Third-party Projects
Published on 15.10.2025
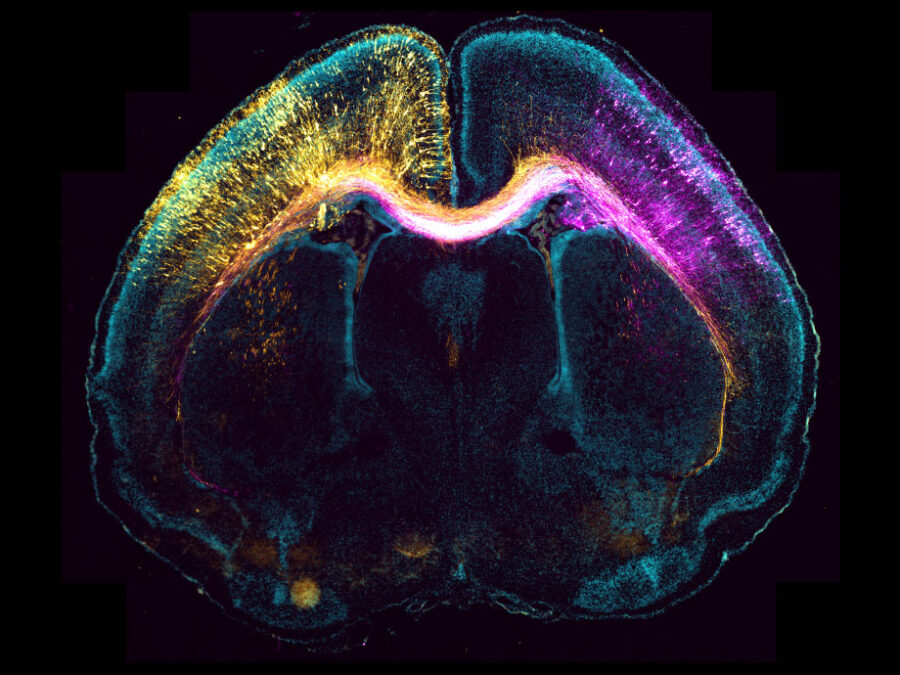
Spatio-temporal inverse approaches for EEG/MEG reconstruction of neural networks in the human brain
This project aims to develop novel methods for reconstructing brain activity from dynamic EEG and MEG measurements. By using realistic, individualized finite element models and advanced regularization techniques, including machine learning, we seek to solve this inverse problem in real patient settings, ultimately improving the diagnosis and treatment of medication-resistant focal epilepsy.
Published on 14.04.2025
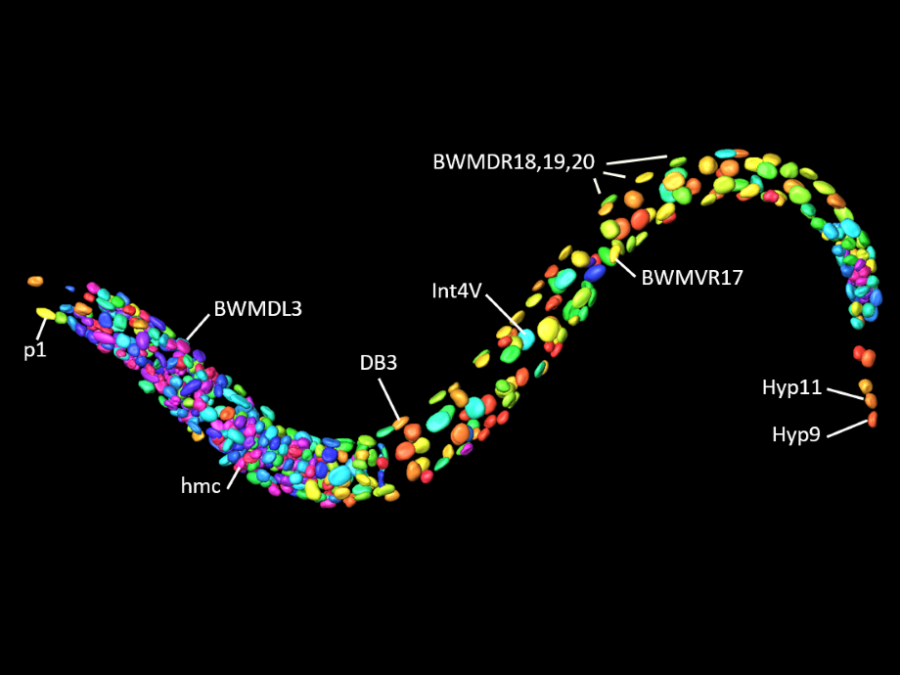
UMDISTO: Unsupervised Model Discovery
The project aims to develop novel methods for unsupervised multi-matching to map cellular-level correspondences in organisms like C. elegans.
Published on 02.04.2025
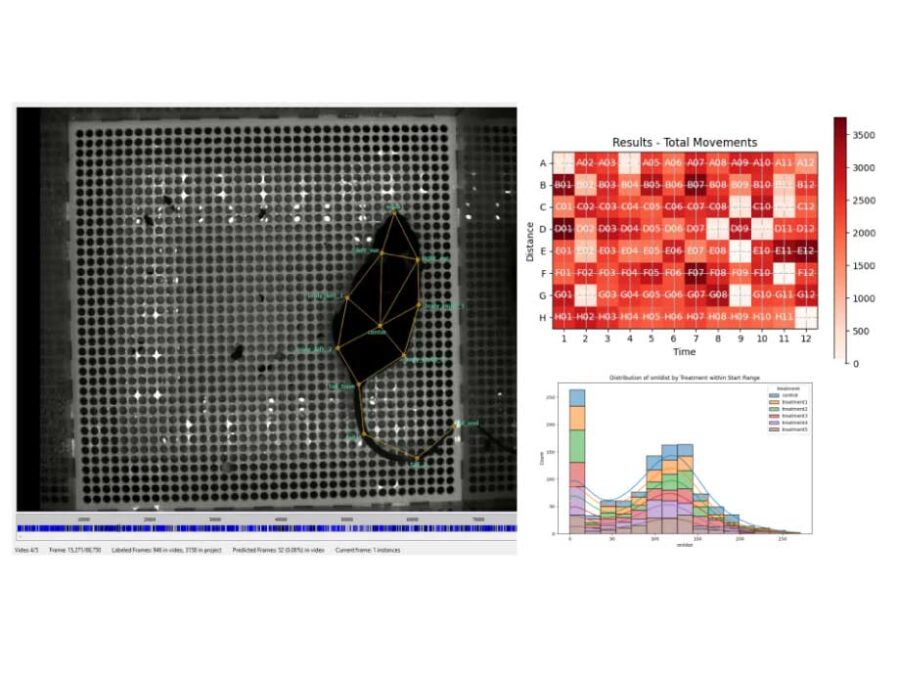
FONDA: Dependability, Adaptability and Uncertainty Quantification for Data Analysis Workflows in Large-Scale Biomedical Image Analysis
The project aims to enhance infrastructures for machine learning (ML)-intensive DAWs in advanced biomedical imaging applications.
Published on 02.04.2025
COMFORT
COMFORT aims to achieve breakthroughs in developing compact, flexible, and robust machine learning models for image, audio, and network data. In doing so, its application-oriented research program will advance the mathematical understanding of machine learning at the intersection of effectiveness and robustness.
Published on 13.12.2024
GLAM: Generative lung architecture modeling
This project is developing generative methods for designing bio-printable lung tissues across a spectrum of disease severity in the specific context of mouse and human lung disease.
Published on 11.03.2024
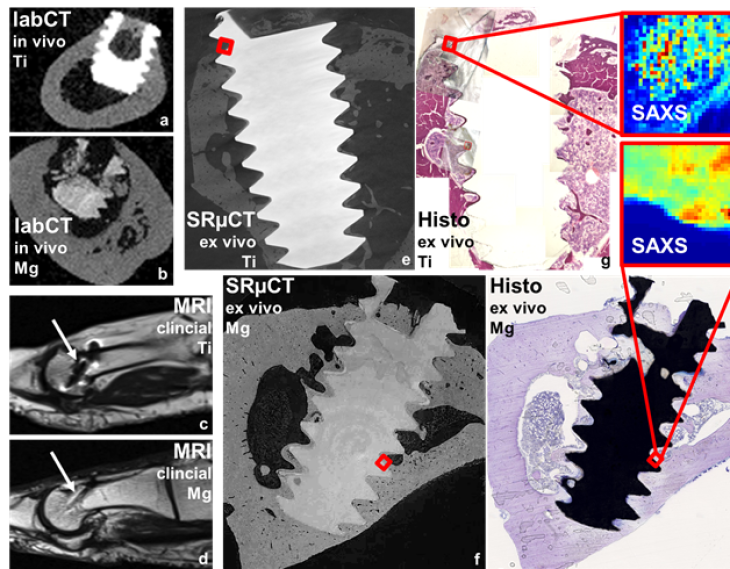
Multi-task Deep Learning for Large-scale Multimodal Biomedical Image Analysis (MDLMA)
The MDLMA project aims to optimize biodegradable Mg-based implants by analyzing vast multimodal biomedical image data. Through deep learning, it seeks to improve implant properties by understanding the interplay of microstructure, mechanics, biology, and degradation. The project will develop multi-task deep learning methods for enhanced image analysis, offering a unified framework for broader application in biomedical imaging.
Published on 11.01.2024
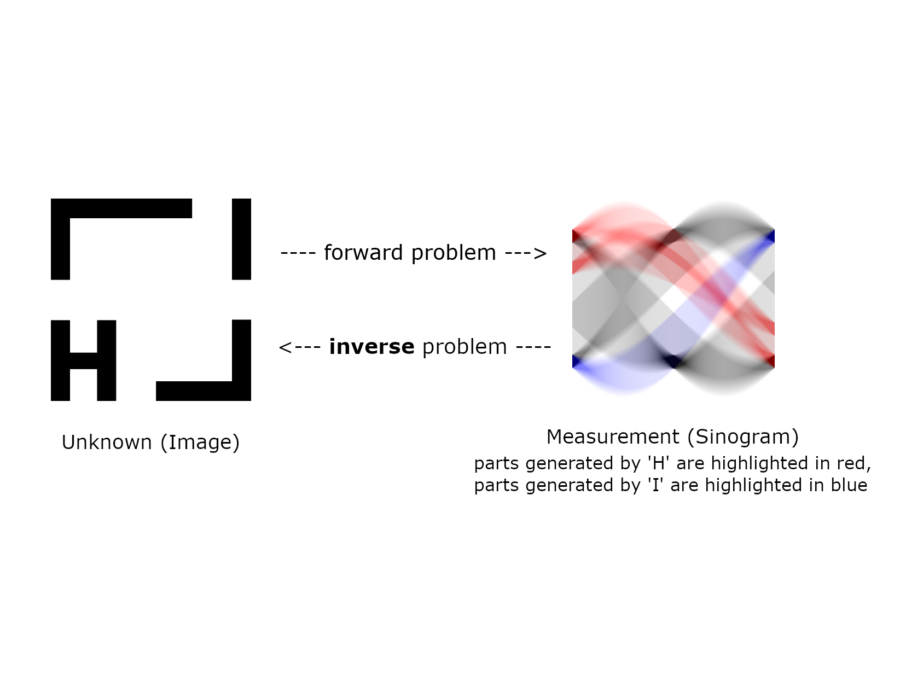
Deep Learning based Regularization for Inverse Problems
This project aims to investigate the construction of regularization methods for ill-posed inverse problems based on deep learning and their theoretical foundations. Specific objectives include the development of robust and interpretable results, requiring the initial development of new concepts of robustness and interpretability in this context.
Published on 10.01.2024
Foundations of Supervised Deep Learning for Inverse Problems
Recently, deep learning methods have excelled at various data processing tasks including the solution of ill-posed inverse problems. The goal of this project is to contribute to the theoretical foundation for truly understanding deep networks as regularization techniques which can reestablish a continuous dependence of the solution on the data.
Published on 05.01.2024
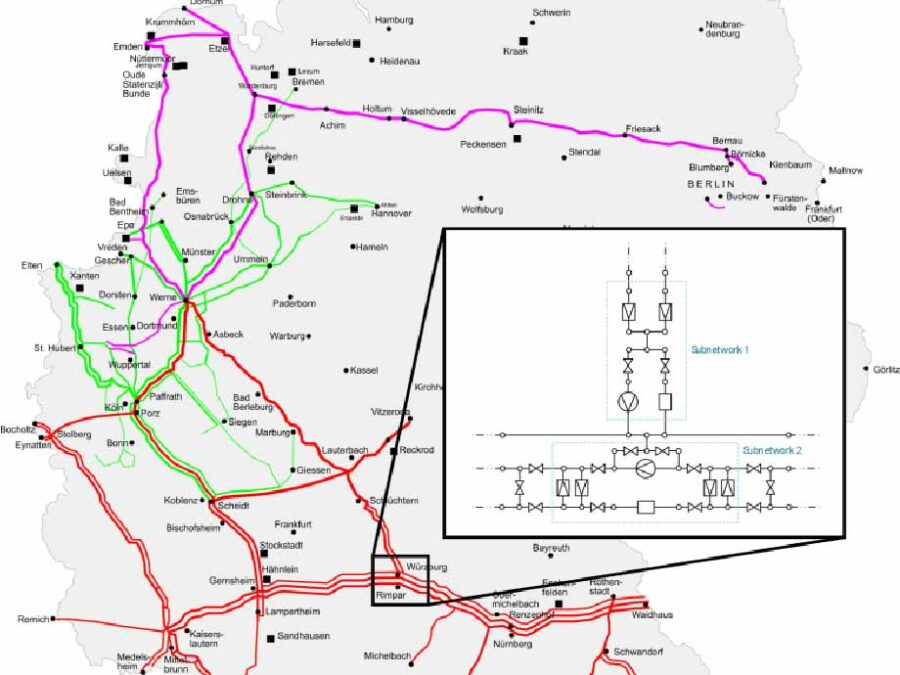
SFB Transregio 154 – C06: Transport metrics for analysis and optimization of network problems
SFB TRR 154 is a project of the German Research Foundation (DFG) and combines integer-continuous methods, model adaptation, and numerical simulation, to analyze and optimize gas markets, infrastructure, and control of networks. The third funding period specifically focuses on the transition from natural gas to hydrogen.
Published on 05.01.2024
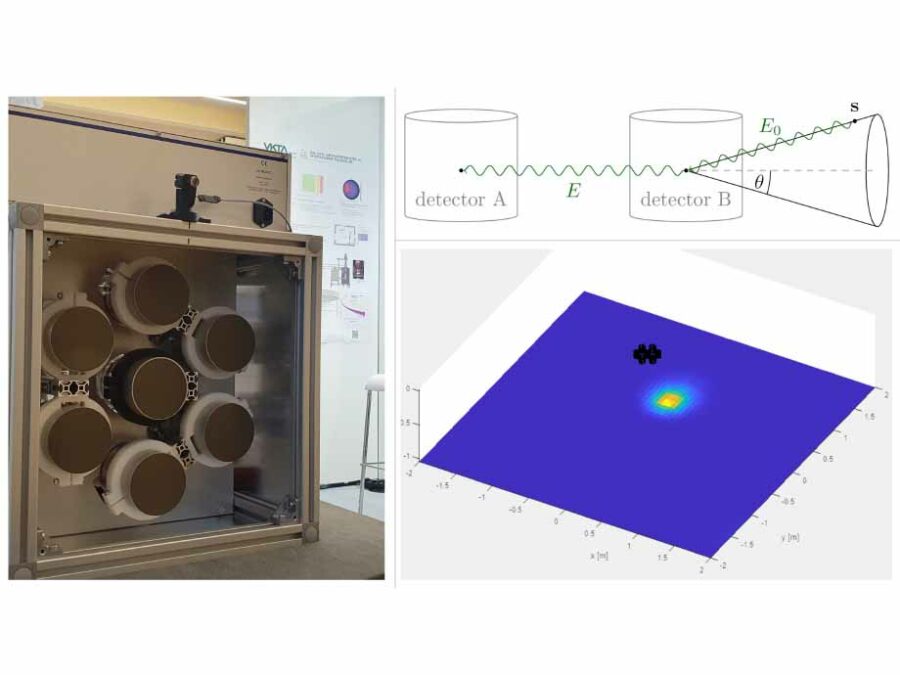
QGRIS: Quantitative Gamma-Ray Imaging System
Compton cameras are used for the radiological characterization of nuclear power plants. In this project, a suitable camera system is designed, and the associated algorithms for image reconstruction and nuclide characterization are implemented as user software.
Published on 05.01.2024
Bayesian Computations for Large-scale (Nonlinear) Inverse Problems in Imaging
During research stays with the collaborating group at Caltech, we aim to investigate various aspects of statistical inverse problems. This includes inquiries into particle- and PDE-based sampling methods, as well as robust regularization using neural networks.