info
Best Scientific Image Contest 2021
The call for Best Scientific Image 2021 resulted in more than 100 submitted images that demonstrate the outstanding portfolio and imaging expertise of the Helmholtz Association. Discover the best 20 images in this virtual gallery!
Gallery
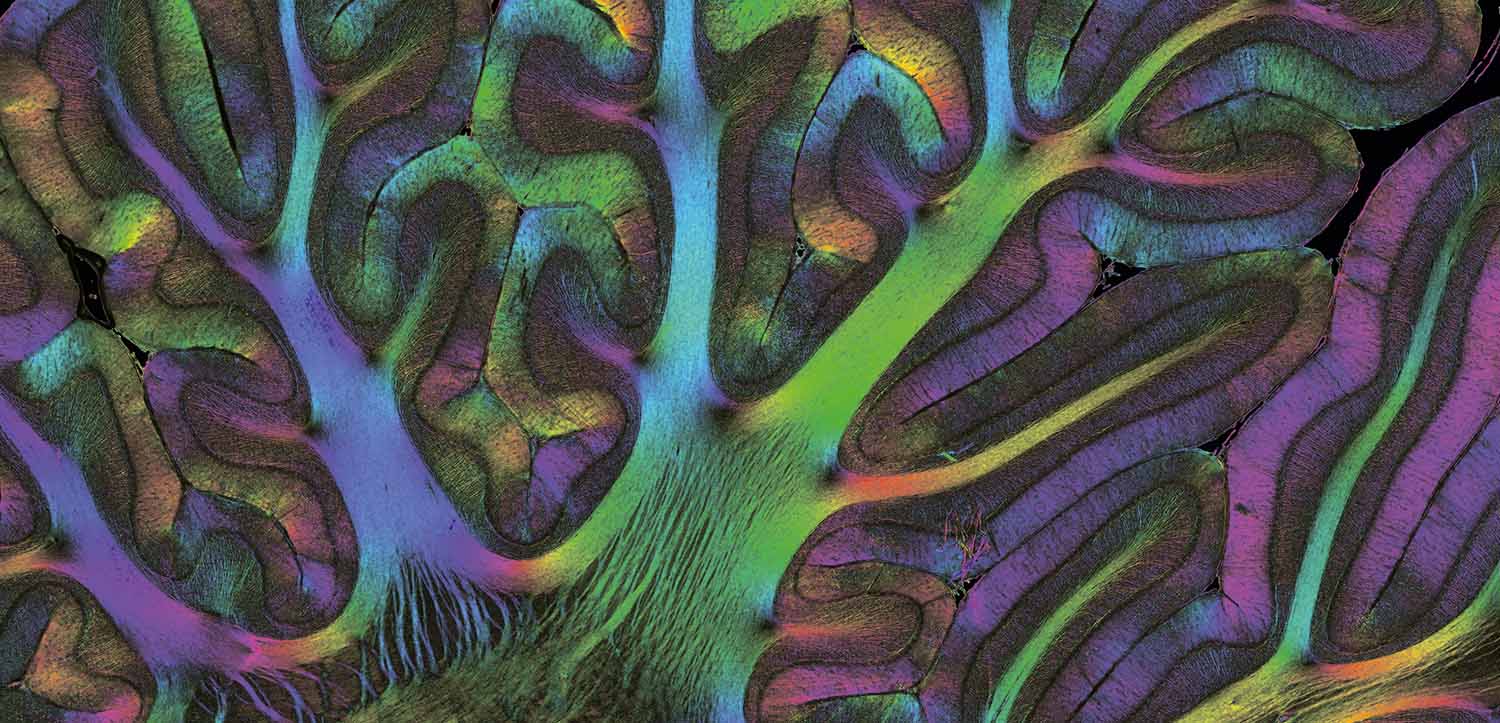

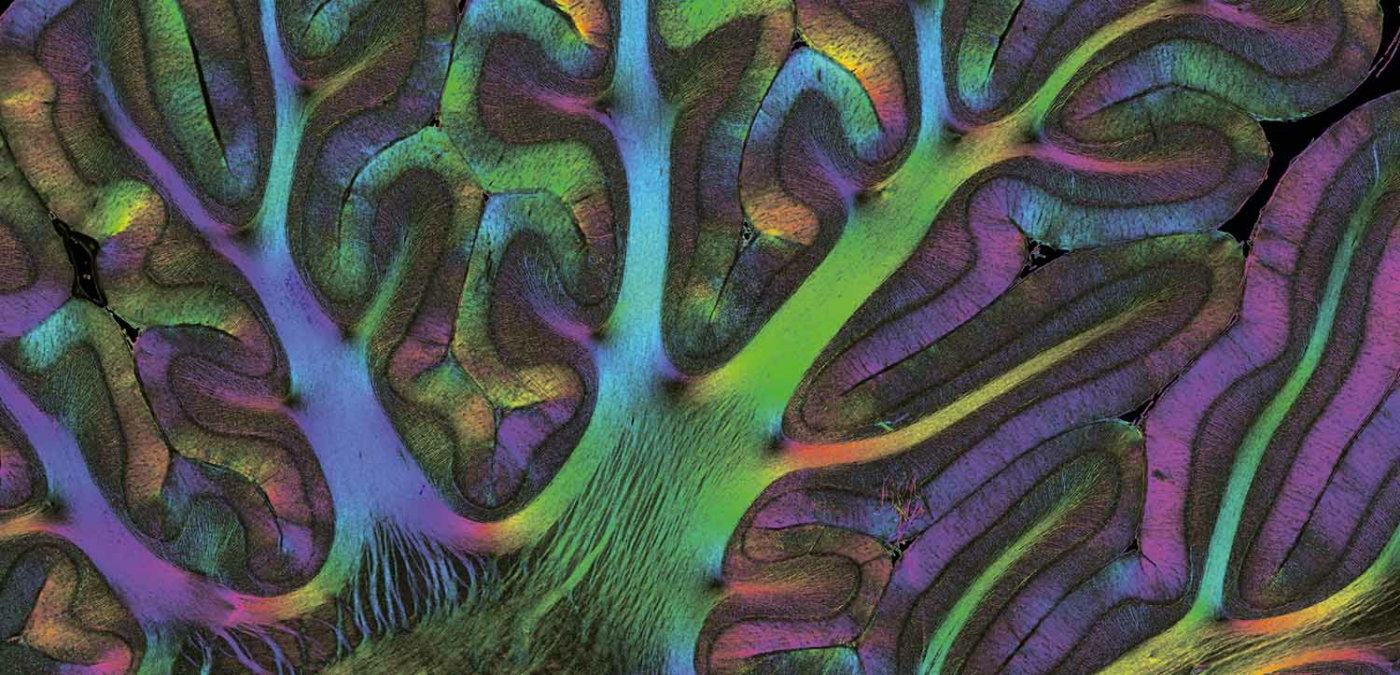
The monkey's fiber architecture revealed by Polarized Light Imaging (1st place, Jury Award)
Markus Axer, FZJ
The image shows the courses/orientations of nerve fibers in the cerebellum of a teenage vervet monkey brain section (60um thickness) at micrometer resolution, called Fiber Orientation Map. The cryosectioned, unstained brain section was scanned and analyzed with the Polarized Light Imaging (PLI) technique utilizing the tissue intrinsic birefringence properties of myelinated axons to generate contrast and to (super)compute 3D fiber orientations per image pixel. Each fiber orientation is assigned a unique color (see HSV color sphere) resulting in the colorful image. Since PLI is highly sensitive to myelin, it is applicable to the normal or the developing (shown here) brain, but also to brains afflicted with degenerative diseases. This image will contribute to a vervet monkey brain fiber atlas assembled by the Human Brain Project. Nerve fiber/connectivity research is typically carried out on large series of consecutive sections that have been non-linearly realigned/registered to reconstruct the original 3D brain shape.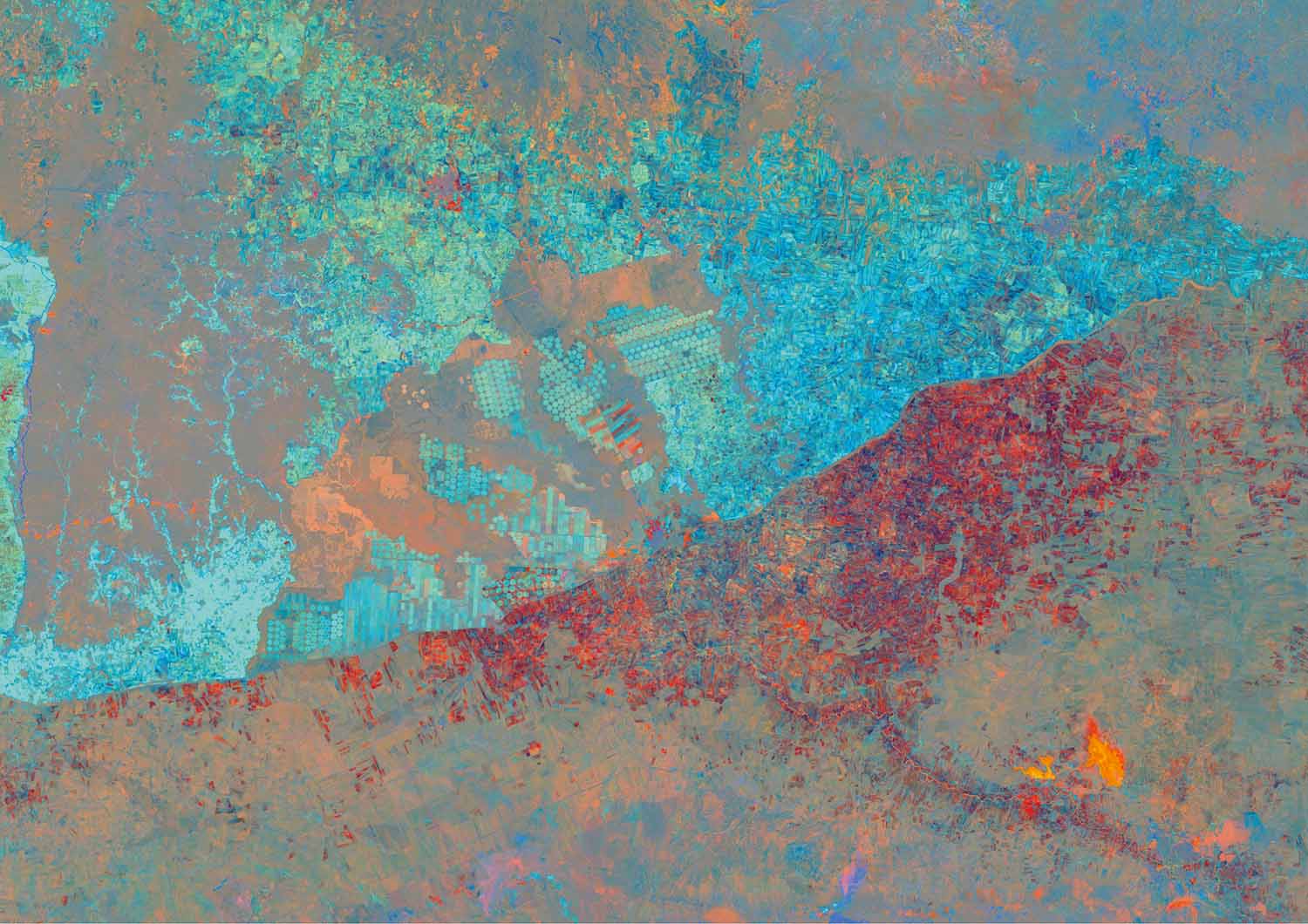

War and Border (2nd Place, Jury Award)
Ingmar Nitze, AWI
This image is visualizing the land surfaces changes from 2000-2019 on the Turkey-Syria border based on the analysis of Landsat satellite image time-series in 30 meter resolution. The light blue colors on the Turkish side in the north indicate a strong increase in vegetation abundance due to the development of mostly irrigated agricultural areas, e.g. center-pivot irrigation fields. Meanwhile vegetation in agricultural areas decreased strongly on the Syrian side in the south shown by the red colors, likely caused by the war in Syria. Furthermore, the main river and large water reservoir in the southeastern corner (yellow and orange colors) shows signs of drying up. Although the landscape is almost the same on both sides of the border, the development caused by human influence could not be greater. Originally this visualization method was developed to detect landscape dynamics in Arctic permafrost landscapes, but was expanded continental spatial scales.

Gentle gelatinous giant (3rd Place, Jury Award)
Henk-Jan hhoving, GEOMAR
The 'rabbit-eared' comb jellyfish Kiyohimea usagi as observed in 2018 by GEOMAR's manned submersible JAGO in the Cabo Verde deep sea at 115 m of depth. The relatively large species (imaged individual is ~40 cm long) is named for its ear-like processes ('usagi' = 'rabbit' in Japanese) that protrude from the animal. Kiyohimea usagi, swims slowly by pulsating its rows of “combs”, modified hair-like cilia that reflect light. It is an efficient predator and ambush hunter. The lobes contain mucus and sticky tentacles that entangle crustacean prey. Fragile, gelatinous organisms like these cannot be captured by nets and underwater observations are the only way to document them. Kiyohimea usagi is described from the Pacific and our encounters off Cabo Verde were the first published observations of this species in the Atlantic. This illustrates the hidden biodiversity and unexplored nature of the deep oceanic water column, the largest habitat on the planet.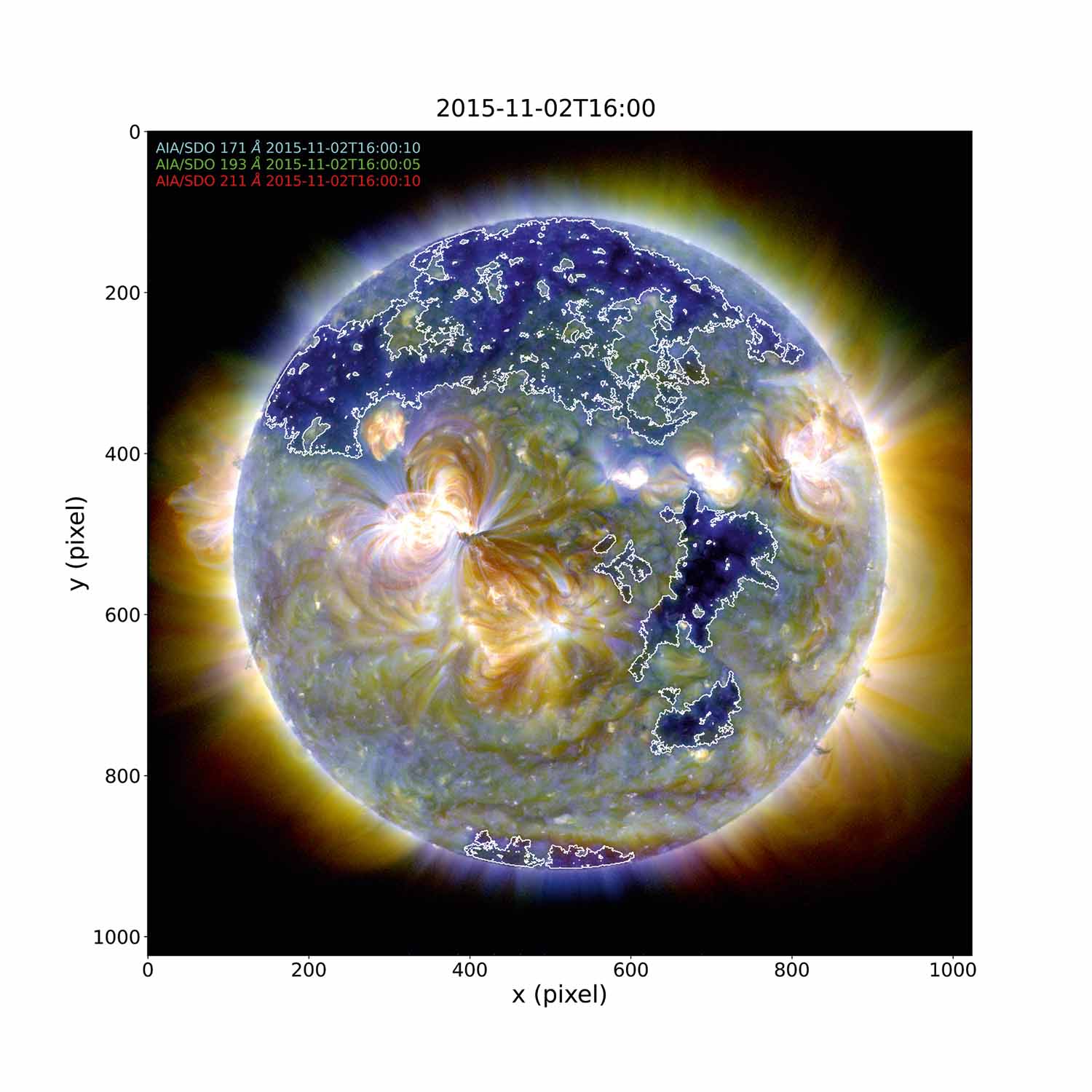

Identified Coronal Hole (contours) on the Sun using AIA/SDO data
Fadil Inceoglu, GFZ
We used an unsupervised machine learning method, k-means, to identify a Coronal Hole (CH) on the Sun, which is shown via white contours. To achieve this, we created a composite image of the Sun using data from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) in three different wavelengths. These wavelengths are in Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) and they are sensitive to the solar corona at different heights and magnetic activity structures therein. We identified CHs using different combinations of data from these three wavelengths and k-means method. We study the CHs as they are one of the main contributors to solar wind, which governs the space weather in Earth's vicinity. Understanding the space weather is crucial because it has a direct effect on the satellites orbiting the Earth, our ground-based power grids, and even astronauts during their space walks.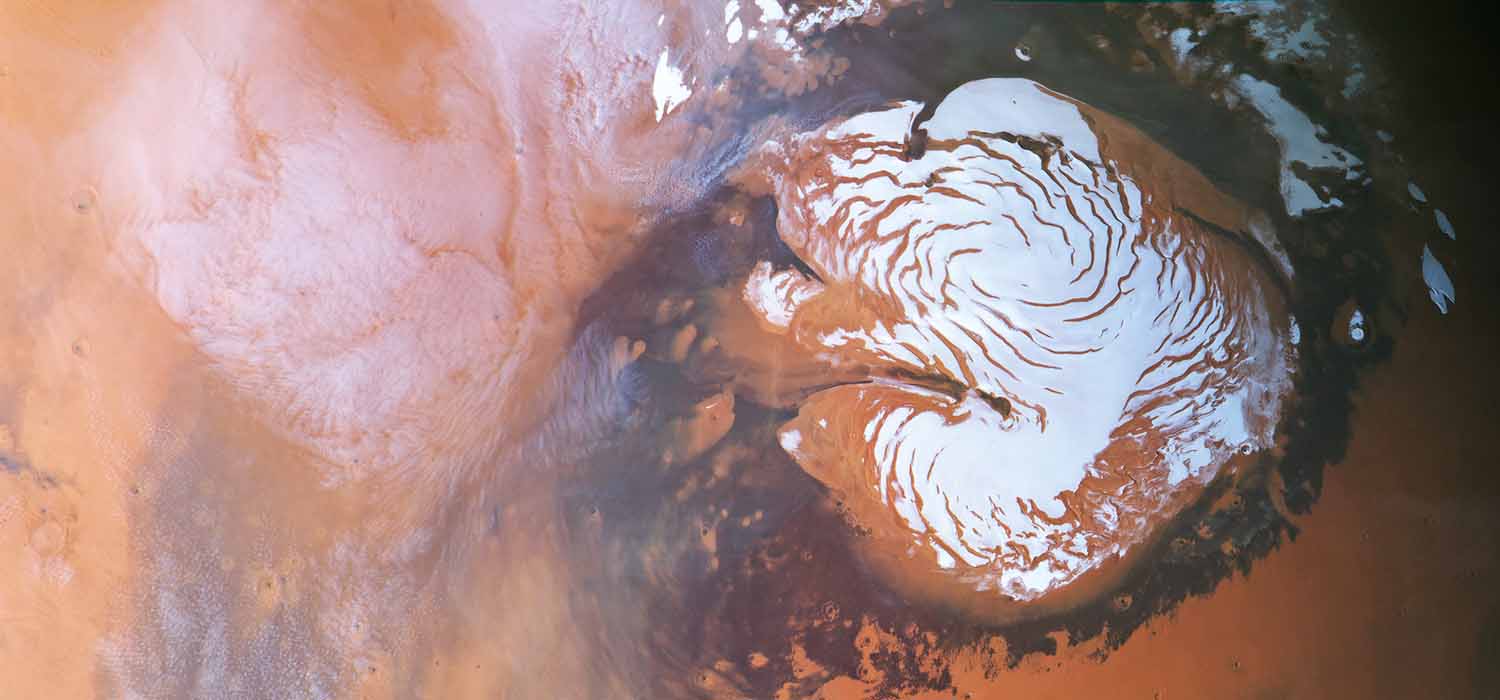

Clouds at the North Polar Ice Cap of Mars
Ernst Hauber and the HRSC Team, DLR
This image was acquired by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) onboard ESA's Mars Express spacecraft, which orbits the Red Planet since December 2003. It shows the ice cap at the north pole of Mars on the right, surrounded by darker dune fields. Several hypotheses have been put forward to explain the characteristic spiral troughs. On the left, delicate cloud patterns are clearly visible. HRSC, developed at and operated by DLR, is a pushbroom imaging device that takes images simultaneously in 9 channels at slightly different viewing angles, enabling stereo geometries. Digital photogrammetric methods are applied to generate color images and co-registered Digital Elevation Models (DEMs). The image was taken on 02 May, 2014 and has a map-projected ground pixel size of 800 m. The diameter of the polar cap on the right is about 1,000 km.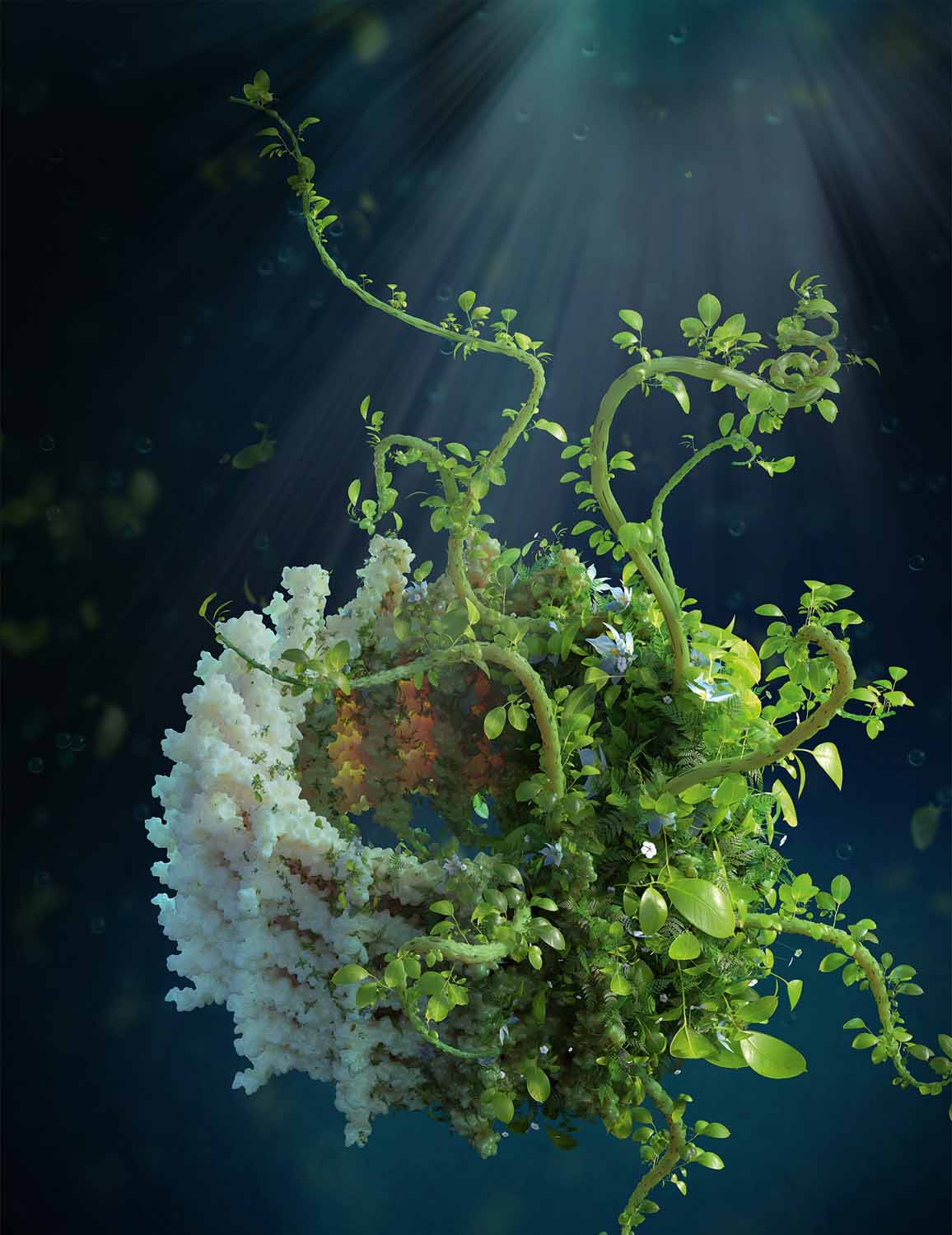

The Greening Protein
Ben Engel, HMGU
Vesicle-Inducing Protein in Plastids (VIPP1) is a conserved membrane remodeling protein that builds the thylakoid membranes of cyanobacteria, algae, and plants. These photosynthetic membranes harness the power of sunlight to generate the biochemical energy and oxygen that sustain most of the life on Earth. A landmark new study (Gupta et al. 2021, Cell) used cryo-electron microscopy to image the high-resolution structure of VIPP1, revealing how this essential protein binds and shapes lipids to construct the thylakoid membrane system, while also protecting these light-harvesting membranes from environmental stress. This image depicts lush plant life growing from the oligomeric VIPP1 structure, representing VIPP1’s directing role in thylakoid biogenesis.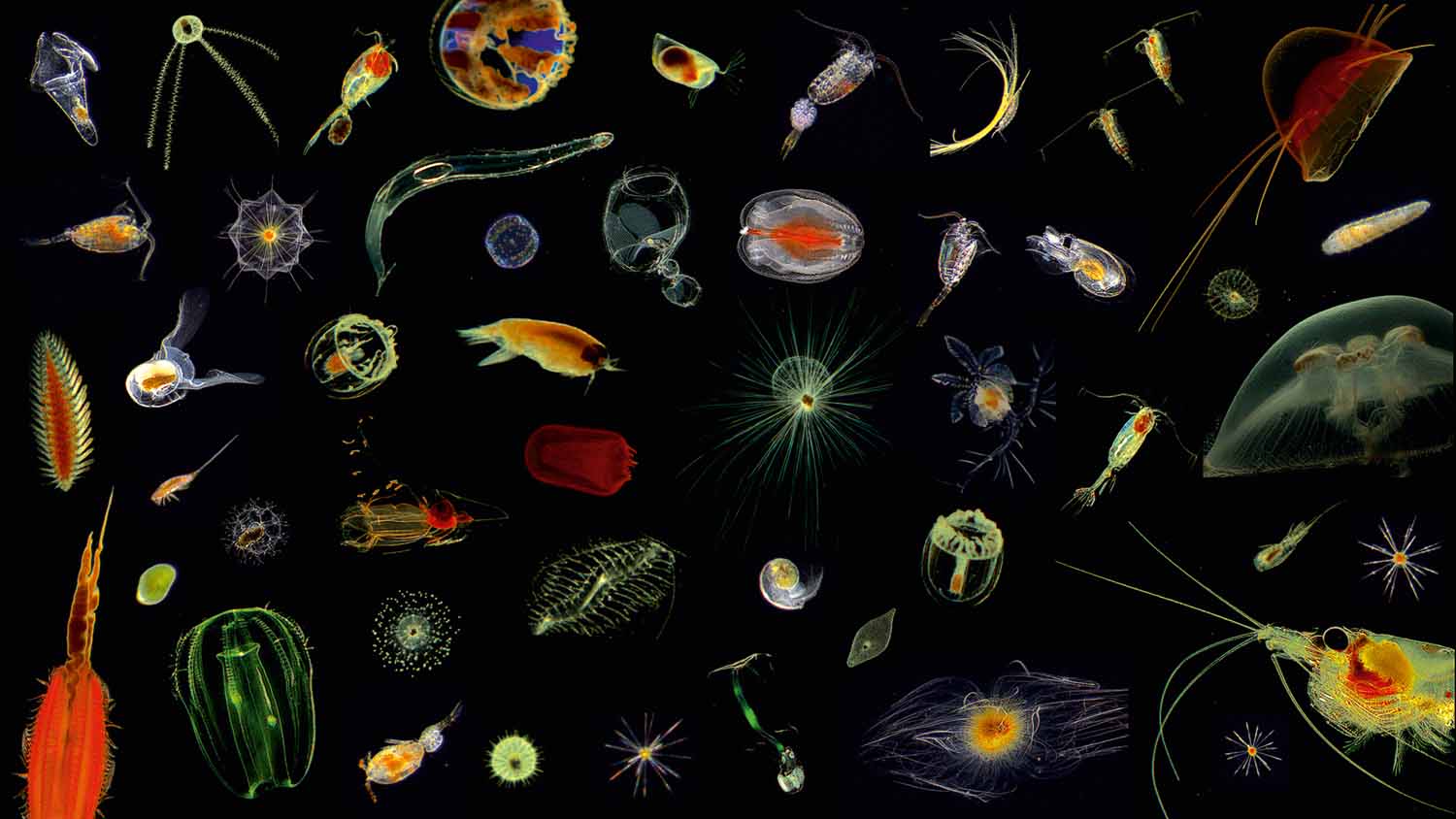
Klas Ove Möller, HEREON

Microcosmos of the Ocean
Klas Ove Möller, Hereon
Plankton are tiny floating microorganisms which are not only fascinating, colorful and beautiful - they are also exceedingly powerful. Plankton plays a key role in regulating our global climate, perform every night the largest migration on Earth and are also the base of the food chain. The presented images are showing a glance of the manifold shapes, forms and colors of these fascinating organisms, including bioluminescent jellyfishes, transparent crustaceans and starshaped radiolarians. All plankton organisms were imaged in the Atlantic Ocean between surface and 6000 m depth and are invisible to our eyes with a size range of micrometers to only a few millimeters. At the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon we are using and developing high-resolution underwater imaging systems to study the impact on carbon flux, biodiversity and how climate change and global warming are reshaping marine ecosystems.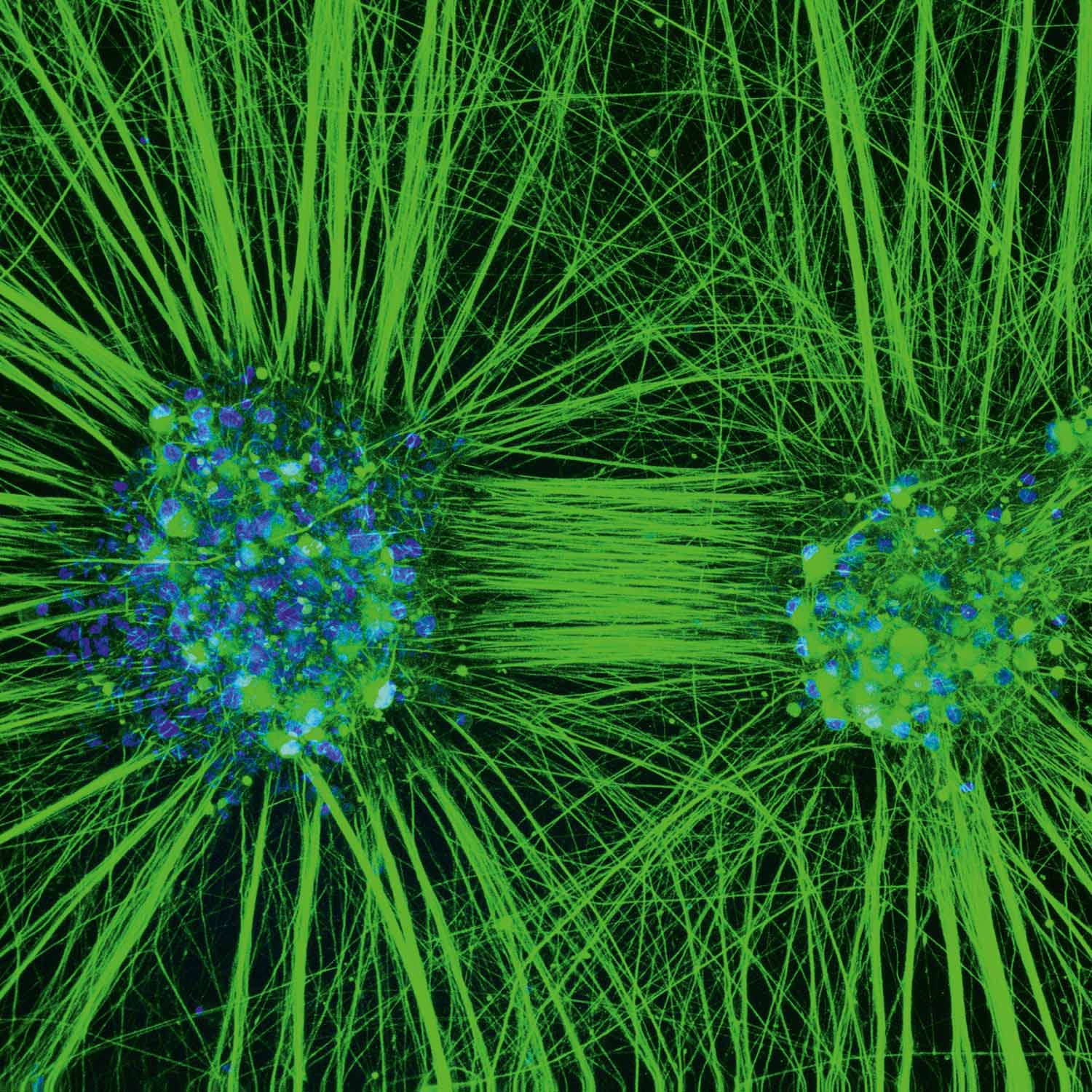

iPSC-derived sensory neurons as a patient specific model of neurotoxicity
Christian Schinke, DZNE
Chemotherapy induced neuropathy (CIN) is a highly prevalent, potentially irreversible adverse effect of antineoplastic treatment. It is characterized by altered sensation, sensory loss or neuropathic pain which profoundly affect the quality of life in cancer survivors. This confocal microscopy image depicts ganglia maturated 50 days that consist of functional sensory neurons. Ganglia were derived from stem cells reprogrammed from leukocytes of a woman breast cancer survivor who suffered from severe sensory neuropathy after paclitaxel treatment. We stained elements of the neuronal cytoskeleton and counterstained the nucleus using DRAQ5. Neuroaxonal damage can be assessed in-vitro when treatment with antineoplastic drugs are compared with vehicle treatment. With the help of this human invitro model, we aim to elucidate mechanisms of toxic neurodegeneration and to assess the biological underpinnings of the differential susceptibility for CIN known from patients.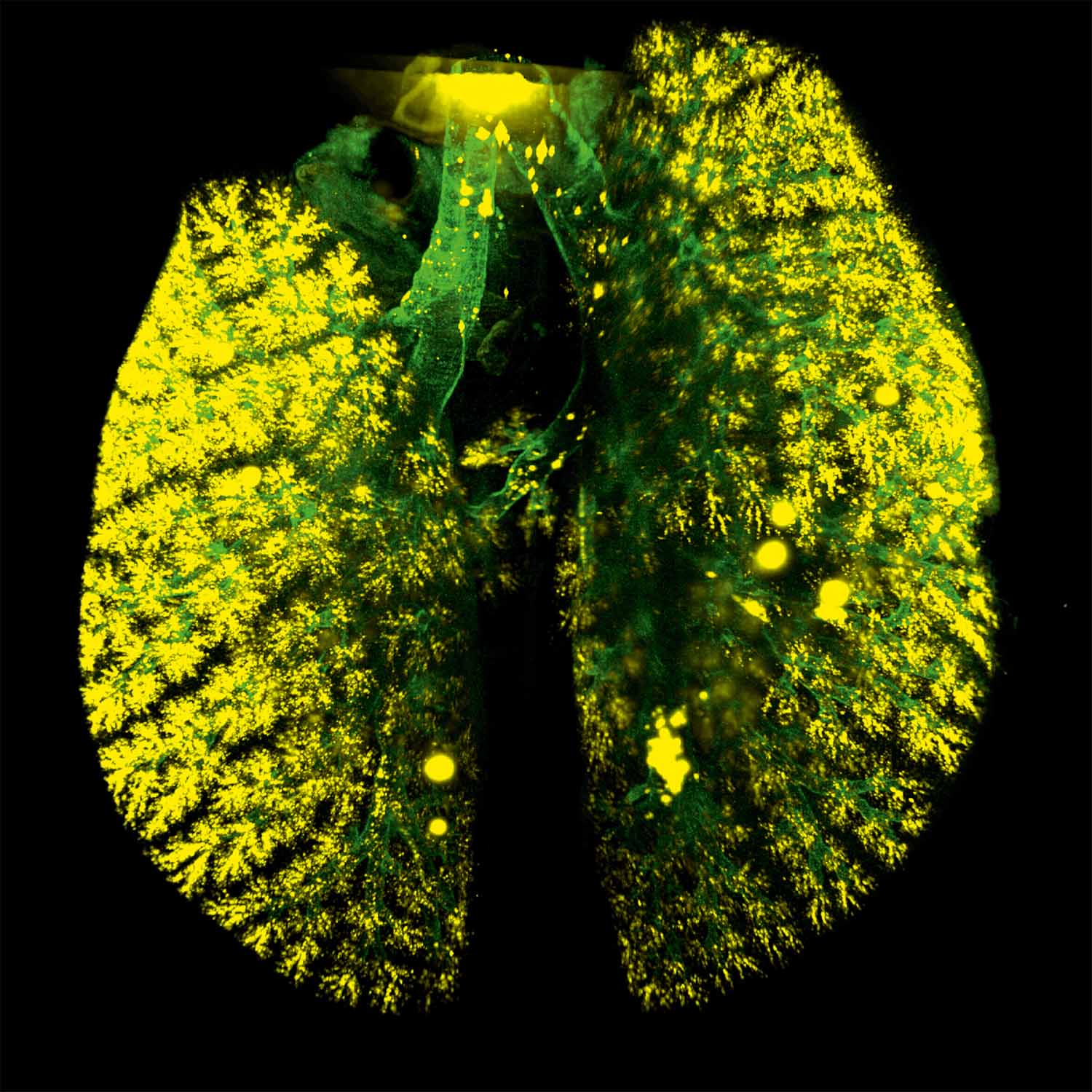

Lung tissue autofluorescence and drug aerosols
Lin Yang, HMGU
Pulmonary drug delivery is the main route for many types of diseases particularly lung diseases. The 3D image presented here displays a co-mapping of lung morphology and uniform distribution of inhaled drug aerosols (fluorescence-labeled) in the mouse by using our custom designed ventilator-assisted aerosol delivery technology. The drug aerosols were delivered evenly to the central and peripheral lung regions, which holds great promises for the treatment of lung diseases. Tissue (airway) autofluorescence in green (Imaged by LSFM); Inhaled drug aerosols in yellow (Imaged by LSFM).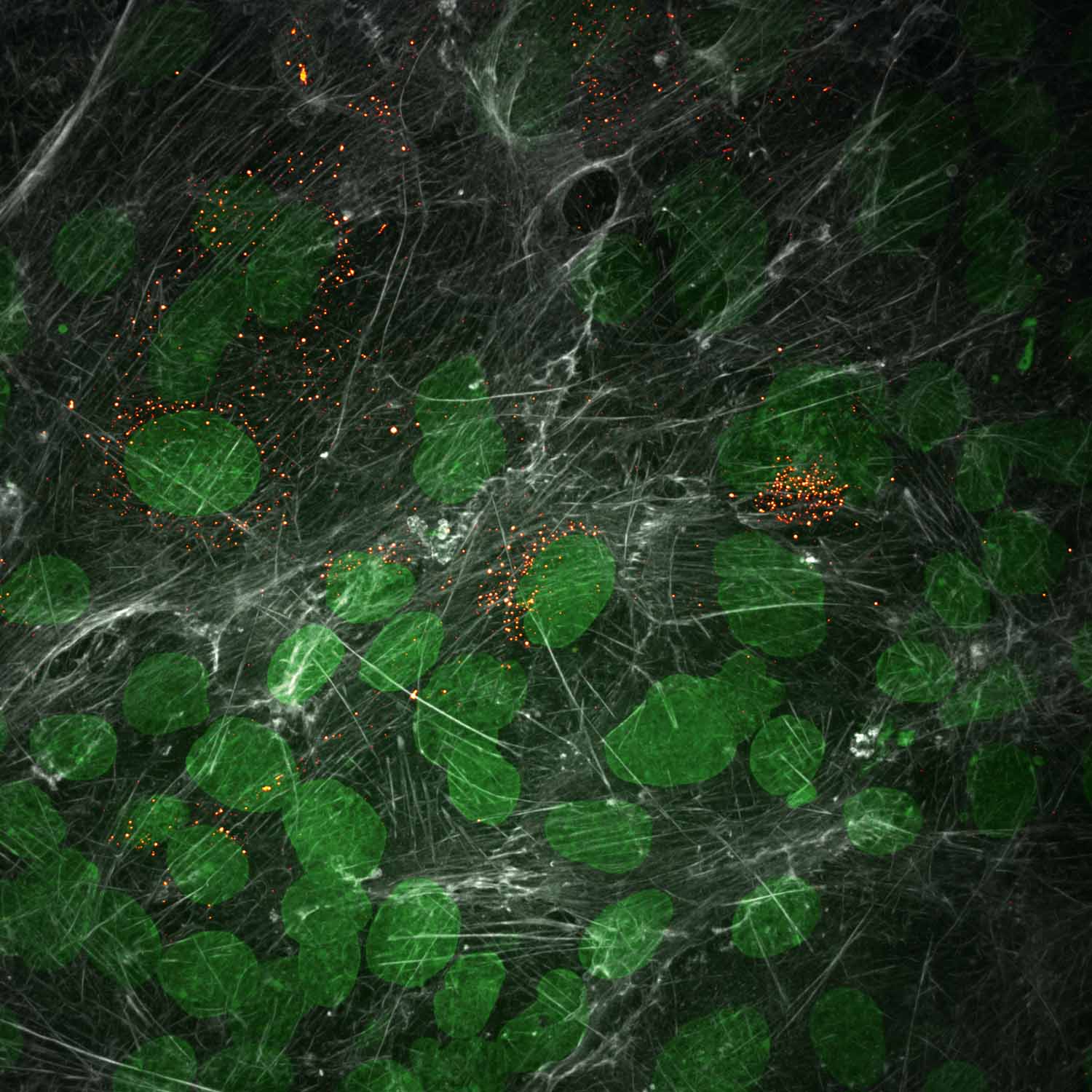

Hantavirus Assembly Factories
Christian Sieben, HZI
Hantaviruses are zoonotic pathogens that have their main animal reservoir in rodents. Upon transmission into humans, hantaviruses can cause severe pulmonary or hemorrhagic fever. To understand these processes, we study hantavirus infection in both animal and human cells using fluorescence microscopy. The image shows rodent lung epithelial cells that were infected with hantaviruses. The cells have an unusual actin cytoskeleton (grey), which we hypothesize to be critical for virus infection. Virus-infected cells are labelled with an antibody against the viral N protein (orange). For segmentation purposes, the cell’s nucleus is counterstained with DAPI (green). Using computational routines, we can now analyze the actin meshwork in infected cells.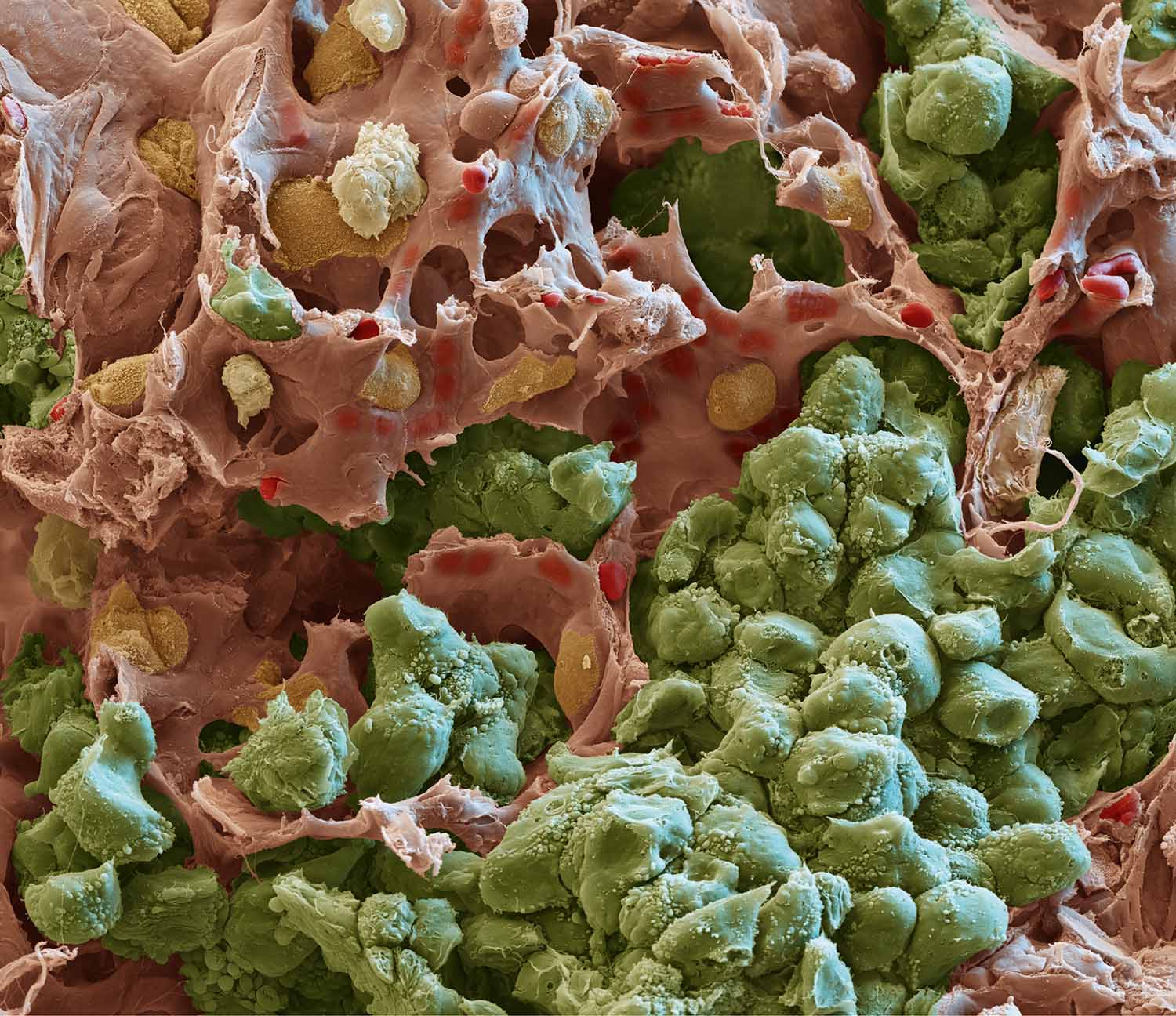

Metastatic tumor cells in the lung
Hellmut Augustin, DKFZ
Animated scanning electron micrograph showing metastatic mouse tumor cells (in green) invading the lung parenchyma and stroma in close contact with nearby capillaries (red).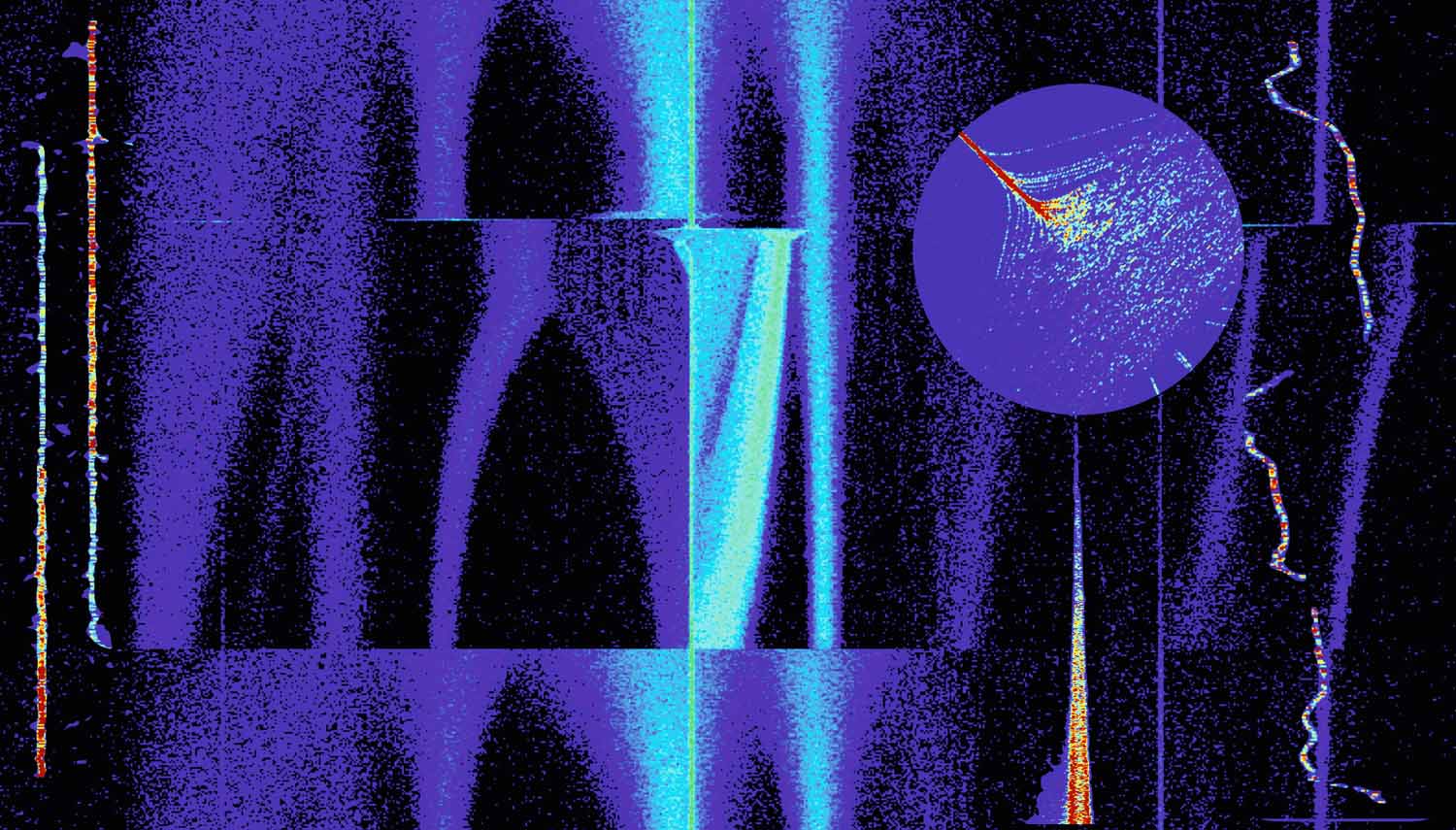

A window to the microcosmic impermanence
Shahab Sanjari, GSI
In the darkest corners of the universe, from distances farther than the vastness between the suns to those even closer than here and now, matter and energy dance to an eternal tune. Ions are injected into the heavy ion storage ring ESR at the GSI Helmholtz Center. They start their revolution, while their motion turns into a masterpiece of choreography due to their interaction with the surroundings. By processing the signals from fast and sensitive detectors that have picked up their tune, their eternal dance can be made visible. This picture is a collage. The background: stacking of Xenon ions in different accelerating steps. The left inset: 3 Promethium ions that decay one by one into Neodymium. The round inset: paths caused by the forces of the electron cooler. The pillar holding the round inset is a decaying beam. The right inset: a wondering particle unstable on its path.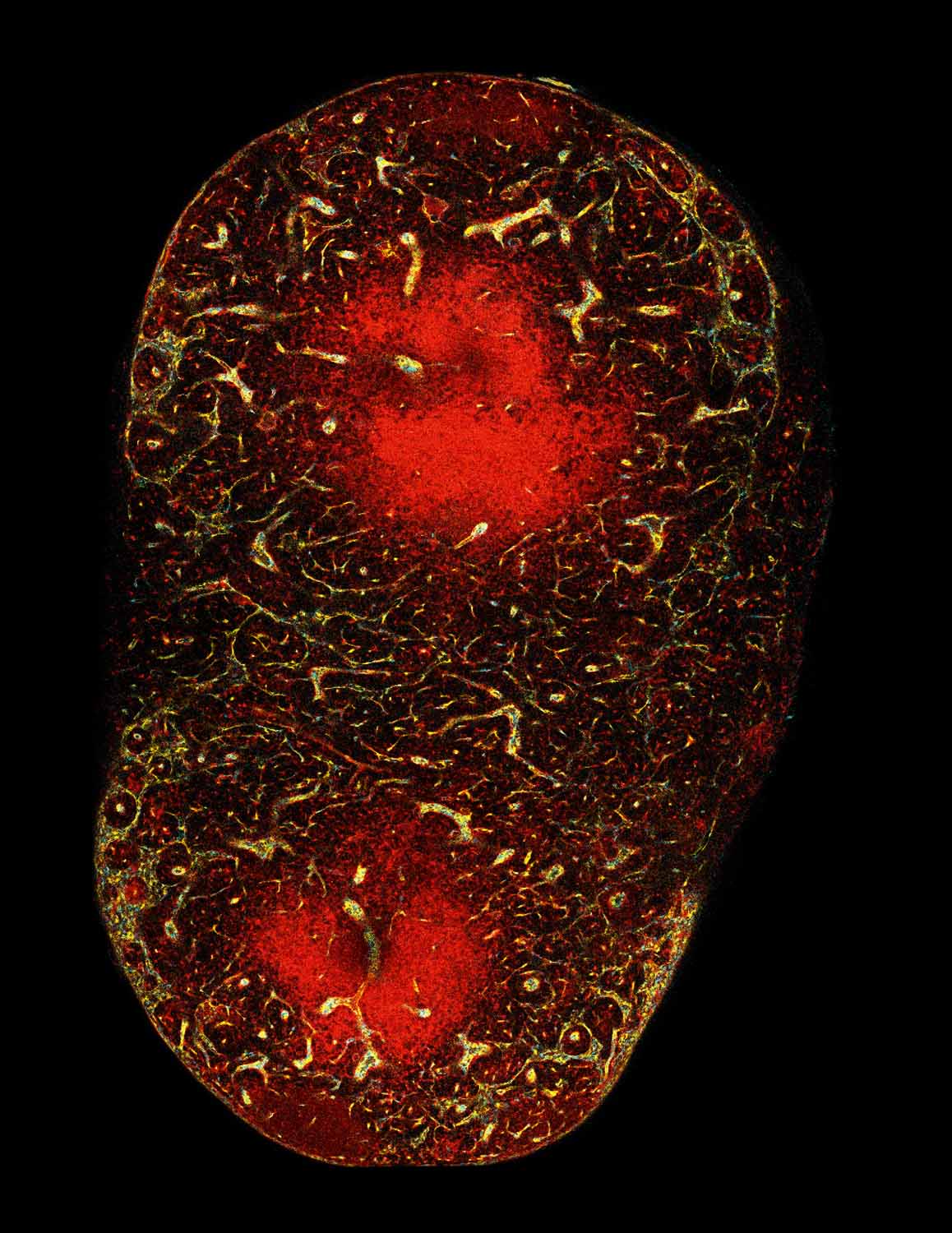

Clonal expansion of endothelial cells during lymph node angiogenesis
Lutz Menzel, MDC
In transgenic Cadherin5-CreERT2xUbow mice, all cells express TdTomato. After recombination, cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) or yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) is exclusively expressed by each copy of the Brainbow construct. The mice were treated with tamoxifen and lymphoma cells were transferred 2 weeks after last injection. 200 μm thick lymph node sections were tissue cleared for transparency and imaged by confocal microscopy. Quiescent endothelial cells undergo Cre-mediated recombination of the two Brainbow constructs and stochastically acquire various colors. During lymphoma induced endothelial activation and angiogenesis, proliferating endothelial cells transmit their colors to their progeny, highlighting the cellular dynamics of the LN vascular expansion. Equal division of all endothelial cells results in numerous but small colored segments of blood vessels throughout the vascular tree appear. Alternatively, if only some EPCs proliferate during vessel expansion, expanded vasculature would harbor large mono-colored segments of the blood endothelium.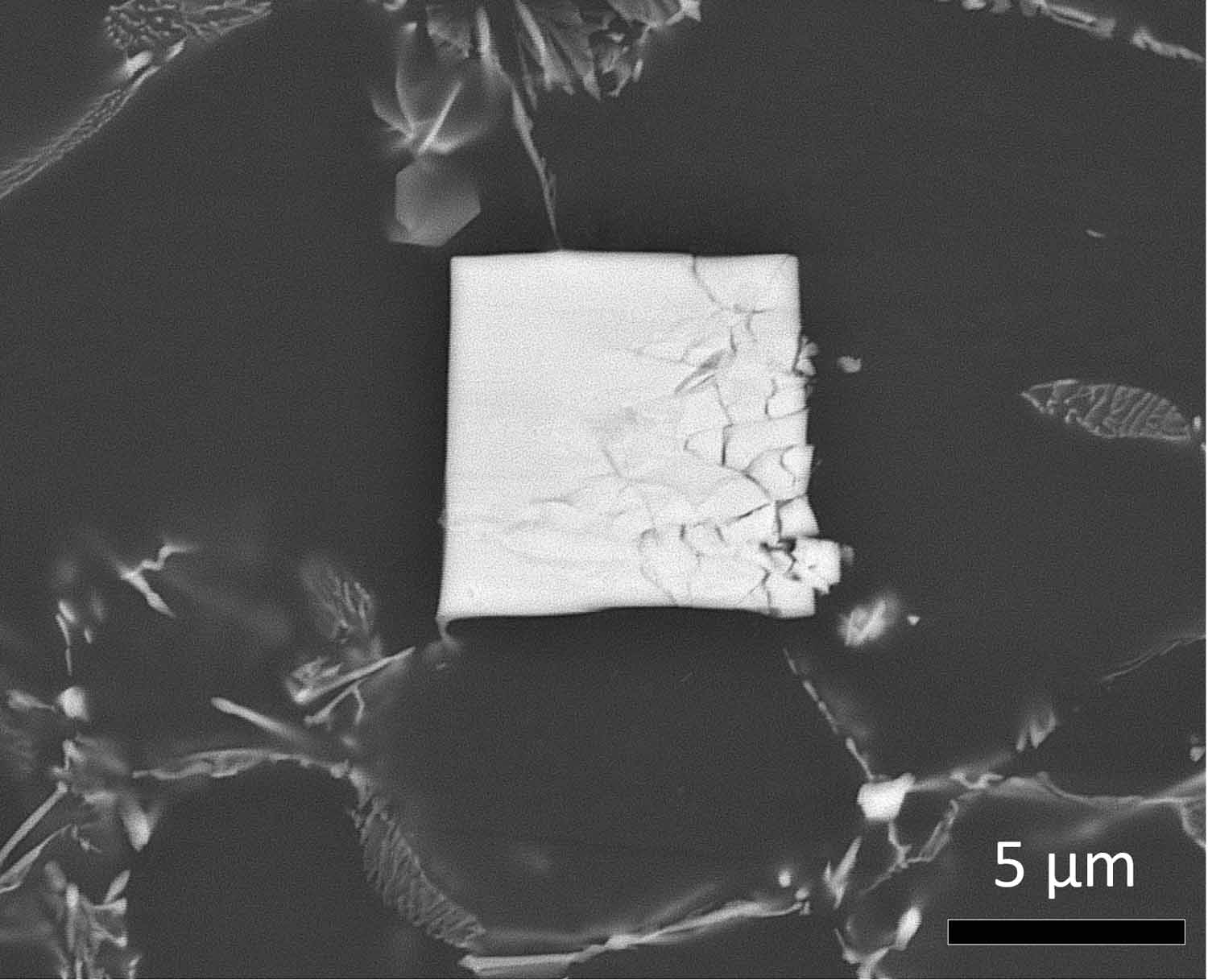

Cracked Cracker
Sarkis Gavras, Hereon
One could be forgiven that this is just a picture of a cracked cracker. However, no matter how large or small (in this case relatively small) the subtle effects of creep, a slow but yet powerful destructive force, are readily apparent in this scanning electron microscope image. We can see that an otherwise perfect square (a cube if viewable in 3 dimensions) composed of magnesium-aluminium and a rare earth element called neodymium has been shattered like a plate under a compressive force. It is through the understanding of how to strengthen such magnesium alloys which will eventually allow us to replace existing heavier components in every day applications such as engines in automobiles with lighter materials such as magnesium. This in turn will help reduce harmful greenhouse gas emissions through the great weight savings achieved by using light weight magnesium alloys.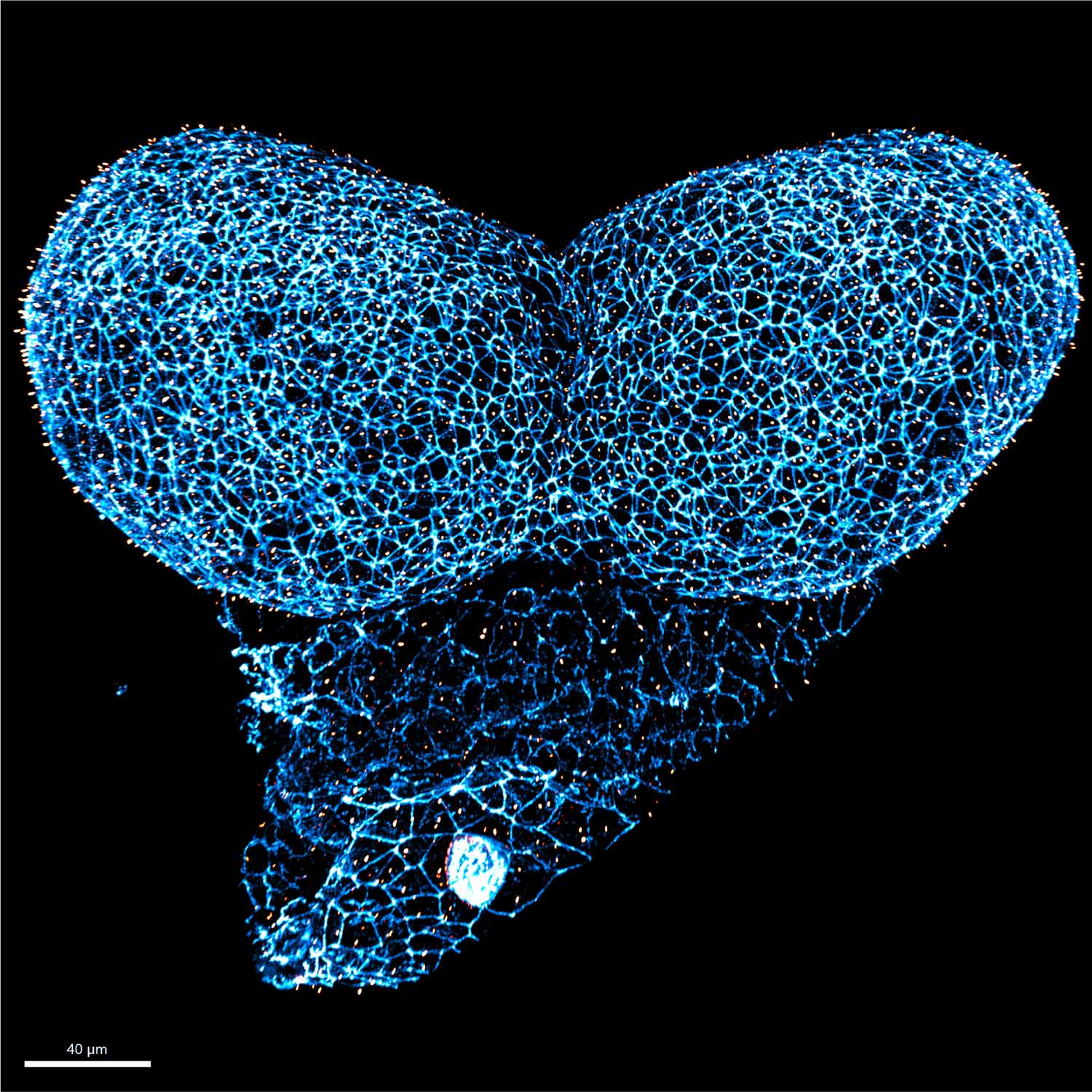

Origin of brain development
Izabela Kowalczyk, MDC
Neurulation consists of tightly coordinated morphogenetic changes that govern the elevation of initially flat neural plate in order to form the neural tube. Variable clinical manifestations of congenital brain disorders demonstrate there is a high demand on better understanding of the disease etiology. Using mouse model, we examine the crosstalk between pivotal signaling pathways and the biomechanical changes taking place during neural tube morphogenesis. Wholemount confocal image presents the anterior neural folds of E8.5 mouse embryo prior the neural tube formation. The tissue consists of a single layer of neuroepithelial cells delineated with junctional protein ZO-1 (cyan). Each neuroepithelial cell is decorated with a single antenna-like structure, called primary cilium, labelled with ARL13b (orange). Primary cilia sense the extracellular and intracellular cues, thus they integrate the control of cell identity and cell morphology, allowing for the large-scale morphogenesis of neural tube.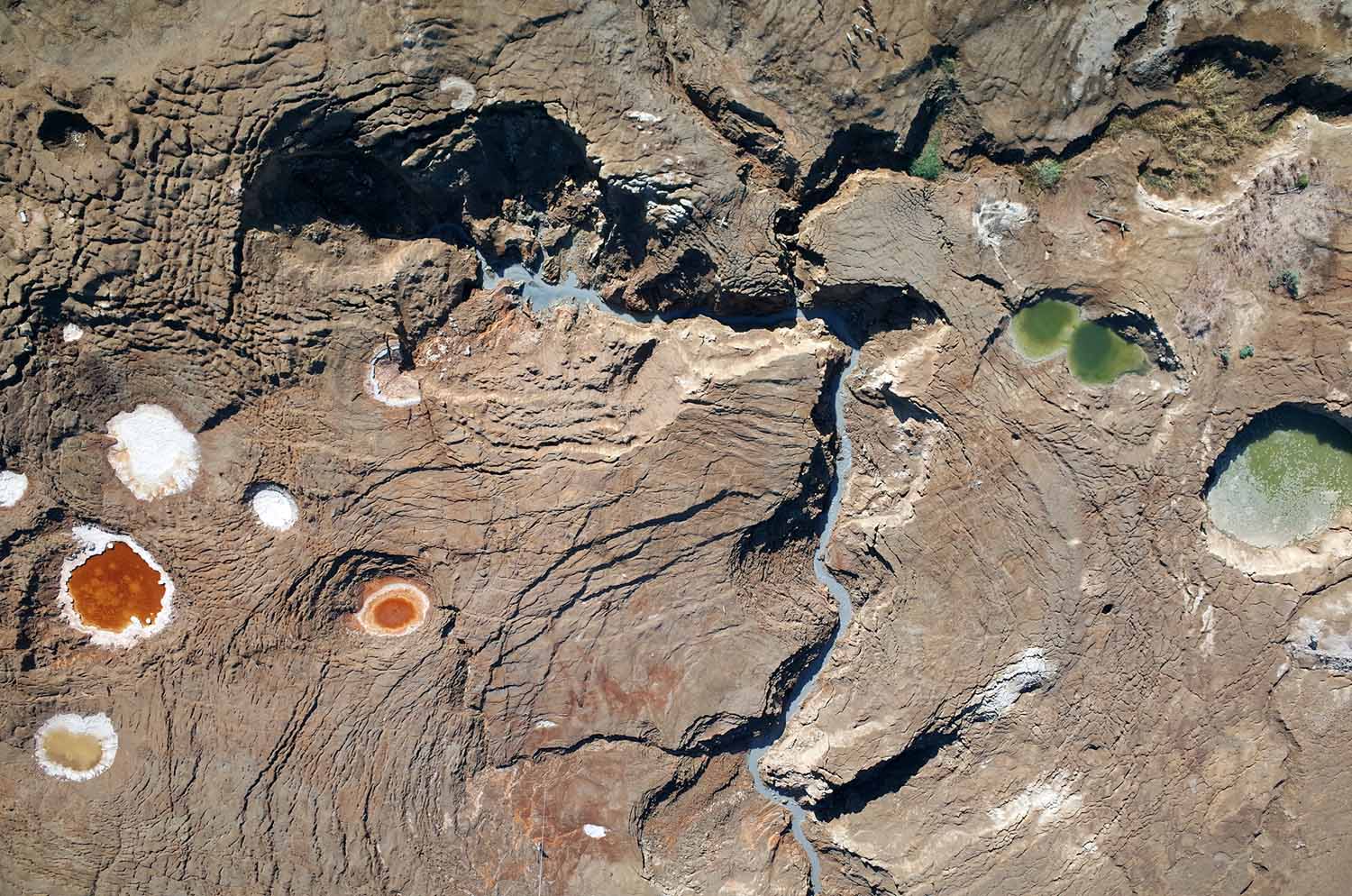

A dynamic spring-canyon-sinkhole system at the former Dead Sea shoreline
Djamil Al-Halbouni, GEOMAR
Aerial photo of the former lake bottom of the Dead Sea, taken from 150 m altitude by a ¬¬-ground-controlled Helium balloon. The regression of the water leaves an extensive mud-flat and a lot of salt. An increasing sinkhole development occurs in this area due to dissolution processes in the underground. On the image one can distinguish a fresh-water source, a recent canyon and ellipsoid sinkhole structures with varying colors due to the composition of the water. Reddish colors indicate iron oxides, greenish reflect under-saturated water and whitish are the margins of sinkholes formerly filled by saltwater. At the lower margin the balloon holding person and the cord can be seen. Aerial photo analysis enables the development of detailed, high-resolution topographic models and change detection, which helps to better understand background processes and formation of such natural sinkhole phenomena and to develop a hazard assessment for the region.

Micro water jet explosions
Johannes Hagemann, DESY
This image shows the expansion of a microfluidic water jet after pumping with a ns infrared laser pulse. The panels show the state of the jet 4 ns, 9 ns, 16 ns and 30 ns after pumping. Each individual image was acquired with a single femtosecond long hard x-ray pulse exposure. The images shown here depict the quantitative phase shift of water, this is obtained via phase retrieval algorithms from holographic measurements (not shown). These holograms were acquired in a lens-less imaging setup at the MID end station at the European XFEL. These quantitative images allow new insides in the dynamics of ultra-fast hydrodynamics and other phenomena from high energy density physics.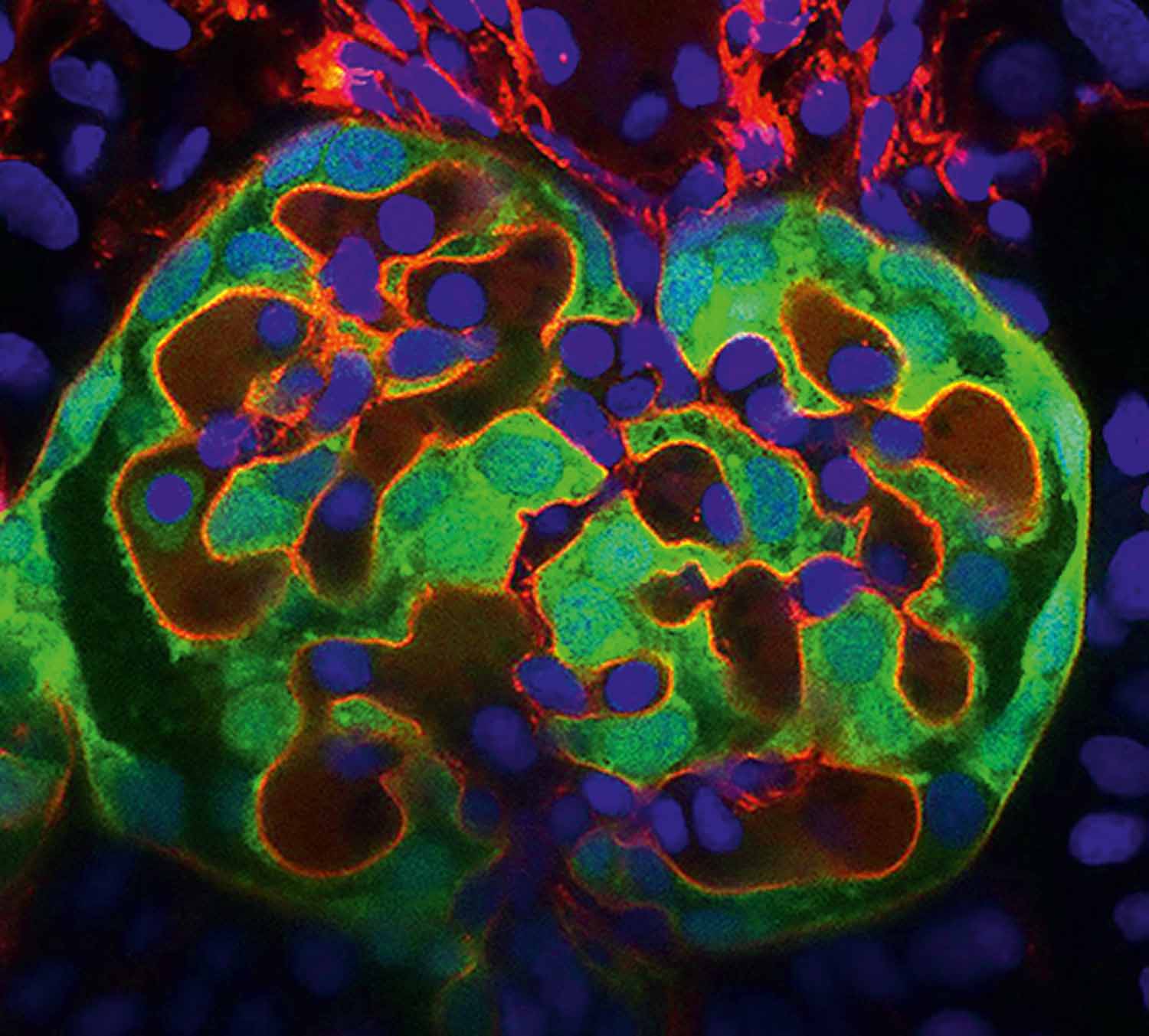

Inside the zebrafish developing kidney
Aikaterini Kourpa, MDC
In the recent years, use of zebrafish model has considerably advanced the study of kidney development and glomerular filtration function. Here, we show a high-resolution confocal image of the zebrafish embryonic renal glomeruli at 120 hours post fertilization (hpf). All cells’ nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Podocytes’ cell bodies and parietal epithelial cells are visible with Green Fluorescent Protein (EGFP in green) coming from the transgenic line Tg[wt1b: EGFP]. Injection of BSA-Alexa Fluor 594 (red) allows the labeling of vascular endothelium and blood flow. In addition, the afferent and efferent arterioles, responsible for the supply of blood in (unfiltered) and out (filtered) of the glomerulus, respectively, are clearly visible. This image reveals a highly detailed glomerular morphology that we harness for studying the complex and so far, poorly understood endothelial-podocytes interactions during glomerular formation. Interdigitating podocytes are forming a basket-like structure that envelopes around the future capillary tuft.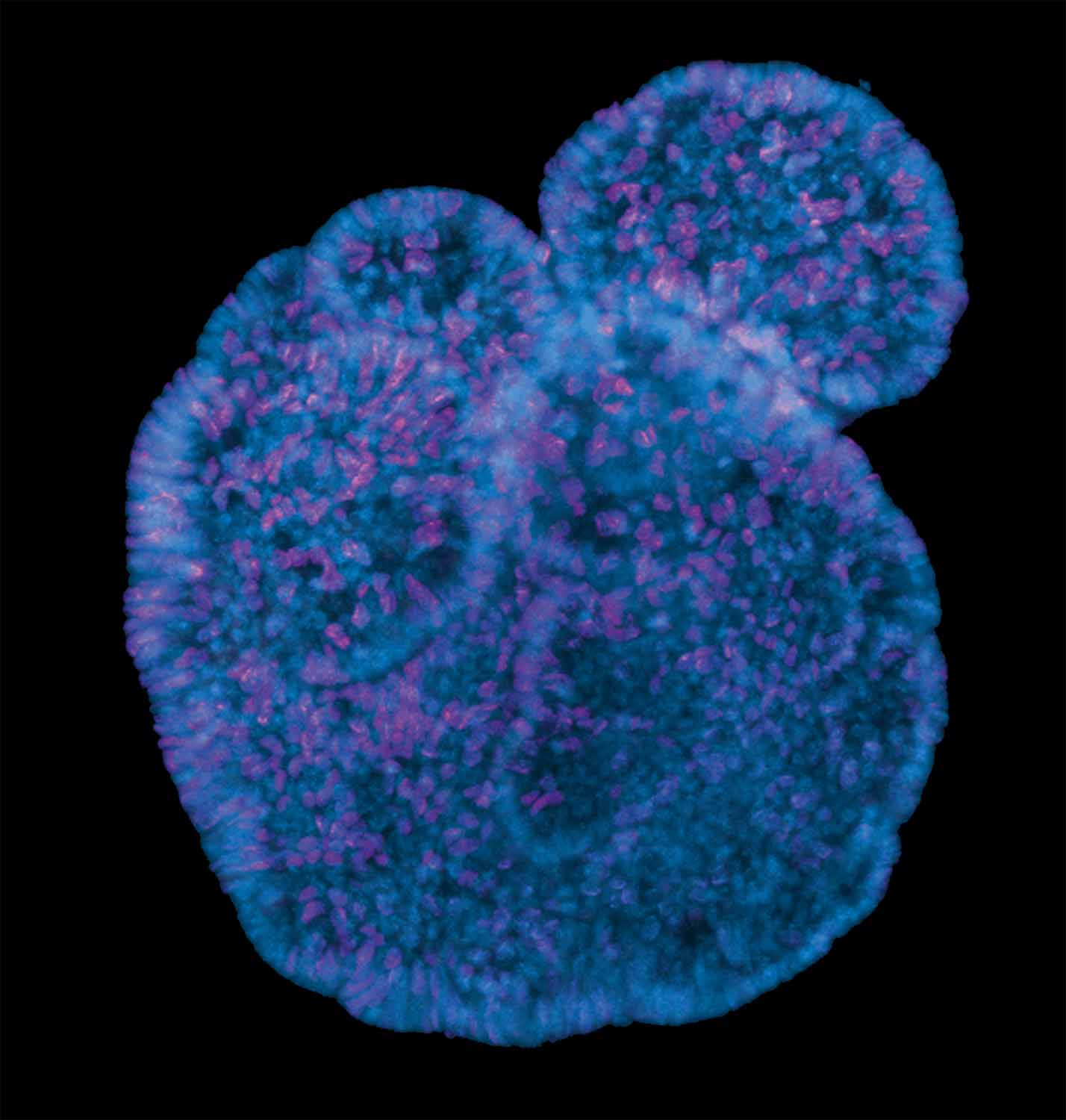

Hug me
Cristina Brischetto, MDC
Z-stack imaging of a 3D mouse intestinal organoid during budding formations. Proliferative cells are stained in magenta and nuclei in blue. Spheroid structures differentiate into budding organoids in standard culture conditions. Each budded structure represents intestinal crypt regions and descends from the pool of stem/progenitor cells that proliferate and differentiate into specific mature epithelial cells. Through the analysis of the number of crypt buds, we were able to show that the mutation of our protein candidate can interfere with the pool of adult stem cells and consequently with the organoid morphology and their cell fate decision. Instrument: Zeiss microscope LSM 800

The Calving of Brunt Ice Shelf
Celia Baumhoer, DLR
The presented image shows a Sentinel-1 SAR-scene of Brunt Ice Shelf a few days after the major calving event on 26 February, 2021. In white, the newly formed coastline is depicted which was automatically extracted with “IceLines”. IceLines allows to continuously monitor calving front change through a modified U-Net architecture which was trained on dual-polarized satellite imagery of the Antarctic coastline. With traditional imaging techniques it was not possible to automatically delineate ice shelf fronts because of changes in radar backscatter, low contrast between ice sheet and ocean due to sea ice and various shapes of glaciers, icebergs and ice shelves. IceLines replaces the tedious manual delineation of fronts from satellite imagery and finally allows large-scale analysis of Antarctic ice shelf front movement. Moreover, the unprecedented temporal dense time series of calving front change create new possibilities for ice sheet modelers with regard to more accurate sea level rise projections.