Extracting clinically relevant parameters from real-time MRI images of fontan hearts
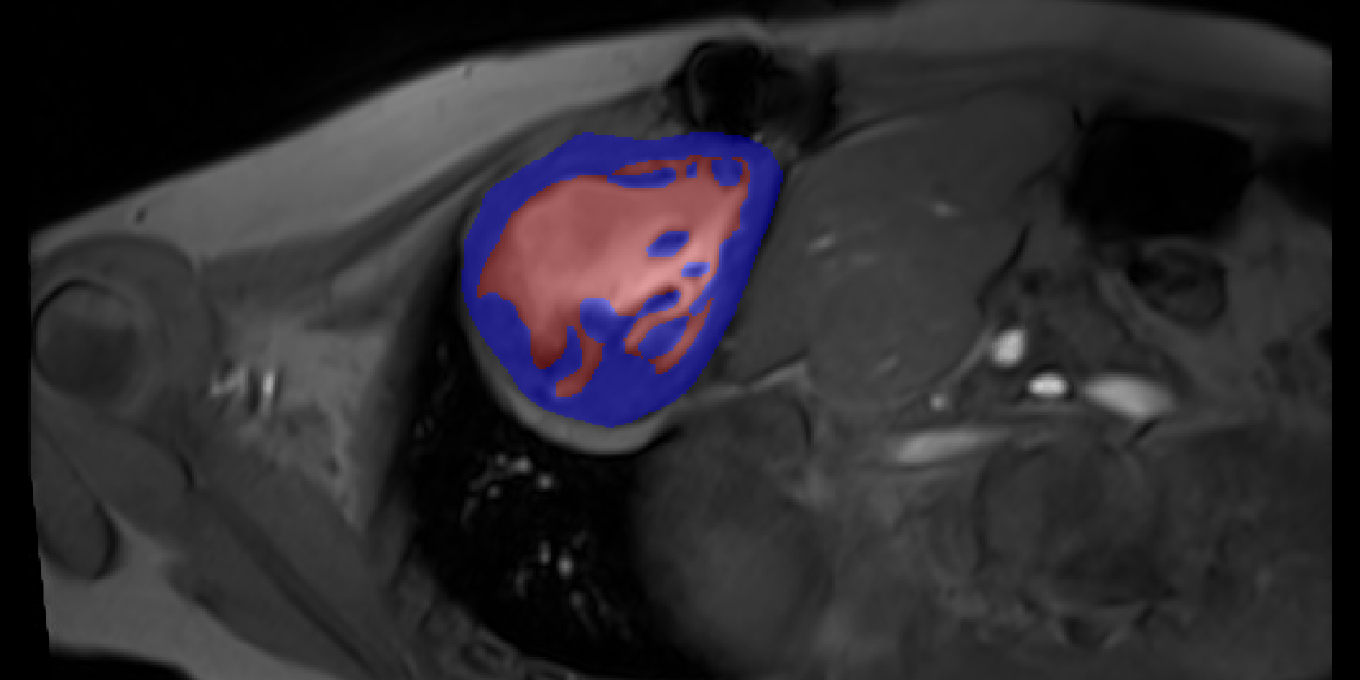
Obtaining accurate segmentations of the heart in real-time MRI allows a more realistic view on clinically relevant parameters, such as the stroke volume. Cardiac real-time MRI can assess diastolic filling under breath maneuvers or other cardiac load situations which potentially enhances diagnostics other than CINE breath hold cardiac MRI. Real-time MRI allows rapid acquisitions during spontaneous breathing, so that it is suited for a wide variety of patients. However, this is a challenging task due to changing heart shapes during contraction and relaxation within a cardiac cycle and heart movement with respiration. In particular, univentricular Fontan hearts are more challenging to detect due to their varying forms. Within this project we support the development of a segmentation pipeline that facilitates the identification of the breathing and heartbeat cycles, thus facilitating the 3D+t reconstruction of the heart from multiple 2D+t real-time sequences.
Other Collaborations
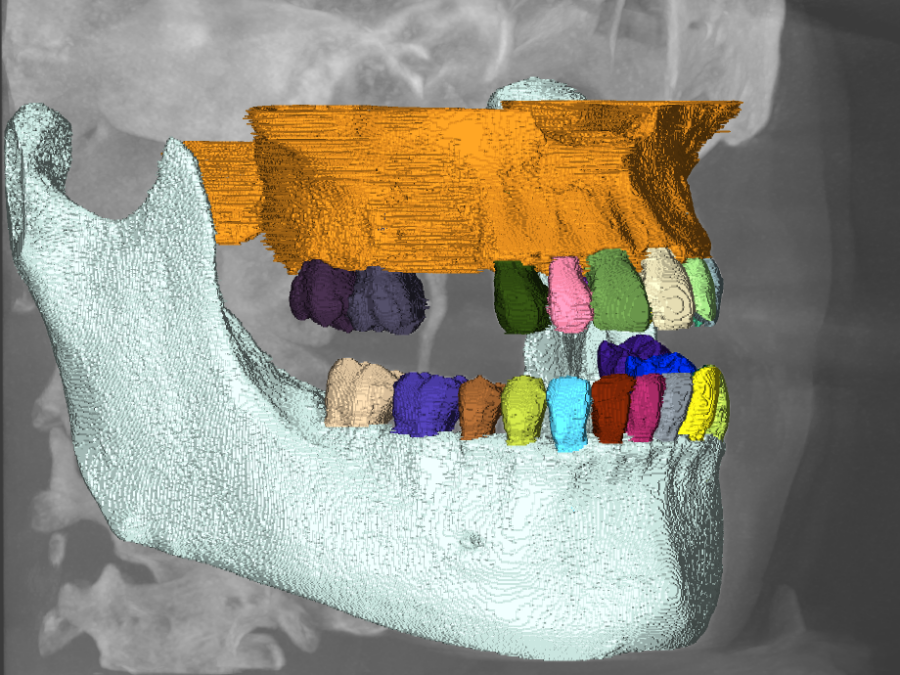
Segmentation and identification of tooth instances in cone-beam CT scans
The three dimensional labeling and identification of teeth in cone-beam CT scans is a time-consuming and challenging process which is exacerbated by (partially) missing teeth, tooth misalignments as well as the presence of implants or other utilities like metal plates or wires. As part of this project we develop an AI-based instance segmentation algorithm to […]
Understanding and analyzing plant roots using semantic segmentation of MRI images
The optimization of plants has long focused on the above-ground parts. Recently, new efforts are being made to exploit the potential below ground. To this end, our partners at the FZJ have developed an imaging system which enables imaging the root system throughout the growth of the plants using MRI. Besides qualitative analysis, a precise […]