JIMM2
3D Myelin Mapping with AI and Uncertainty Quantification

Myelin, a lipid-rich substance surrounding nerve fibers, is essential for fast and efficient signal transmission in the brain. Myelin water imaging (MWI) offers a non-invasive way to measure myelin content, making it a valuable diagnostic tool. However, conventional MWI methods struggle with accuracy due to the complex nature of MRI signal inversion.
This project builds on prior work showing that combining two MRI contrasts improves MWI. Now, we propose a more advanced approach: jointly inverting up to four myelin-sensitive MRI contrasts using global search strategies. This will reduce bias introduced by regularization and improve image quality.
From these results, we will generate a high-resolution myelin atlas and train deep learning models that can perform rapid 3D MWI with uncertainty quantification. This will allow rapid MWI at unprecedented high spatial resolution and accuracy, and it will enable a truly quantitative diagnostics free of regularization biases and mislead optimization.
Other projects
BrainShapes
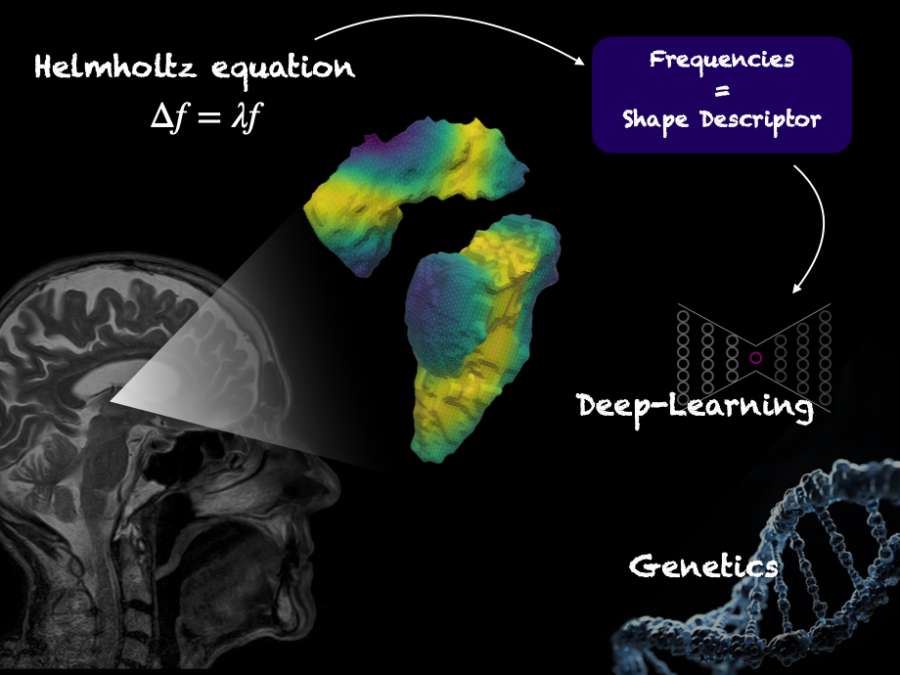
Laplace-Beltrami shape descriptors of brain structures: Comparative optimization and genetic dissection
The project explores the 3D structure of the human brain by creating a digital 'map' of the brain and examining its unique genetic properties, potentially linking genetic variations to brain disorders.HighLine
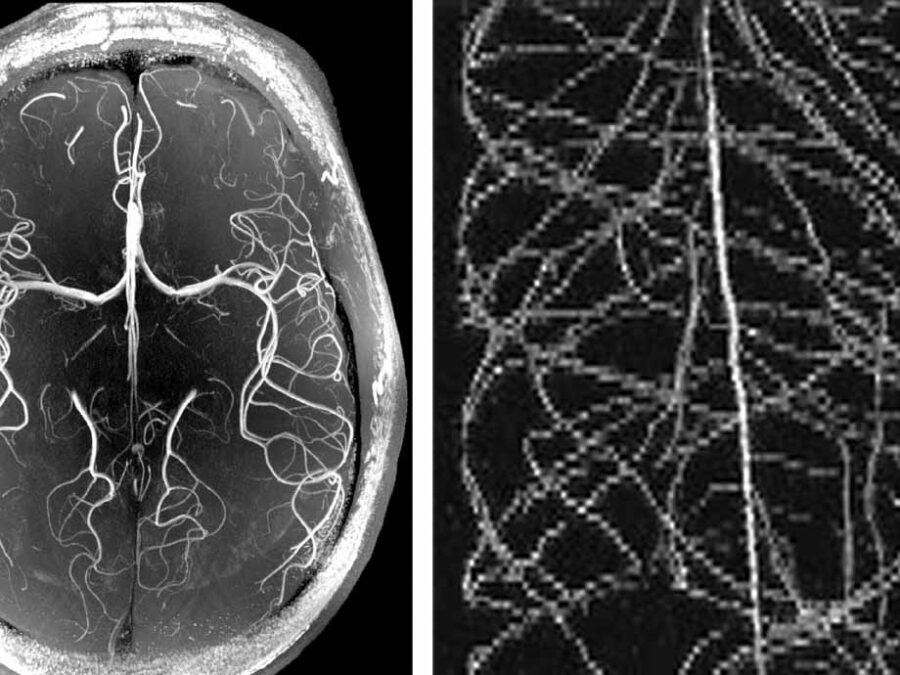
High Image Quality for Lines in MRI: From Roots to Angiograms
MR images of roots and vessels are very similar: both display thin, line-like objects. The aim of the project is to increase image quality of both kind of MR data by exploiting their similarity. HighLine aims at obtaining high quality images in reduced scan time to lower patient burden and increase patient and plant throughput by adapting state-of-the-art 3D image enhancement methods, and developing new deep-learning based methods.HYPER-AMPLIFAI
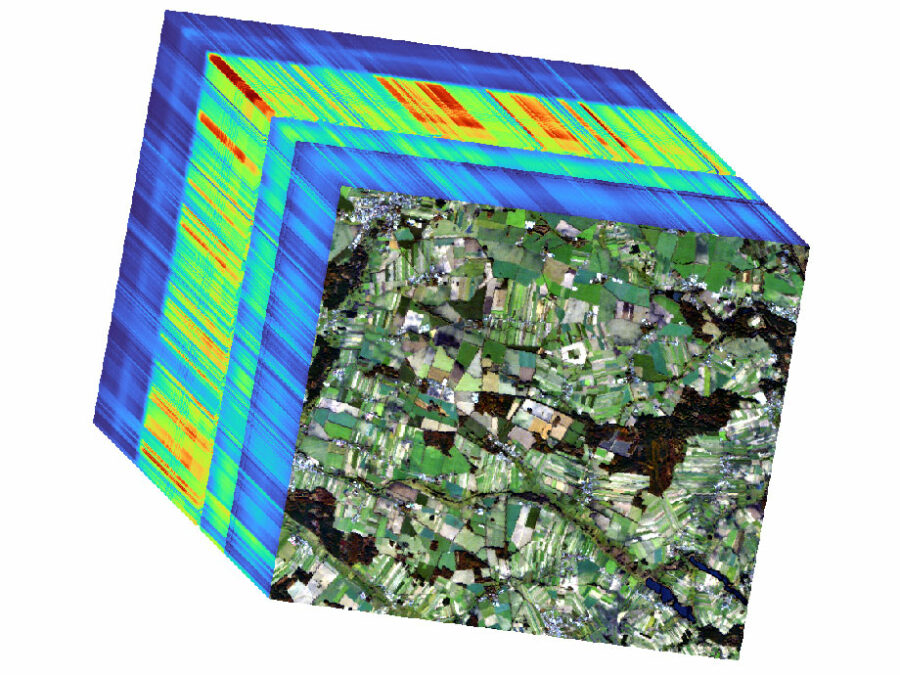
Advancing Visual Foundation Models for Multi-/Hyperspectral Image Analysis in Agriculture/Forestry
The project aims to make advanced AI models accessible for Hyperspectral Earth Observation, reducing computational demands, and improving environmental assessments through user-friendly interfaces.