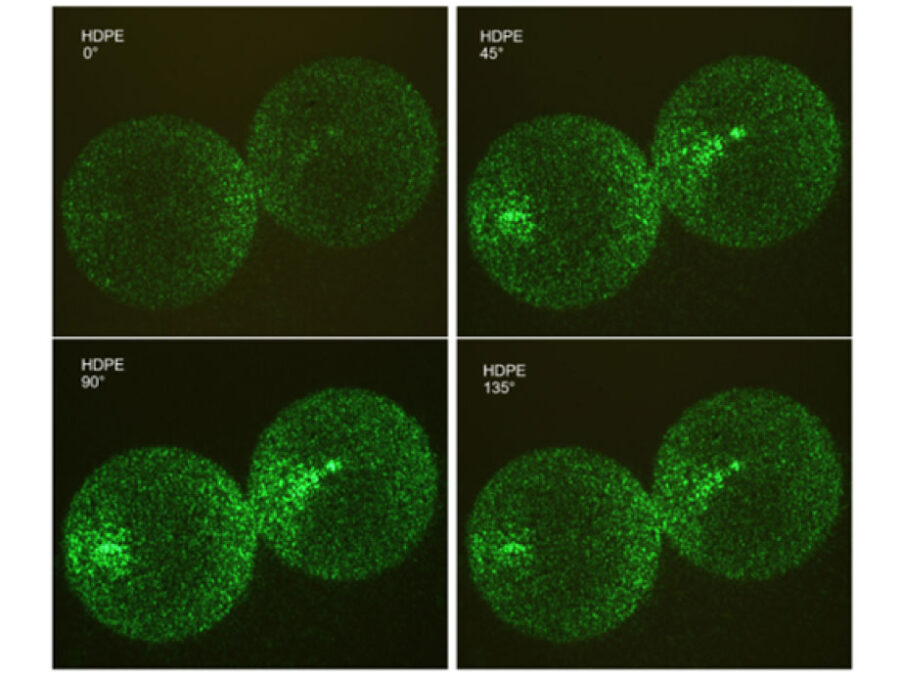
Microplastic Detection with the PlastiScope
Water quality is essential for ecosystems and human health, yet it’s increasingly threatened by microplastics. This project develops image-based methods for detecting both plankton and microplastics using a new low-cost, mobile system.
POINTR
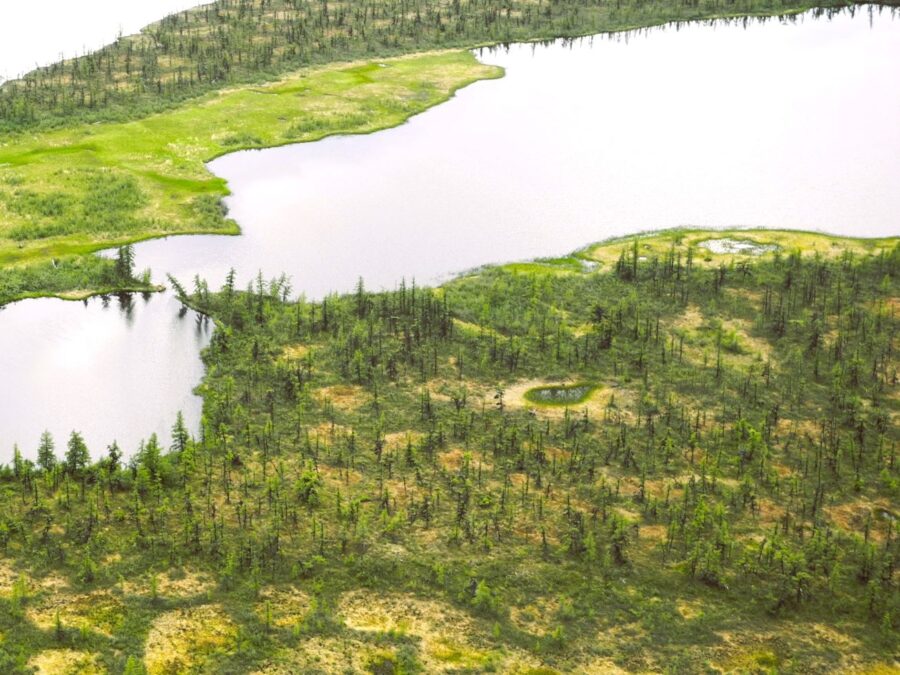
Mapping Boreal Forest Change Using 3D Radar and Point Cloud Data
Global warming is reshaping northern boreal forests. This project maps forest structure and ecosystem services using high-resolution radar satellite monitoring combined with 3D imaging data.
SyNaToSe
Leveraging Cross-Domain Synergies for Efficient Machine Learning of Nanoscale Tomogram Segmentation
The aim is to develop an adaptable algorithm that can be used to perform different tasks in data and image analysis without needing to be trained with new, laboriously annotated images for each separate task.
TerraByte-DNN2Sim
On the trail of the mystery of the laws of calving
Researchers still face a mystery when it comes to the laws by which glaciers calve. This project aims to use satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, mathematical optimisation and a new data processing pipeline to track the movements of glacier fronts in Antarctica to get closer to solving the mystery.
WeMonitor
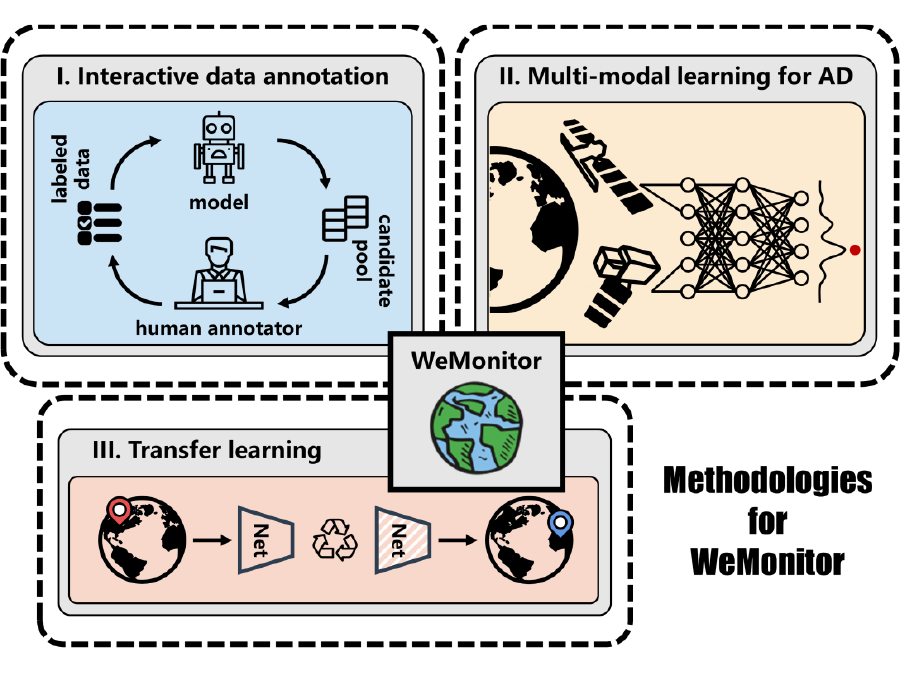
Satellite-based Earth observation to detect natural hazards
Satellite imagery makes it possible to detect spatio-temporal anomalies on the Earth’s surface, including natural hazards such as landslides, deforestation, or the emergence of large waste dump sites. This project aims to use artificial intelligence to detect these changes at an early stage and to be able to monitor their progress.
X-BRAIN
Cross-modality representation learning for brain analysis and data integration
This project aims to develop AI methods that support the integration of multimodal imaging data into human brain atlases, thereby advancing the analysis of brain structure in both health and disease.