Projects
With our Helmholtz Imaging Projects, Helmholtz Foundation Model Initiative (HFMI) and third-party funded projects, we aim to initiate cross-cutting research collaborations and identify innovative research topics in the field of imaging and data science.
Helmholtz Imaging offers a funding line of Helmholtz Imaging Projects, striving to seed collaborations between centers and across research fields. They are a strong incentive to enable interdisciplinary collaboration across the Helmholtz Association and an incubator and accelerator of the Helmholtz Imaging network.
In addition to our Helmholtz Imaging Projects, the Helmholtz Imaging team has secured external funding for third-party projects contributing their knowledge and expertise on cutting-edge imaging methodology.
Join us in unlocking the limitless potential of Helmholtz Imaging!
Find out more about Helmholtz Imaging Project call in this summary.
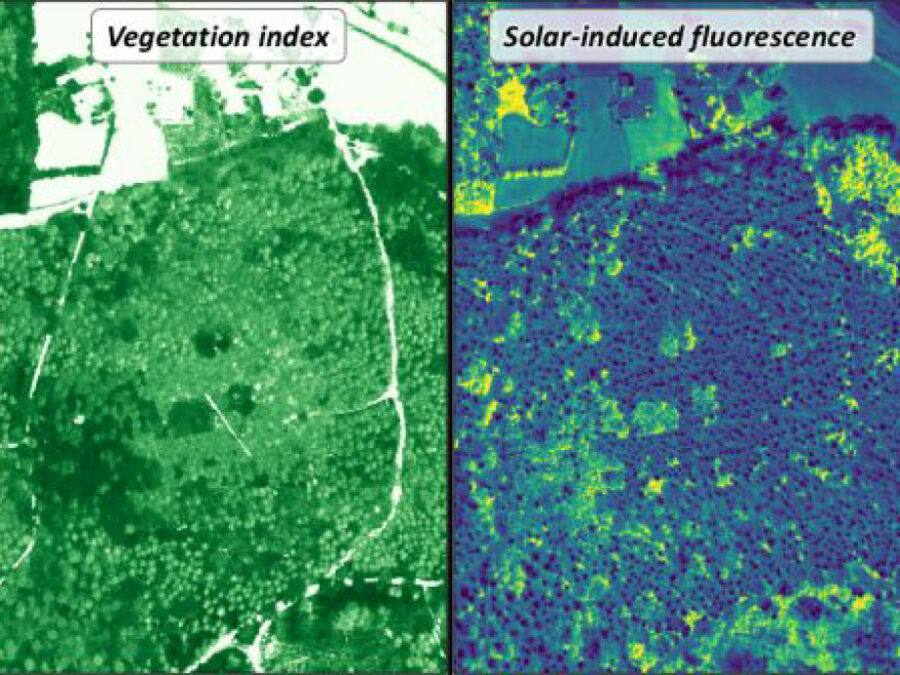
3DforestSIF
Understanding the solar-induced fluorescence (SIF) signal of natural, complex tree canopies
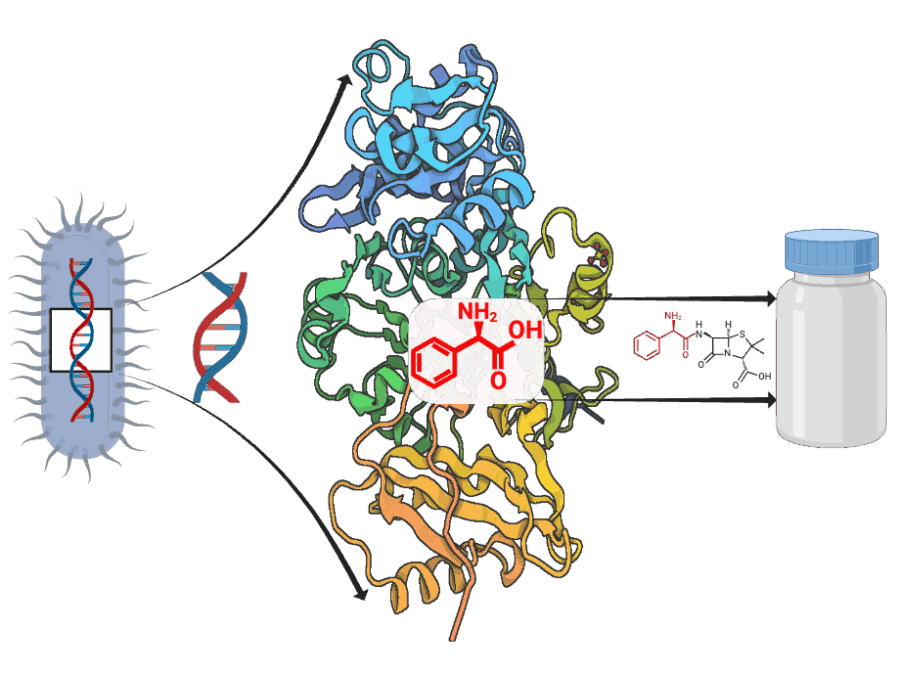
ADD-ON: Adenylation Domain Database and Online Benchmarking Platform
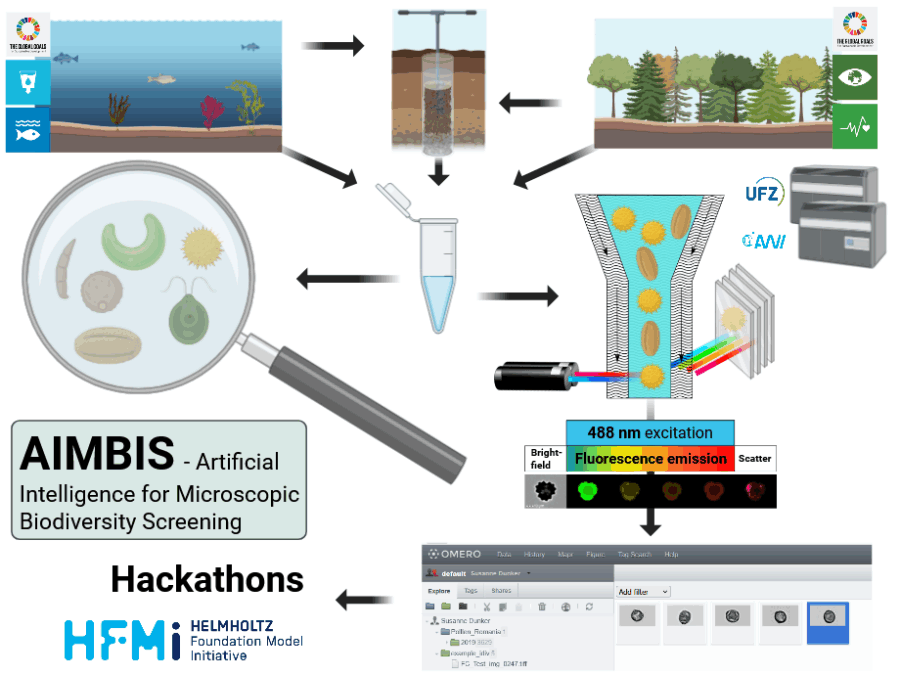
ADD-ON addresses the lack of reliable data for predicting how microbial enzymes assemble peptide-based natural products. By enabling accurate AI-driven structure prediction, it accelerates the discovery of new bioactive compounds and ultimately supports efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance.AIMBIS – Artificial Intelligence for Microscopic Biodiversity Screening
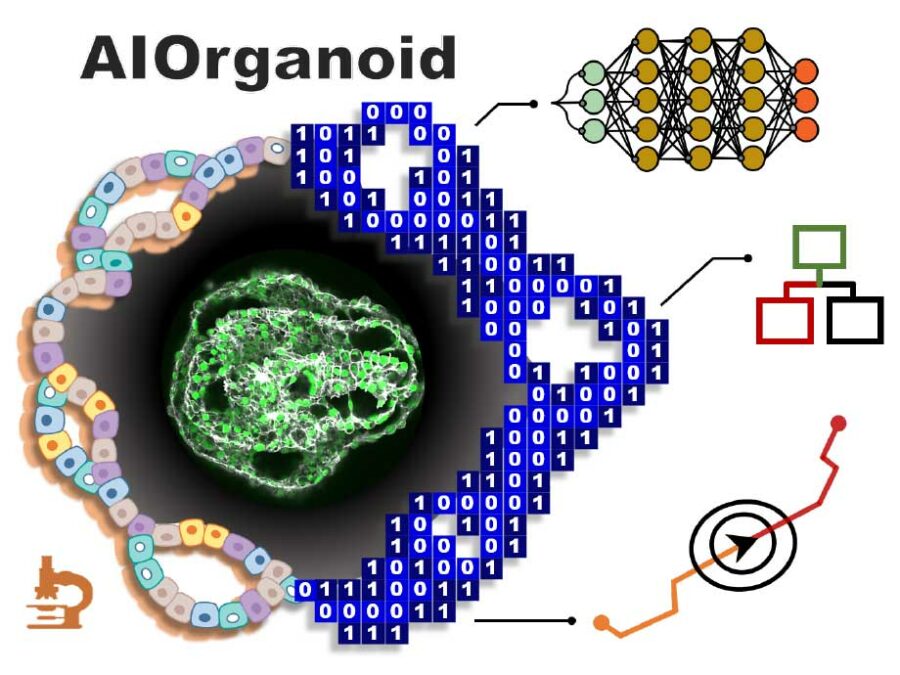
Manual microscopic biodiversity monitoring is time-consuming and requires expert knowledge, limiting the potential for biodiversity monitoring, hence to recognize the impacts of climate and environmental change on crucial ecosystem functions.AIOrganoid
Artificial Intelligence Assisted-Imaging for Creating High-yield, High-fidelity Human Lung Organoid
AMOEBE: lArge-scale Multi-mOdal Microbial livE-cell imaging BEnchmark
Building a large-scale, FAIR benchmark for AI-driven analysis of microbial communities using time-lapse microscopy to advance understanding of microbial dynamics, ecosystem stability, and their role in health and biotechnology.AqQua
AqQua aims to build the first foundational pelagic imaging model using billions of aquatic images worldwide. These images, spanning species from plankton, will help an AI classify species, extract traits, and estimate carbon content, offering key insights into biodiversity, ecosystem health, and the biological carbon pump's role in climate regulation.AsoftXm
Advanced Soft-X-Ray Microscopy Solutions
AutoCoast
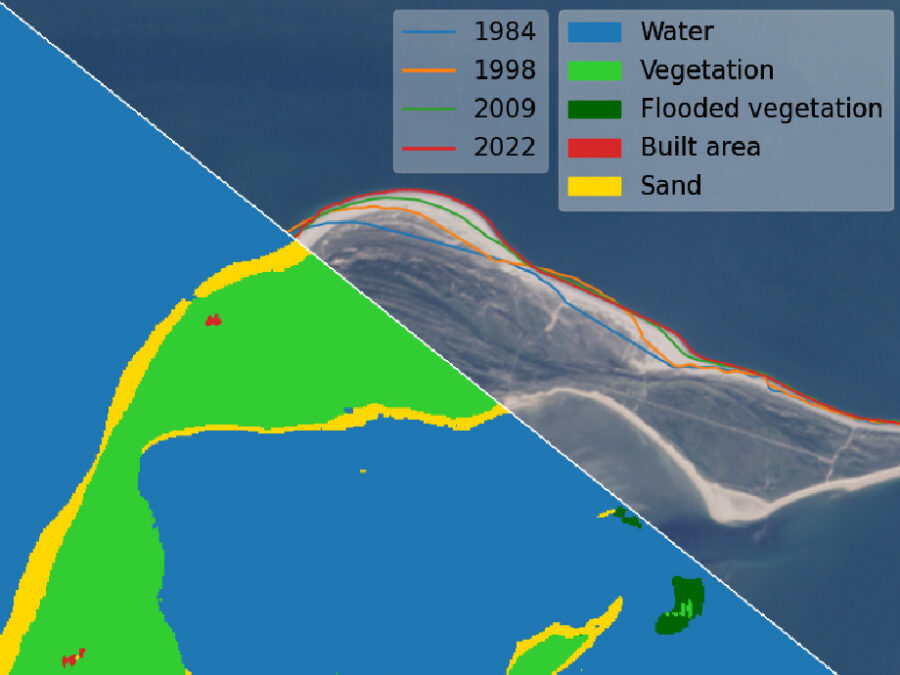
Automatic detection of coastline change and causal linkage with natural and human drivers
Avanti
X-ray tomoscopy of dynamic manufacturing processes
BASE: Benchmarking Agro-environmental database for Sustainable agriculture intensification
Building a BASE dataset enables robust predictions of yield potential, resource efficiency, and sustainability thresholds, driving climate resilience and sustainable agricultural intensificationBayesian Computations for Large-scale (Nonlinear) Inverse Problems in Imaging
During research stays with the collaborating group at Caltech, we aim to investigate various aspects of statistical inverse problems. This includes inquiries into particle- and PDE-based sampling methods, as well as robust regularization using neural networks.BENIGN
Biocompatible and Efficient Nanocrystals for Shortwave Infrared Imaging
BestMeta
Behavioral Standard Metadata
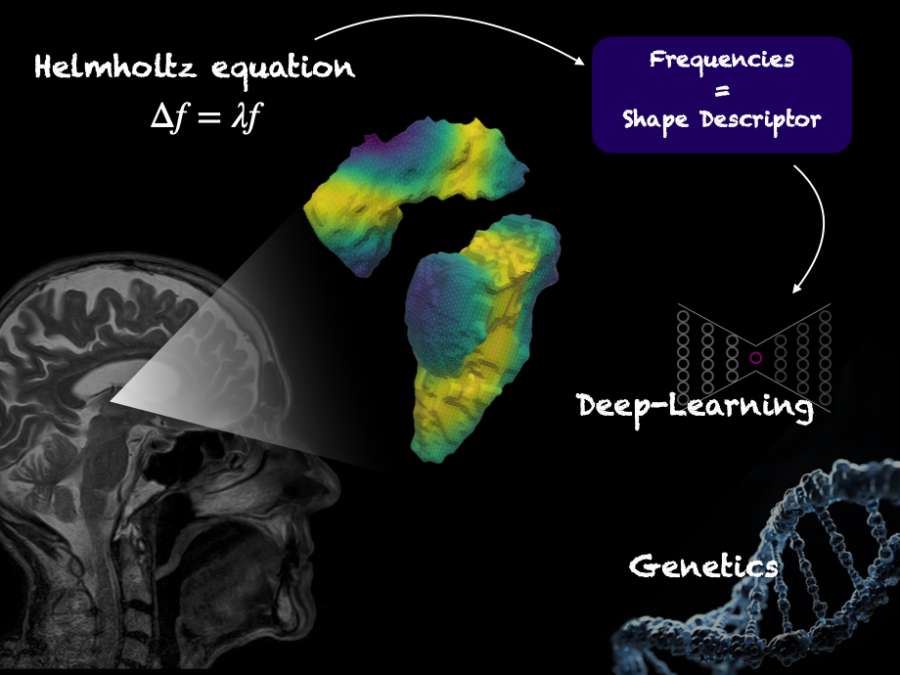
BrainShapes
Laplace-Beltrami shape descriptors of brain structures: Comparative optimization and genetic dissection
BRLEMM
Breaking resolution limit of electron microscopy for magnetic materials
CLARITY
CineMR-guided ML-driven Breathing Models for Adaptive Radiotherapy
COMFORT
COMFORT aims to achieve breakthroughs in developing compact, flexible, and robust machine learning models for image, audio, and network data. In doing so, its application-oriented research program will advance the mathematical understanding of machine learning at the intersection of effectiveness and robustness.cryoFocal
3D Reconstruction from defocused cryo-EM images
Deep Learning based Regularization for Inverse Problems
This project aims to investigate the construction of regularization methods for ill-posed inverse problems based on deep learning and their theoretical foundations. Specific objectives include the development of robust and interpretable results, requiring the initial development of new concepts of robustness and interpretability in this context.Deep4OM
Deep learning powered optoacoustic mesoscopy for non-invasive diagnostics of skin diseases
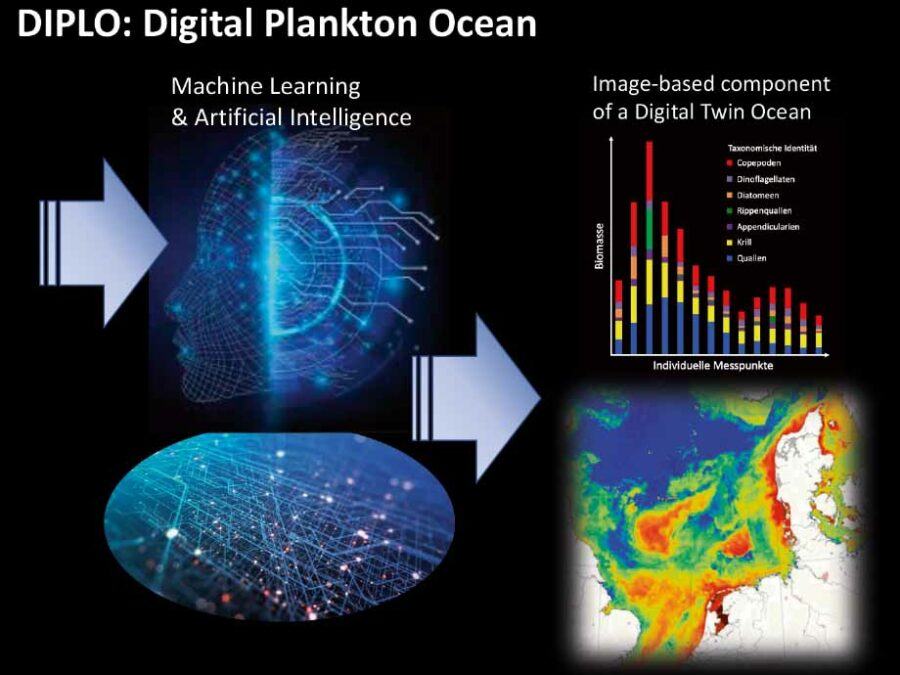
DIPLO
Paving the way from in situ plankton image data to a Digital Twin Ocean
EMSIG
Event-driven Microscopy for Smart Microfluidic Single-cell Analysis
Fast-EMI
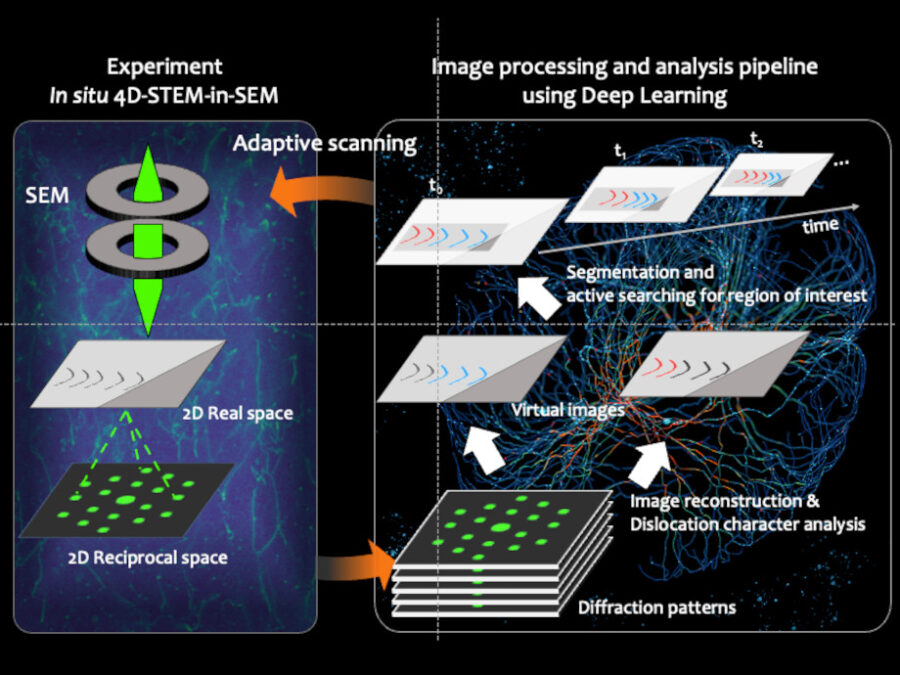
Deep-learning assisted fast in situ 4D electron microscope imaging
FOMIA
A Foundation Model for Microscopy Image Analysis
FONDA: Dependability, Adaptability and Uncertainty Quantification for Data Analysis Workflows in Large-Scale Biomedical Image Analysis
The project aims to enhance infrastructures for machine learning (ML)-intensive DAWs in advanced biomedical imaging applications.
ForestUNLOCK: A multi-modal Multiscale Benchmark Dataset for AI-Driven Boreal Forest Monitoring and Carbon Accounting
Building the first consistent multi-modal single tree benchmark for forest structure and carbon stock assessments of the northern boreal forestFoundations of Supervised Deep Learning for Inverse Problems
Recently, deep learning methods have excelled at various data processing tasks including the solution of ill-posed inverse problems. The goal of this project is to contribute to the theoretical foundation for truly understanding deep networks as regularization techniques which can reestablish a continuous dependence of the solution on the data.GLAM: Generative lung architecture modeling
This project is developing generative methods for designing bio-printable lung tissues across a spectrum of disease severity in the specific context of mouse and human lung disease.GRIDMARK – Generating Reproducible Insights through Data Benchmarking for AI in Energy Systems
Transforming energy systems toward climate neutrality: Distribution grids have the potential to be catalysts for the energy transition. Unfortunately, most Distribution System Operators lack the resources to fully monitor their systems. Therefore, there is an urgent need for more high-quality data, particularly to develop and test machine learning models.HighLine
High Image Quality for Lines in MRI: From Roots to Angiograms
HIT Permafrost
The Hidden Image of Thawing Permafrost
HYPER-AMPLIFAI
Advancing Visual Foundation Models for Multi-/Hyperspectral Image Analysis in Agriculture/Forestry
Hyper 3D-AI
Artificial Intelligence for 3D multimodal point cloud classification
ImageTox
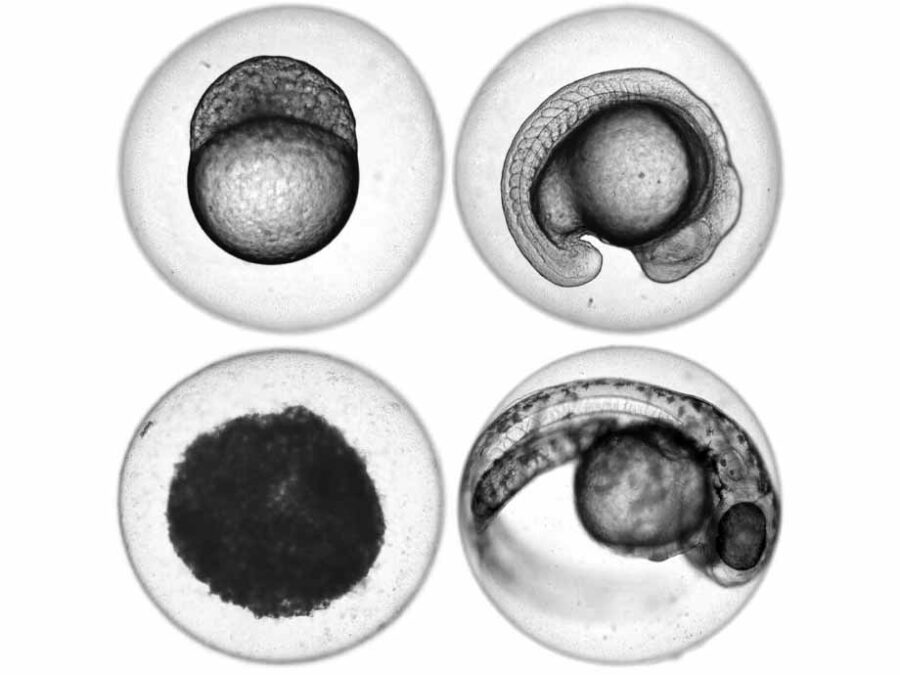
Automated image-based Detection of Early Toxicity Events in Zebrafish Larvae
JIMM
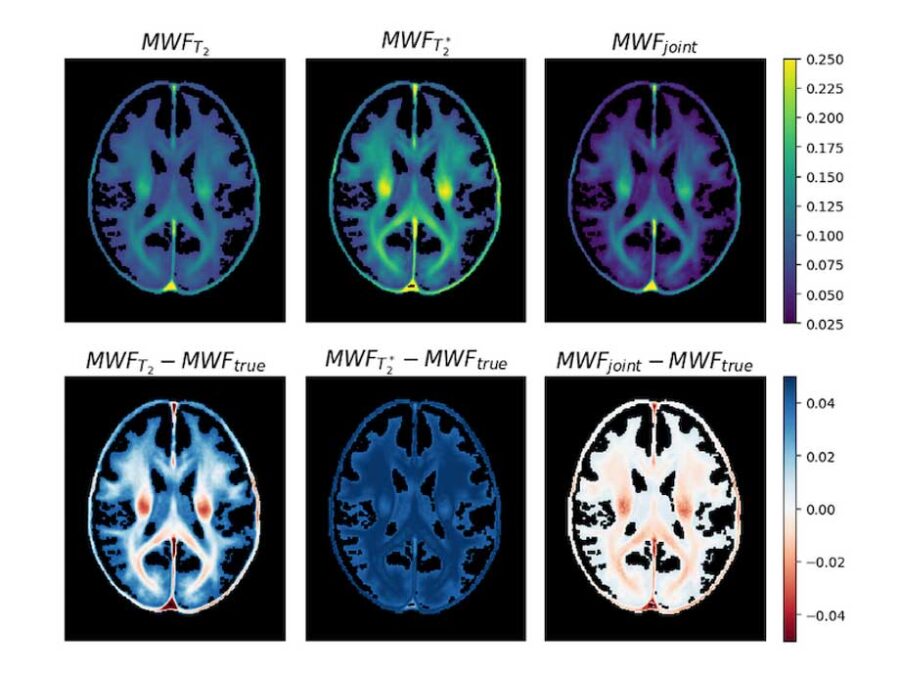
Geophysical Joint Inversion for Accurate Brain Myelin Mapping
JIMM2
3D Myelin Mapping with AI and Uncertainty Quantification
Multi-task Deep Learning for Large-scale Multimodal Biomedical Image Analysis (MDLMA)
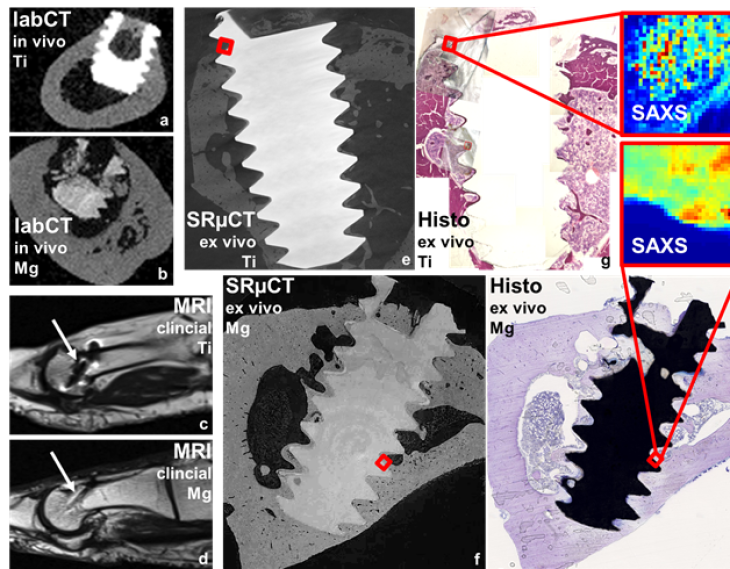
The MDLMA project aims to optimize biodegradable Mg-based implants by analyzing vast multimodal biomedical image data. Through deep learning, it seeks to improve implant properties by understanding the interplay of microstructure, mechanics, biology, and degradation. The project will develop multi-task deep learning methods for enhanced image analysis, offering a unified framework for broader application in biomedical imaging.MultiSaT4SLOWS
Multi-Satellite imaging for Space-based Landslide Occurrence and Warning Service
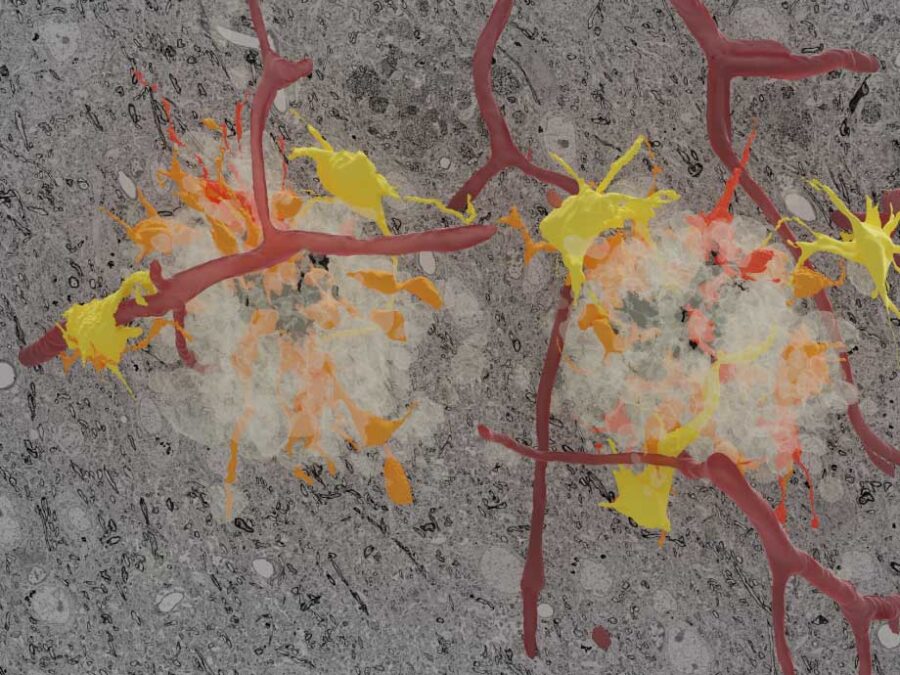
NeuroHarmonize – A Benchmark Decentralized Data Harmonization Workflow for AI-Driven Alzheimer’s Disease Management
The benchmark addresses the lack of harmonized, reproducible, and privacy-preserving multimodal datasets for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). NeuroHarmonize creates a FAIR-compliant, decentralized benchmarking framework to accelerate reliable, transparent, and collaborative AI for AD diagnosis, prognosis, and long-term monitoring.NImRLS
Neuroimaging Biomarkers for Restless Leg Syndrome
Pero – Unlocking ML Potential: Benchmark Datasets on Perovskite Thin Film Processing
Addressing the lack of standardized, FAIR benchmark datasets in perovskite photovoltaics. Pero enables reproducible AI models for efficiency prediction, material classification, and defect detection, which are critical for industrial scaling of sustainable energy technologies.PlastoView
Microplastic Detection with the PlastiScope
POINTR
Mapping Boreal Forest Change Using 3D Radar and Point Cloud Data
QGRIS: Quantitative Gamma-Ray Imaging System
Compton cameras are used for the radiological characterization of nuclear power plants. In this project, a suitable camera system is designed, and the associated algorithms for image reconstruction and nuclide characterization are implemented as user software.RenewBench – A Global Benchmark for Renewable Energy Generation
Renewable energy’s variability makes grid management complex. RenewBench aims to provide standardized, high-quality data to advance trustworthy AI models and accelerate the transition to sustainable energy.SATOMI
Tackling the segmentation and tracking challenges of growing colonies and microbialdiversity
SCHEMA – profiling Spatial Cancer HEterogeneity across modalities to benchmark Metastasis risk prediction
SCHEMA creates a benchmark dataset linking tumor samples with metastasis outcomes to enable machine-learning models that predict metastasis risk and support clinical decision-making.SFB Transregio 154 – C06: Transport metrics for analysis and optimization of network problems
SFB TRR 154 is a project of the German Research Foundation (DFG) and combines integer-continuous methods, model adaptation, and numerical simulation, to analyze and optimize gas markets, infrastructure, and control of networks. The third funding period specifically focuses on the transition from natural gas to hydrogen.SIM
Solar Image-based Modelling
SmartPhase
Fast, intelligent 3-D X-ray images for material examination
Spatio-temporal inverse approaches for EEG/MEG reconstruction of neural networks in the human brain
This project aims to develop novel methods for reconstructing brain activity from dynamic EEG and MEG measurements. By using realistic, individualized finite element models and advanced regularization techniques, including machine learning, we seek to solve this inverse problem in real patient settings, ultimately improving the diagnosis and treatment of medication-resistant focal epilepsy.SyNaToSe
Leveraging Cross-Domain Synergies for Efficient Machine Learning of Nanoscale Tomogram Segmentation
Synergy Unit
The Synergy Unit amplifies the Helmholtz Foundation Model Initiative's impact by developing AI principles for diverse fields. Collaborating with HFMI projects, it focuses on knowledge sharing, community building, and representation to ensure the initiative's lasting influence.TerraByte-DNN2Sim
On the trail of the mystery of the laws of calving
The Human Radiome Project (THRP)
The Human Radiome Project (THRP) aims to drive a paradigm shift in medical research, providing novel insights into human health and disease through the power of AI. By integrating diverse radiological data, it seeks to enable groundbreaking advancements in personalized medicine, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving patient care.TIMELY: Time-series Integration across Modalities for Evaluation of Latent DYnamics
TIMELY provides the first comprehensive benchmark for multimodal biological time-series data, addressing the lack of standardized, high-quality datasets for modeling complex dynamical systems. It fosters the development of statistical and foundation models tailored to the analytical needs of research in biomedicine and neuroscience.UCS
Ultra Content Screening for Clinical Diagnostics and Deep Phenotyping
UMDISTO: Unsupervised Model Discovery
The project aims to develop novel methods for unsupervised multi-matching to map cellular-level correspondences in organisms like C. elegans.UQOB – Uncertainty Quantification in Object-detection Benchmark
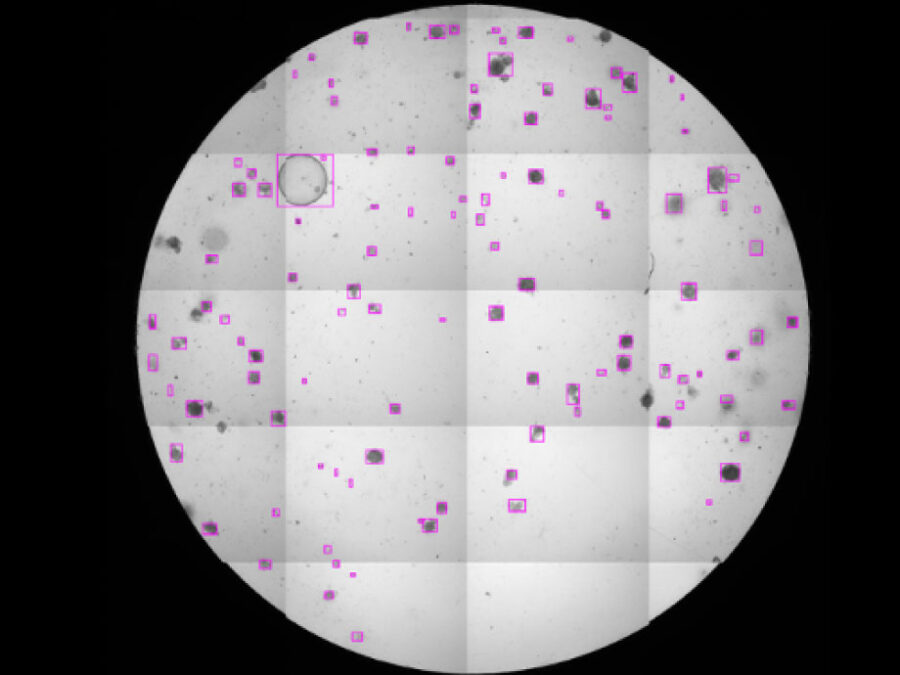
Creating a benchmark dataset for object-detection and Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) in a multi-rater setting, to address annotation variability and AI model evaluation.UTILE
Autonomous image analysis to accelerate energy materials discovery and integration
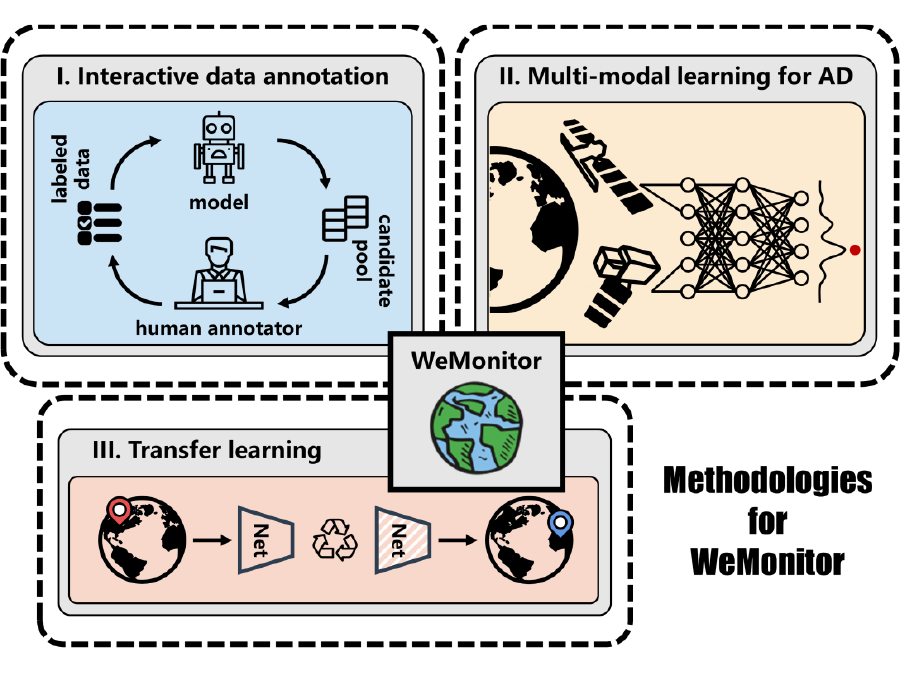
WeMonitor
Satellite-based Earth observation to detect natural hazards
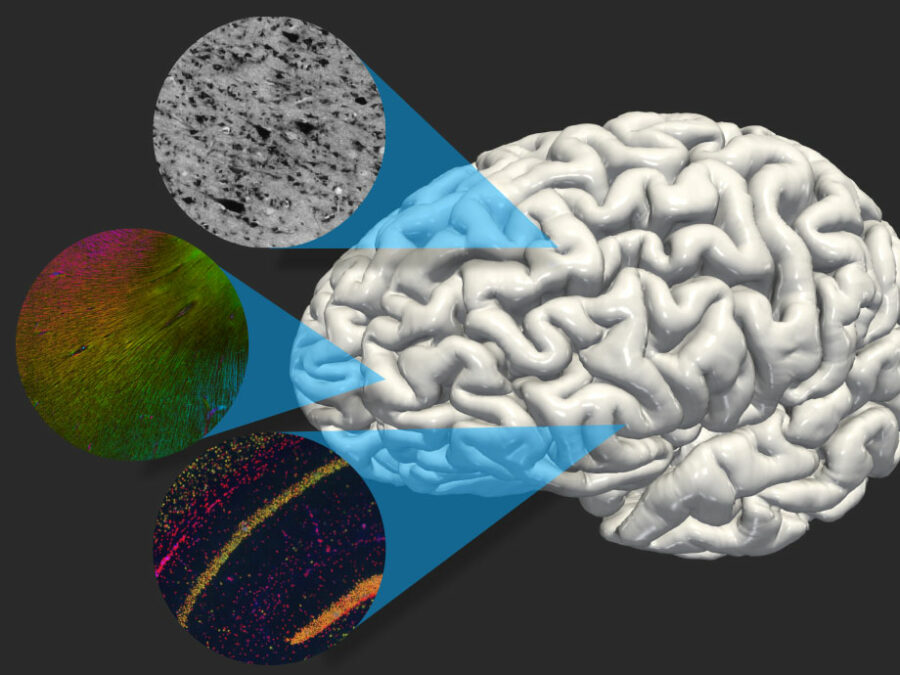
X-BRAIN
Cross-modality representation learning for brain analysis and data integration