Hyper 3D-AI
Artificial Intelligence for 3D multimodal point cloud classification
The aim of this project is to develop software tools that can efficiently analyse images in a three-dimensional context – for example medical images or pictures from cameras mounted on self-driving cars. Artificial intelligence (AI) is already capable of detecting anomalies in MRI images, for example, by classifying the image data. However, many of the existing AI algorithms only work with two-dimensional images. While they can analyse neighbouring pixels in the image, they cannot recognise whether they reside on the same plane as each other in reality.
“We work with point clouds, where we have three-dimensional coordinates for each point,” says Dr. Sandra Lorenz of the Helmholtz Institute Freiberg for Resource Technology. “That is a completely different architecture from what is used for analysing pixels in photos. However, the current methods can’t really cope properly with these point clouds yet, even though point clouds offer a much better depiction of the real world.” The researchers now want to close this gap. By characterising pixels in 3D space, this will open up new possibilities in fields like exploration and mining, medicine and autonomous systems.
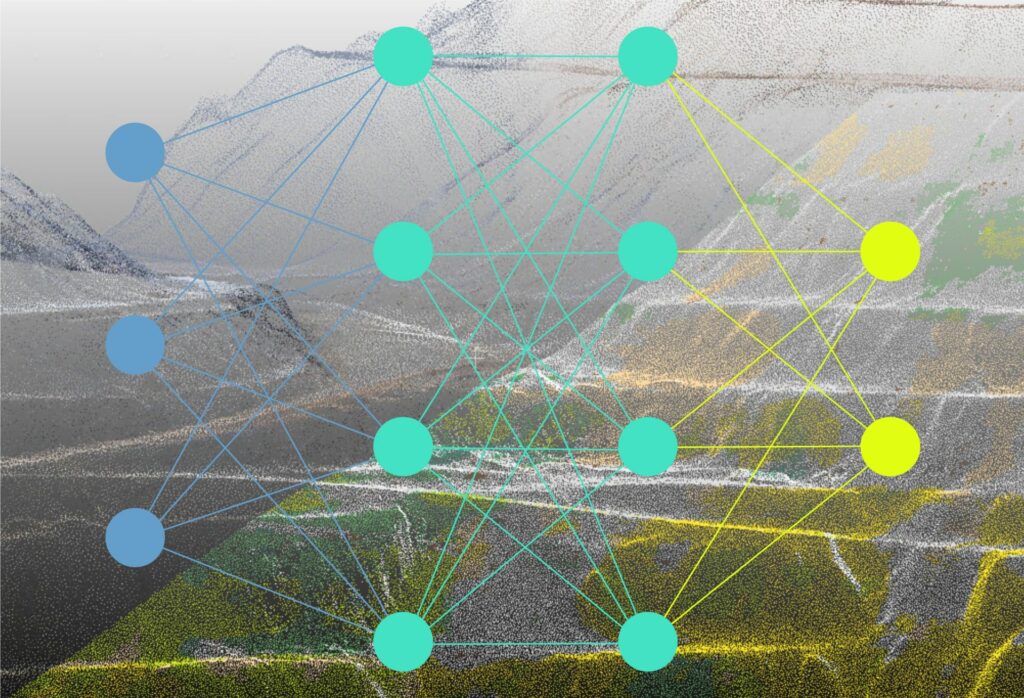

AI should then be able to achieve multimodal classification, or in other words distinguish objects or domains out of data coming from multiple sensors. For mining, as one possible application, this could mean the software would automatically recognise deposits of mineral raw materials, for example, based on spectral properties or colours.
Other projects
Avanti
X-ray tomoscopy of dynamic manufacturing processes
How can the manufacturing processes of materials be mapped at the smallest level? How do you train an artificial intelligence to analyze these processes automatically? That's the focus of the Avanti project, which aims to improve X-ray tomoscopy – the imaging and quantification of three-dimensional images of very fast-moving processes.SATOMI
Tackling the segmentation and tracking challenges of growing colonies and microbialdiversity
An artificial intelligence will observe the growth of bacteria: from microscope images of bacterial cultures taken at regular intervals, it will precisely track the development and division of individual cells – even when multiple bacterial species are cultivated together.HYPER-AMPLIFAI
Advancing Visual Foundation Models for Multi-/Hyperspectral Image Analysis in Agriculture/Forestry
The project aims to make advanced AI models accessible for Hyperspectral Earth Observation, reducing computational demands, and improving environmental assessments through user-friendly interfaces.