BestMeta
Behavioral Standard Metadata
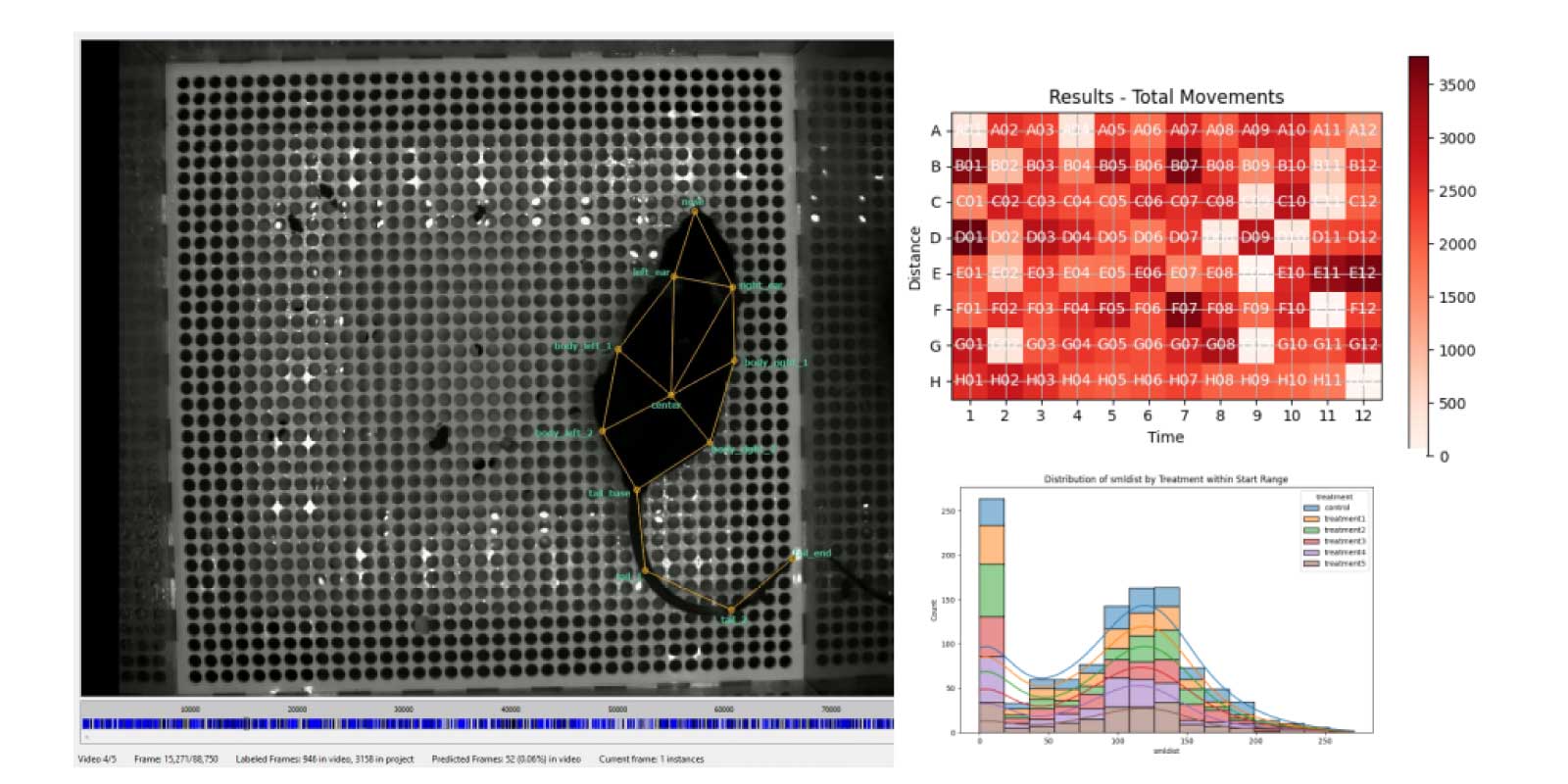
Video tracking assays (VTAs) are important methodologies for measuring and quantifying behavioral changes in single or multicellular organisms. Standardized metadata schemas are still missing for VTAs and lack of reporting protocols are affecting reproducibility and consistency in research findings. Currently, existing standards for VTAs are either too broad or narrowly focused on specific applications.
To address these issues, a team from two Helmholtz programs aims to develop unified metadata standards and harmonized reporting procedures for VTAs.
Standard metadata will not only streamline research processes but also broaden the application of VTAs, enabling more seamless collaboration and data sharing within the scientific community.
Furthermore, we want to actively include the researchers in all career stages by organizing workshops and sharing events to ensure effective use of analysis pipelines and web-based solutions.
BestMeta is a joint project between the Helmholtz Centers MDC and UFZ funded within the HMC Project Cohort 2024.