Fast-EMI
Deep-learning assisted fast in situ 4D electron microscope imaging
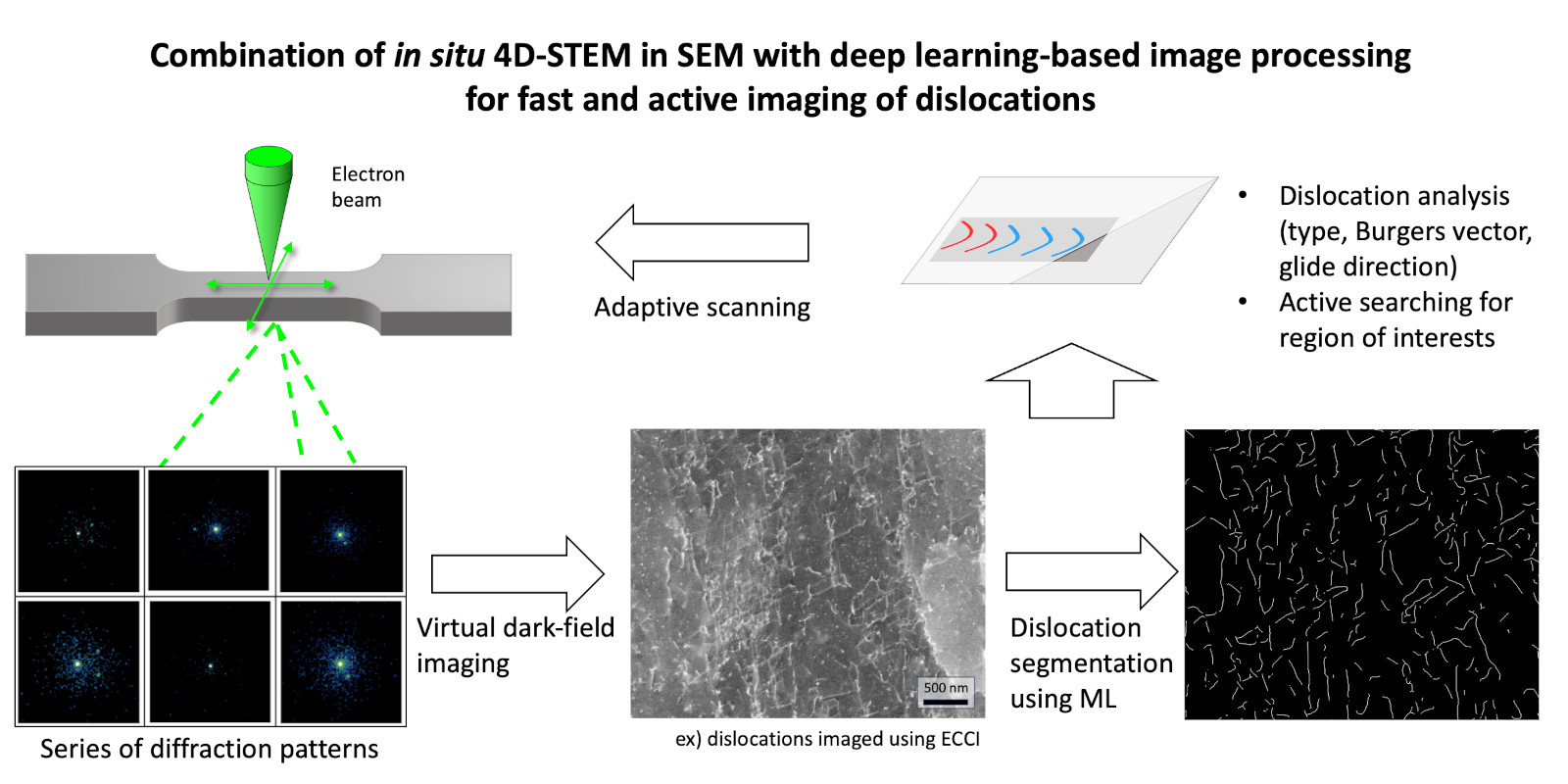
This project advances imaging capabilities by integrating in situ 4D-STEM-in-SEM with deep learning algorithms. The approach utilizes adaptive scanning and real-time feature tracking to significantly enhance the time resolution for in situ and operando imaging of materials.
Another objective is to capture moving dislocations under stress using virtual dark field images, complemented by detailed information computed from reciprocal space, such as strain and phase maps. This innovative setup aims to uncover material degradation mechanisms under mechanical stress in functional materials.
Upon successful implementation, the approach is expected to open new horizons across various research fields beyond materials science, including chemistry and biology. By bringing together experts in image analysis, data science, and microscopy, this project paves the way for new electron microscopy applications and fosters cross-disciplinary innovation.
Other projects
SATOMI
Tackling the segmentation and tracking challenges of growing colonies and microbialdiversity
An artificial intelligence will observe the growth of bacteria: from microscope images of bacterial cultures taken at regular intervals, it will precisely track the development and division of individual cells – even when multiple bacterial species are cultivated together.SIM
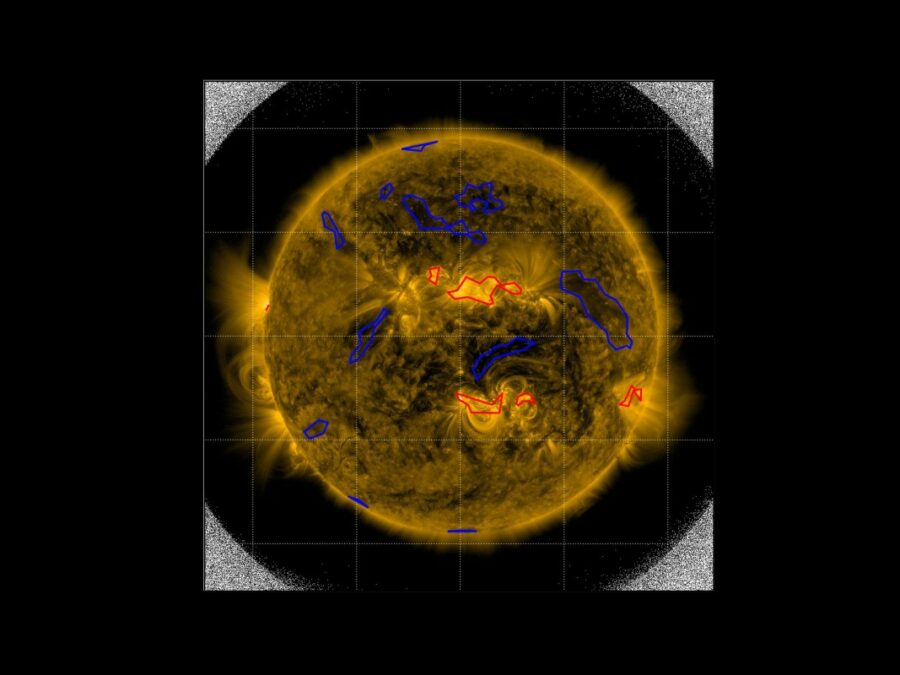
Solar Image-based Modelling
The aim of the project is to develop an algorithm by which computers can automatically predict the space weather. This will make use of datasets of solar images that have been captured from space. The method could replace computationally demanding physics-based models and deliver space weather forecasts long before the effects of solar events are […]AsoftXm
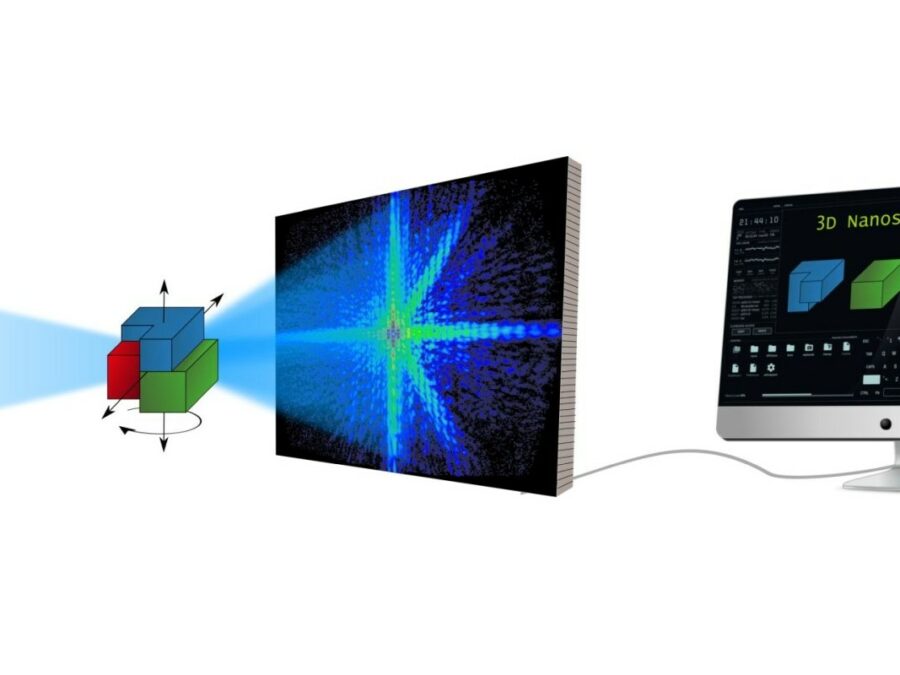
Advanced Soft-X-Ray Microscopy Solutions
The project aims to develop a method that will speed up the analysis of diffraction patterns that arise in UV and soft X-ray light microscopy, so that the structure of the studied sample can be calculated more efficiently. The method could make the three-dimensional study of nanomaterials considerably easier. There are times when researchers need […]