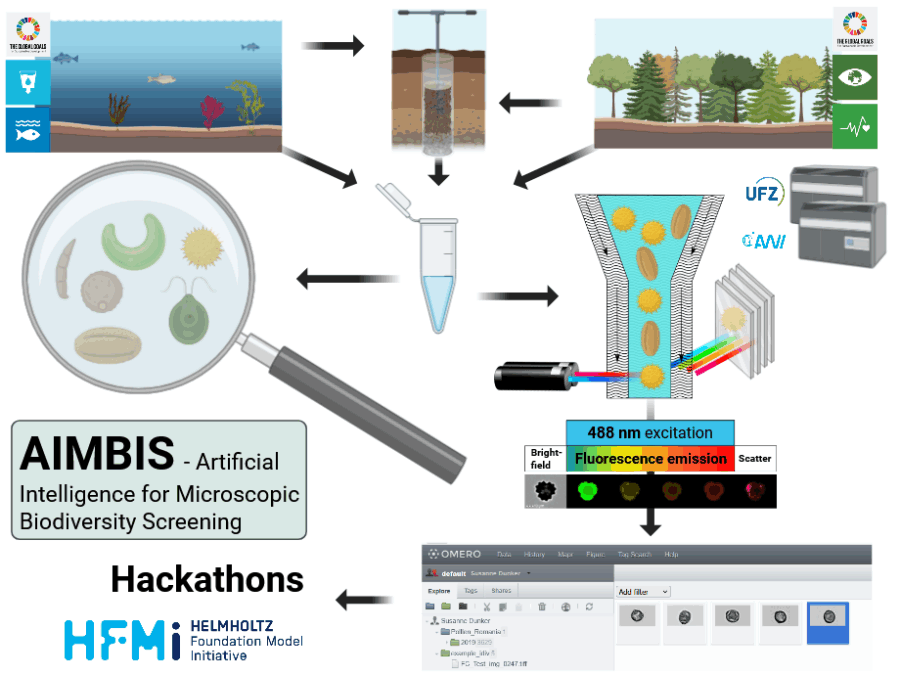
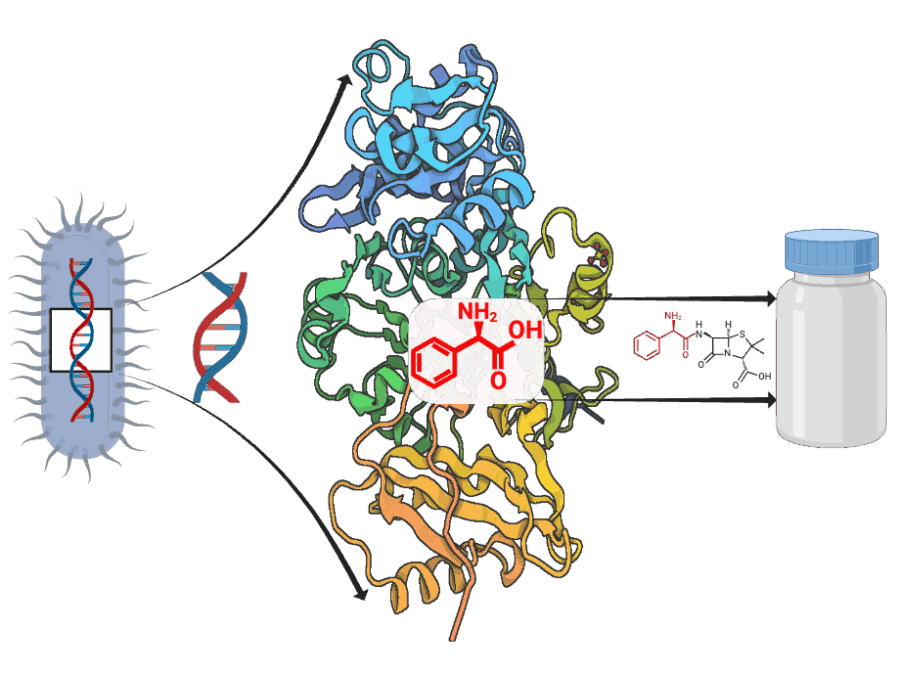
BASE: Benchmarking Agro-environmental database for Sustainable agriculture intensification

What is the project about?
BASE will provide a spatial, crop-resolved benchmark linking yields with inputs, management, climate, and socio-economic drivers. By harmonizing global datasets with farm-survey syntheses and remote-sensing layers, it will enable robust prediction of yield gaps, resource efficiency, and environmental thresholds for sustainable intensification.
What gap in the scientific community led to the creation or expansion of this benchmarking dataset?
The community lacks a standardized, observational dataset that jointly captures region-specific yield-limiting factors—management, water, nutrients, climate, and socio-economic drivers. Existing resources are fragmented and single objective-centric. BASE fills this gap by providing a harmonized, crop-resolved benchmark for robust, comparable analyses.
What impact does the project aim to achieve — within Helmholtz and across the broader research and industry community?
BASE dataset will bridge observational, field-level agricultural data with cutting-edge AI modeling, enabling robust benchmarking for yield prediction, sustainability assessment, and policy insights. It will catalyze interdisciplinary research and evidence-based decision-making within Helmholtz and beyond.