GRIDMARK – Generating Reproducible Insights through Data Benchmarking for AI in Energy Systems

What is the project about?
GRIDMARK develops FAIR data pipelines for distributed energy systems. By curating benchmark datasets from KIT’s EnergyLab and FZJ’s Living Lab, GRIDMARK enables reproducible AI research, fosters cross-center collaboration and lays the foundation for a Helmholtz-wide Energy DataHub.
What main scientific or societal challenge does the benchmark address?
Transforming energy systems toward climate neutrality: Distribution grids have the potential to be catalysts for the energy transition. Unfortunately, most Distribution System Operators lack the resources to fully monitor their systems. Therefore, there is an urgent need for more high-quality data, particularly to develop and test machine learning models.
What motivated you to apply for UNLOCK, and how does the project align with the initiative’s vision?
Our aim is to lower the barriers to using FAIR data, create scalable pipelines and enable the reproducible benchmarking of AI across the Helmholtz centers.
In what ways does the project foster cross-domain, cross-center, or interdisciplinary collaboration?
GRIDMARK links two of the largest Helmholtz energy research centers, KIT and FZJ, while taking into account the needs of industrial and other academic partners. It is interdisciplinary, combining electrical engineering with AI and data science to lay the foundation for future cross-disciplinary benchmarks and a Helmholtz “DataHub Energy”.
What impact does the project aim to achieve — within Helmholtz and across the broader research and industry community?
GRIDMARK will provide reproducible, FAIR-aligned benchmarks to advance AI research in energy systems. Our goal is to set an example for other energy researchers, encouraging them to share their data using the insights and tools developed within GRIDMARK. This includes academics from Helmholtz and beyond, as well as industry actors who own data but are not currently disclosing it. Ultimately, our goal is to support the energy transition by promoting a cultural shift and providing useful tools and data.
Other projects
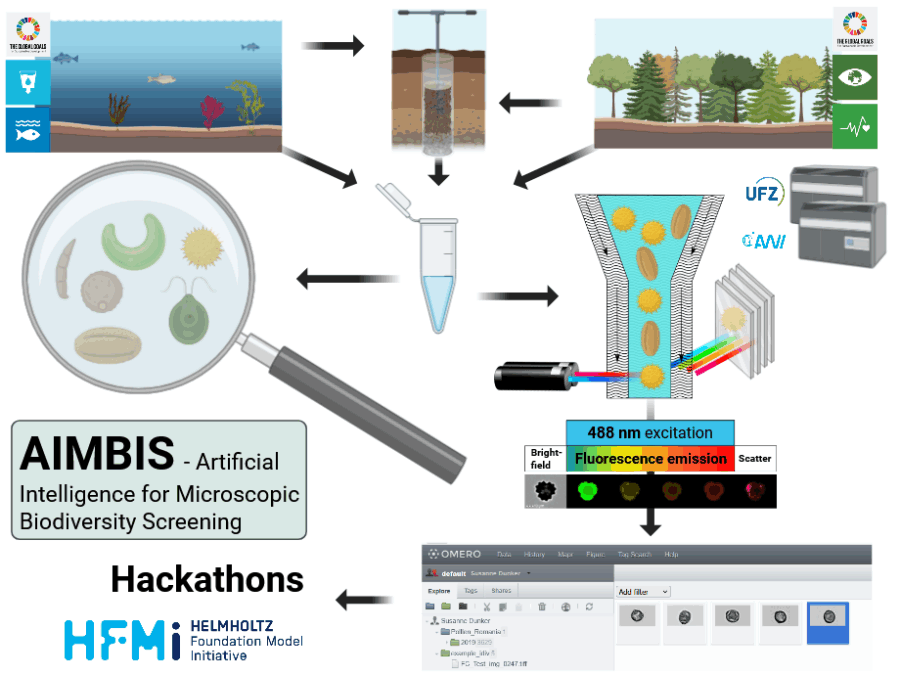
AIMBIS – Artificial Intelligence for Microscopic Biodiversity Screening
Manual microscopic biodiversity monitoring is time-consuming and requires expert knowledge, limiting the potential for biodiversity monitoring, hence to recognize the impacts of climate and environmental change on crucial ecosystem functions.
BASE: Benchmarking Agro-environmental database for Sustainable agriculture intensification
Building a BASE dataset enables robust predictions of yield potential, resource efficiency, and sustainability thresholds, driving climate resilience and sustainable agricultural intensification